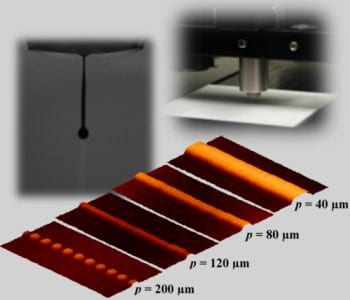
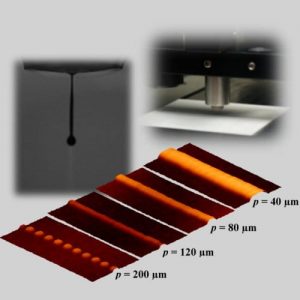
 In the field of dielectric materials, ferroelectric ceramics as well as polymeric materials are used depending on the application area. Ceramics exhibit a high dielectric constant, but require high sintering temperatures and are rigid. In contrast to ceramics, polymers are known for high mechanical flexibility and low temperature processability, but also for a low dielectric constant.
In the field of dielectric materials, ferroelectric ceramics as well as polymeric materials are used depending on the application area. Ceramics exhibit a high dielectric constant, but require high sintering temperatures and are rigid. In contrast to ceramics, polymers are known for high mechanical flexibility and low temperature processability, but also for a low dielectric constant.
Printing technologies, like screen printing or inkjet printing, are more and more used for the manufacturing of dielectric components, e. g. capacitors with ceramic or polymeric dielectric films. Especially inkjet printing is a promising technology for processing functional materials, due to the fact that inkjet printing is a digital technology. Hence, it is a contactless method and therefore allows the fabrication of components directly from a digital model, including cost efficiency and a high flexibility.
Researchers from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have now reported a new approach for the fabrication of flexible dielectric thick films via inkjet printing. To overcome the drawbacks of the single ceramic and polymeric materials, a combination of both material types is used for property tailoring. Therefore, a novel composite ink containing ceramic and polymeric components is developed, which allows a fast and flexible fabrication of composite dielectric thick films in one process step. Investigations of the drying behavior of the developed ink showed that no coffee stain effect is observed and homogeneous composite thick films are achieved. Using the composite ink, they fabricate all-inkjet-printed metal-insulator-metal (MIM) capacitors for the characterization of the dielectric properties. The fabricated composite thick films show excellent film homogeneity as well as promising results for the dielectric properties compared to pure polymers. Furthermore, compared to pure ceramics the use of a composite ink enables a fabrication of dielectric thick films on flexible polymer substrates due to avoiding high temperature sintering.
The use of a composite ink for direct inkjet printing of dielectric thick films offers new possibilities for the printing of dielectric components and devices.