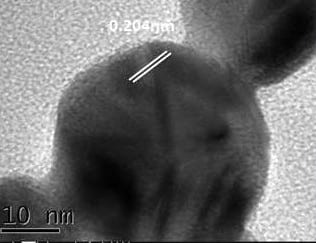
Researchers from Peking University have developed a colloidal gold test strip for Cardiac troponin I (cTn-I) detection based on microplasma generated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) that shows better detection sensitivity than the traditional test strip. Their cTn-I test is based on the specific immune-chemical reactions between antigen and antibody on imunochromatographic test strips using AuNPs. Compared to traditional chemical method, AuNPs generated by microplasma are modified with more negative charges on their surface, which can attract more positively charged antibody, and thus ensure higher detection sensitivity.
Researchers from Peking University have developed a colloidal gold test strip for Cardiac troponin I (cTn-I) detection based on microplasma generated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) that shows better detection sensitivity than the traditional test strip. Their cTn-I test is based on the specific immune-chemical reactions between antigen and antibody on imunochromatographic test strips using AuNPs. Compared to traditional chemical method, AuNPs generated by microplasma are modified with more negative charges on their surface, which can attract more positively charged antibody, and thus ensure higher detection sensitivity.
cTn-I is regarded as a specific marker for cardiac infarction. The level of cTn-I in patients is 2 to 20 thousand times than that of healthy people. The early detection of cTn-I is therefore a key factor of cardiac infarction diagnosis and therapy. Microplasma is a new method for AuNP generation – besides its low energy consumption and low pollution, microplasma gives these AuNPs special surface properties, making them excellent cTn-I detectors. This test has great potential for early detection of cardiac infarction, and the microplasma-assisted synthesis of AuNPs described by the researchers has great potential for a variety of biomedical and therapeutic applications, they believe.