Advanced Healthcare Materials celebrates its 5th birthday this year! Since 2012 we have been bringing you the latest breakthroughs in biomedical materials science with a strong focus on improving human health, and we will continue to do so in 2017. We therefore have launched virtual issues on five hot topics in the field, where you can access some of our best recent papers free of charge!
No access to our published content yet? Make sure to recommend Advanced Healthcare Materials to your librarian. More information can be found here.
In this biweekly feature, we highlight the artwork on the covers of the most recent issue of Advanced Healthcare Materials, and of course the research behind it. You can find this week’s issue here. Click on the titles or cover images below to get to the corresponding papers. Also check out our monthly Most Read and our previous cover art feature.
by Huisuk Yang, Suyong Kim, Geonwoo Kang, Shayan F. Lahiji, Mingyu Jang, Young Mi Kim, Jae-Myung Kim, Sang-Nae Cho, and Hyungil Jung
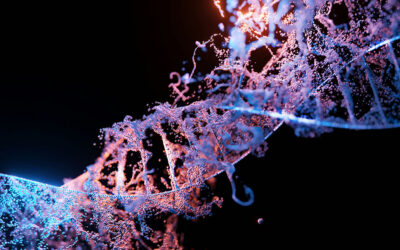
Centrifugal lithography enables fabrication of microstructures via self-shaping of viscous polymer drops during centrifugation. Hyungil Jung and co-workers have fabricated dissolving microneedles, composed of a polymer matrix and biopharmaceutics, by centrifugal lithography under a controlled environment to preserve their activity. The dissolving microneedles once implanted can penetrate into the skin and deliver their ingredients through the skin to induce biopharmaceutical effects with minimal damage.
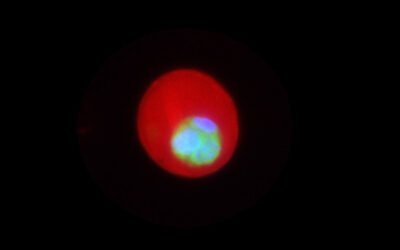
An Advanced Multifunctional Hydrogel-Based Dressing for Wound Monitoring and Drug Delivery
Advanced Multifunctional Hydrogel-Based Dressing for Wound Monitoring and Drug Delivery
by Bahram Mirani, Erik Pagan, Barbara Currie, Mohammad Ali Siddiqui, Reihaneh Hosseinzadeh,
Pooria Mostafalu, Yu Shrike Zhang, Aziz Ghahary, and Mohsen Akbari
Wound management is a major global challenge and poses a significant financial burden to the healthcare system. Mohsen Akbari and co-workers developed an advanced multifunctional dressing (GelDerm) capable of colorimetrically measuring the pH, indicating bacterial infections, and releasing antibiotic agents at the wound site. GelDerm makes wound care easier and less painful for the patient, and more cost-effective for the healthcare system.
by Guangfu Wu, Ziwen Dai, Xin Tang, Zihong Lin, Pik Kwan Lo, M. Meyyappan, and King Wai Chiu Lai
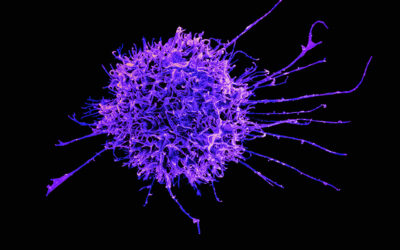
An aptamer-modified graphene field-effect transistor-based biosensor for electrical detection of Escherichia coli is developed by King Wai Chiu Lai and co-workers. The change of the carrier density in graphene due to the attachment of E. coli is correlated with the electrical response of the graphene biosensor. The electrical response is then analyzed and optimized by tuning the gate voltage, which affects the carrier mobility in graphene. The excellent sensing performance (high sensitivity, selectivity, and stability) opens up the possibility to utilize aptamer-modified graphene devices for pathogen detection in food and water quality monitoring and early diagnosis of pathogen infections.
by Pouria Fattahi, Jordan T. Dover, and Justin L. Brown
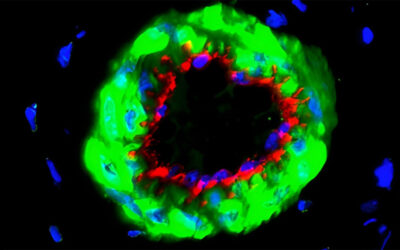
3D near-field electrospinning is capable of depositing single nano- and microfibers with extraordinary precision. This image demonstrates a stem cell attached to perpendicular microfibers. As described by Justin Brown and co-workers, this process can be multiplexed with other 3D printing techniques to build a wide array of complex structures for applications such as regenerative medicine.
Interested in more news about Advanced Healthcare Materials? Also check out our monthly Most Read and our previous cover art feature.
We recently have released a top-level special issue on biomimetic interfaces in biomedical devices.
Discover our new virtual issues now too and read selected articles on nanotherapeutics, regenerative medicine, biofabrication, stem cells, and diagnostic devices for free.


 Lithography: Self-Shaping of Polymer Microstructures Encapsulating Biopharmaceutics by Centrifuging Polymer Drops
Lithography: Self-Shaping of Polymer Microstructures Encapsulating Biopharmaceutics by Centrifuging Polymer Drops Field-Effect Transistors for the Sensitive and Selective Detection of Escherichia coli Using Pyrene-Tagged DNA Aptamer
Field-Effect Transistors for the Sensitive and Selective Detection of Escherichia coli Using Pyrene-Tagged DNA Aptamer Near-Field Electrospinning of Biomaterial Microfibers with Potential for Blended Microfiber-Cell-Loaded Gel Composite Structures
Near-Field Electrospinning of Biomaterial Microfibers with Potential for Blended Microfiber-Cell-Loaded Gel Composite Structures