A new blood sensor utilizes miniaturized channels to monitor for accidental bleeding during colonoscopies.
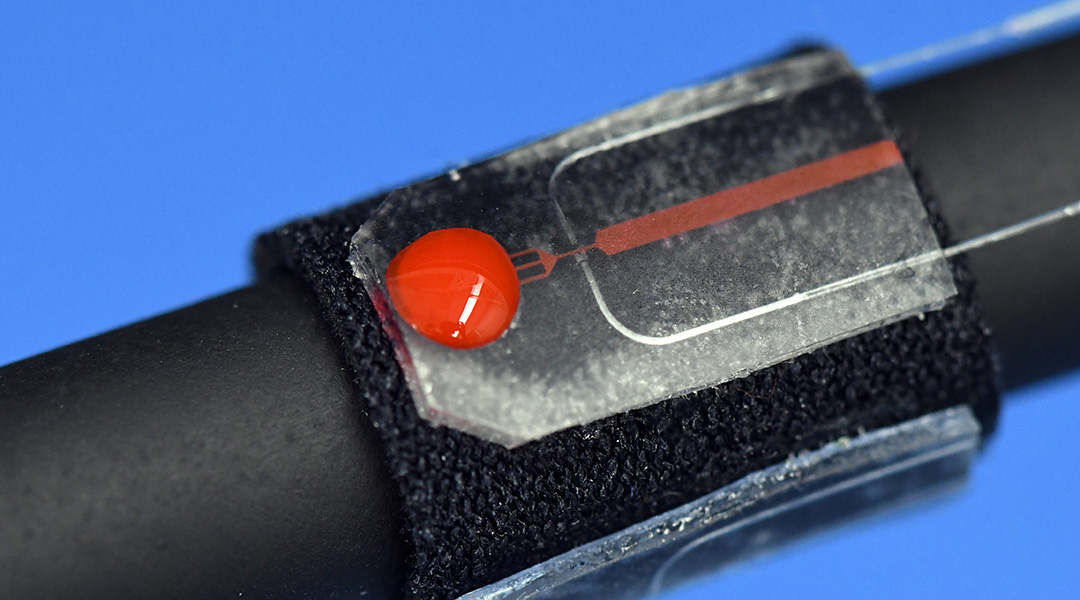

A new blood sensor utilizes miniaturized channels to monitor for accidental bleeding during colonoscopies.
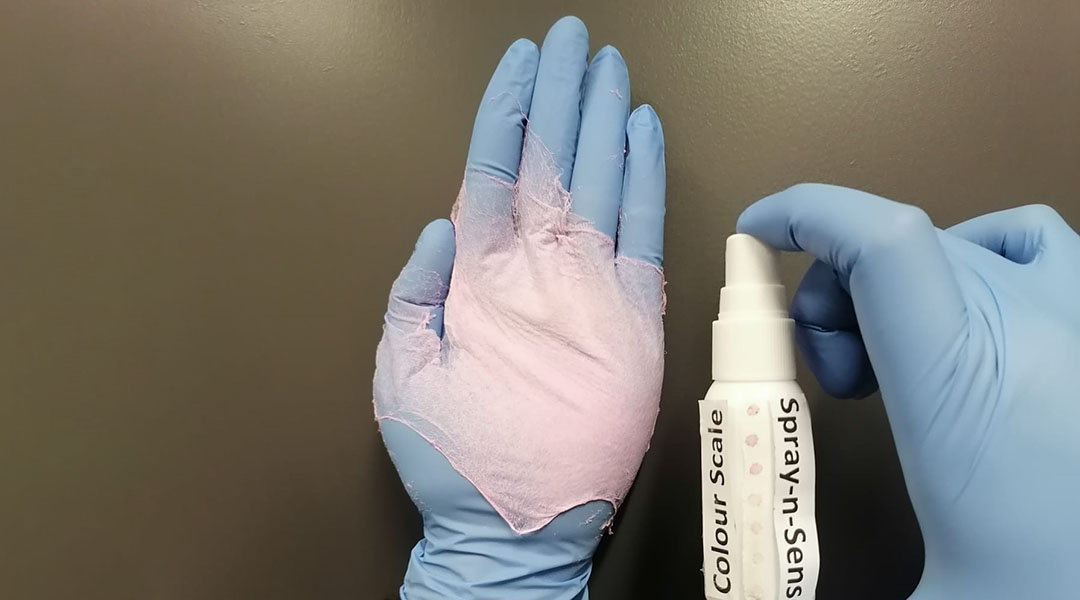
An innovative chemical sensor design could make environmental monitoring in the field more efficient and effective.

Researchers working to understand climate change, find inspiration in the most unlikely of places.

The stability and versatility of gold nanoparticles make them an ideal candidate for implantable sensors
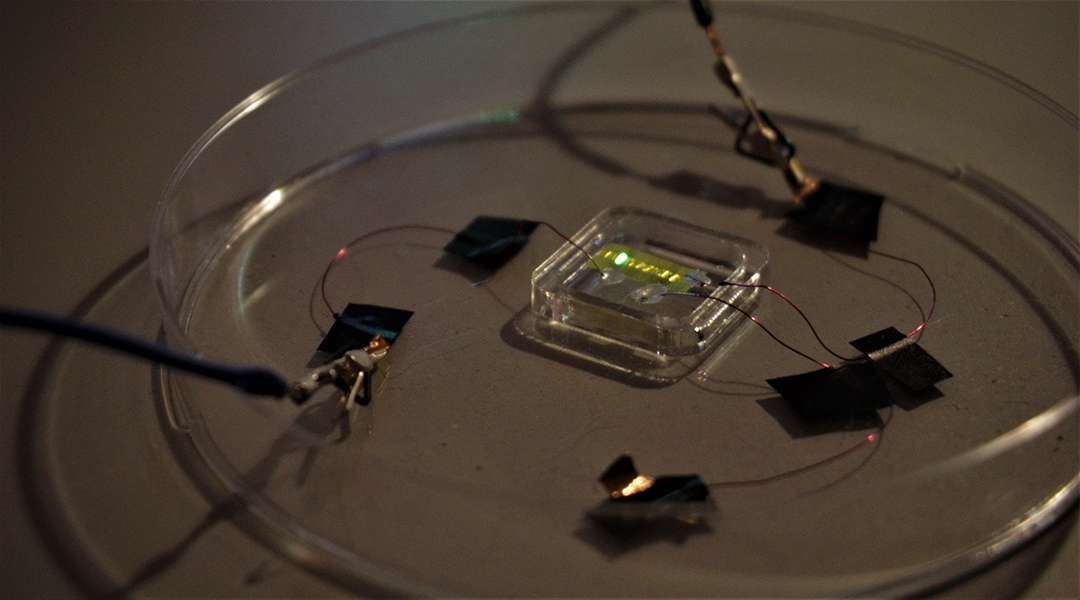
A new fabrication method allows researchers to create ultra-thin OLED materials that can be applied to the skin using temporary tattoo paper.
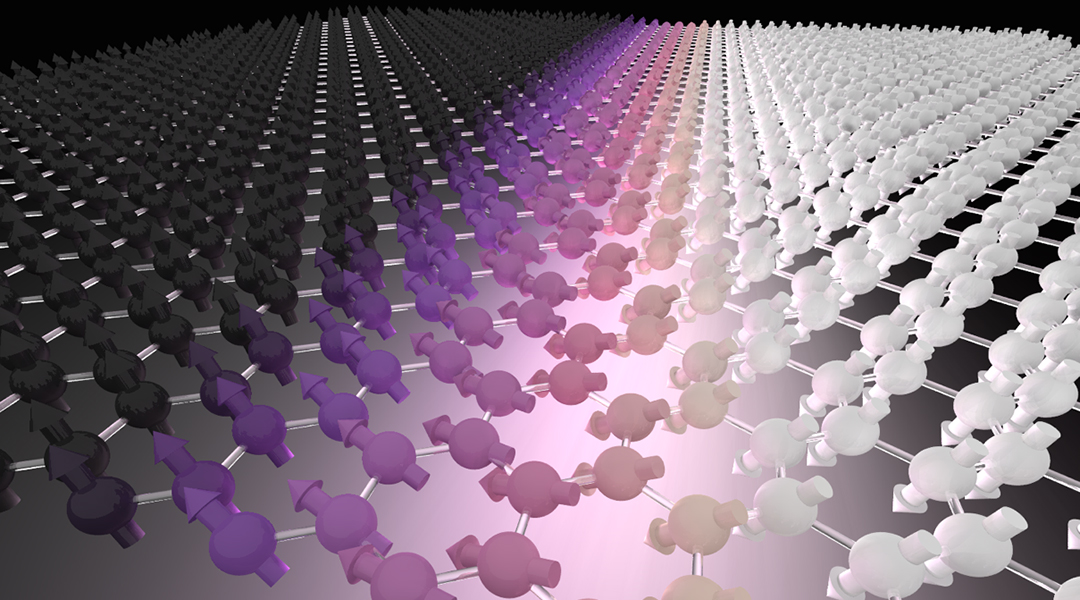
Using theoretical and experimental analysis, researchers aim to better understand the novel and intriguing magnetic properties of 2D materials for the next generation of information technologies.
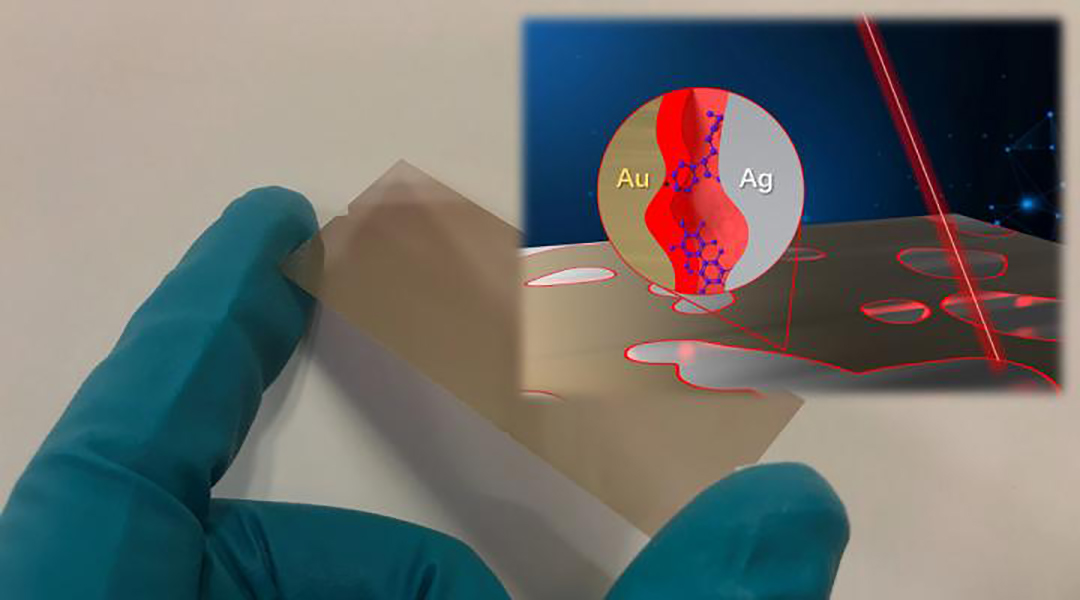
Study shows improvements to chemical sensing chip that aims to quickly and accurately identify drugs and other trace chemicals.

The process of detecting gamma rays causes serious damage to those detectors. Researchers have developed a large, self-healing crystal that might help to solve this problem.
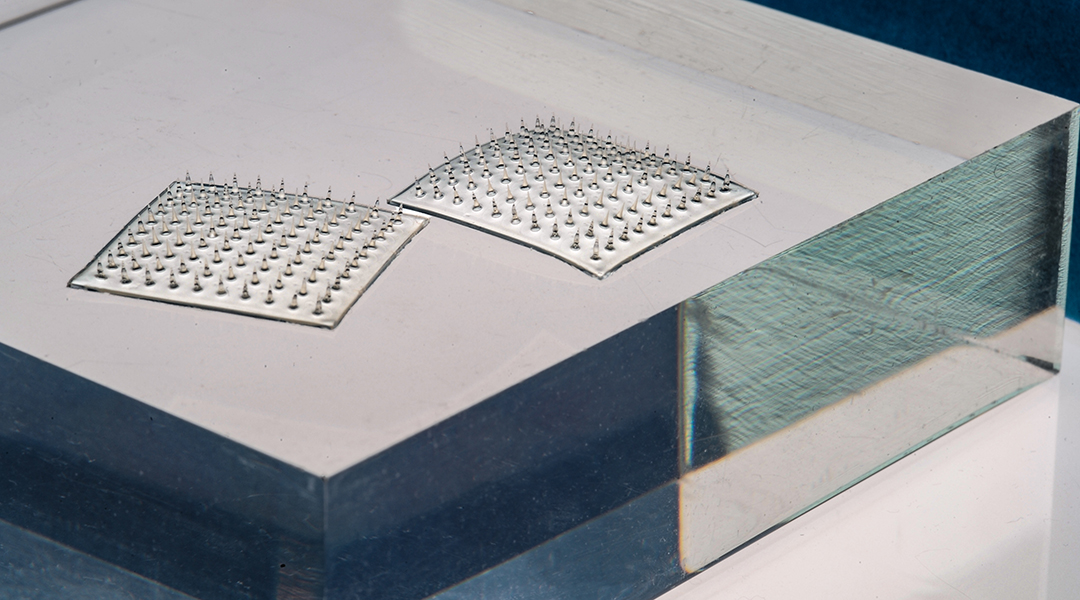
Food-safe microneedles incorporated into a new smart label can effectively collect samples from packaged food and inform consumers about its quality in real time.

Scientists design a stretchable, adhesive, self-healing material that can change color as a result of movement for real-time motion sensors.