Welcome to the latest selection of recent top articles in the physica status solidi journals. Get a glimpse of our publication spectrum and visit our pages by clicking on any of the DOI links below.
Ab-initio calculations and structural studies of (SiTe)2(Sb2Te3)n (n: 1, 2, 4 and 6) phase-change superlattice films [Rapid Research Letter]
Y. Saito, J. Tominaga, P. Fons, A. V. Kolobov, and T. Nakano
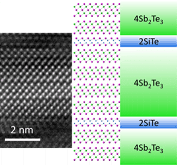 A (SiTe)2(Sb2Te3)n phase-change superlattice possesses a Dirac semimetal-like band structure, where the band gap closes only at the Γ-point and exhibits a linear dispersion. (SiTe)2(Sb2Te3)n structures derived from first-principles simulations are successfully fabricated on a Si substrate by RF-magnetron sputtering, which can be a new material system for interfacial phase-change memory applications.
A (SiTe)2(Sb2Te3)n phase-change superlattice possesses a Dirac semimetal-like band structure, where the band gap closes only at the Γ-point and exhibits a linear dispersion. (SiTe)2(Sb2Te3)n structures derived from first-principles simulations are successfully fabricated on a Si substrate by RF-magnetron sputtering, which can be a new material system for interfacial phase-change memory applications.
Phys. Status Solidi RRL (2014) DOI 10.1002/pssr.201409013
Localization and characterization of annealing-induced shunts in Ni-plated monocrystalline silicon solar cells [Rapid Research Letter · rrl solar]
Andreas Büchler, Sven Kluska, Martin Kasemann, Matthias Breitwieser, Wolfram Kwapil, Angelika Hähnel, Horst Blumtritt, Sybille Hopman, and Markus Glatthaar
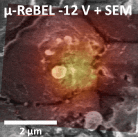 The adhesion and contact resistivity of plated solar cell front contacts on a nickel seed layer can be improved by thermal silicidation of the Ni–Si interface. Formation of deep local nickel sicilide structures harms the cell performance. In the presented Letter, critical silicide structures were localized with a precision of 1 μm in top view. Subsequent cross-section studies reveal micro-defects.
The adhesion and contact resistivity of plated solar cell front contacts on a nickel seed layer can be improved by thermal silicidation of the Ni–Si interface. Formation of deep local nickel sicilide structures harms the cell performance. In the presented Letter, critical silicide structures were localized with a precision of 1 μm in top view. Subsequent cross-section studies reveal micro-defects.
Phys. Status Solidi RRL (2014) DOI 10.1002/pssr.201409036
Template-assisted Co–Ni alloys and multisegmented nanowires with tuned magnetic anisotropy [Invided Article]
Javier García, Victor Vega, Lucia Iglesias, Victor M. Prida, Blanca Hernando, Enrique D. Barriga-Castro, Raquel Mendoza-Reséndez, Carlos Luna, Detlef Görlitz, and Kornelius Nielsch
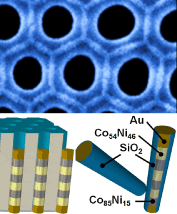 The study of nanostructured magnetic materials synthesized through electrochemical methods by employing anodic aluminum oxide membranes as patterned templates has recently attracted a huge attention. In this work García et al. have electroplated Co100–xNix (15 ≤ x ≤ 61) alloy nanowires of about 180 nm in diameter into the pores of hard-anodic nanoporous alumina membranes, as well as multisegmented Co54Ni46/Co85Ni15 nanowires with an approximate length of 300 nm per segment. The magnetic properties of the nanowire arrays were studied and correlated with the microstructural features of each alloyed/multisegmented system.
The study of nanostructured magnetic materials synthesized through electrochemical methods by employing anodic aluminum oxide membranes as patterned templates has recently attracted a huge attention. In this work García et al. have electroplated Co100–xNix (15 ≤ x ≤ 61) alloy nanowires of about 180 nm in diameter into the pores of hard-anodic nanoporous alumina membranes, as well as multisegmented Co54Ni46/Co85Ni15 nanowires with an approximate length of 300 nm per segment. The magnetic properties of the nanowire arrays were studied and correlated with the microstructural features of each alloyed/multisegmented system.
Phys. Status Solidi A (2014) DOI 10.1002/pssa.201300731
Magnetic ordering in Gd2Fe2Si2C [Original Paper]
R. A. Susilo, J. M. Cadogan, W. D. Hutchison, and S. J. Campbell
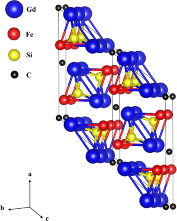 Since the discovery and application of permanent magnets based on the Nd2Fe14B phase and the study of related rare-earth (R) and transition metal (T) intermetallic compounds, many investigations have been devoted to the search for new R–T systems which can be stabilized by the addition of elements such as carbon or boron. The R2Fe2Si2C series of C-stabilized compounds was discovered by Paccard and Paccard (1988). In the work by Susilo et al., the intrinsic magnetism of Gd2Fe2Si2C has been investigated using magnetization and specific heat measurements. The compound orders magnetically below 58 K and a second magnetic event at ∼38 K is also observed in the susceptibility and specific-heat data which might signal a spin-reorientation transition. Field dependent magnetometry suggests that the magnetic structure of this compound is quite complex.
Since the discovery and application of permanent magnets based on the Nd2Fe14B phase and the study of related rare-earth (R) and transition metal (T) intermetallic compounds, many investigations have been devoted to the search for new R–T systems which can be stabilized by the addition of elements such as carbon or boron. The R2Fe2Si2C series of C-stabilized compounds was discovered by Paccard and Paccard (1988). In the work by Susilo et al., the intrinsic magnetism of Gd2Fe2Si2C has been investigated using magnetization and specific heat measurements. The compound orders magnetically below 58 K and a second magnetic event at ∼38 K is also observed in the susceptibility and specific-heat data which might signal a spin-reorientation transition. Field dependent magnetometry suggests that the magnetic structure of this compound is quite complex.
Phys. Status Solidi A (2014) DOI 10.1002/pssa.201330438
Review on TEM analysis of growth twins in nanocrystalline palladium thin films: Towards better understanding of twin-related mechanisms in high stacking fault energy metals [Feature Article]
Hosni Idrissi, Behnam Amin-Ahmadi, Binjie Wang, and Dominique Schryvers
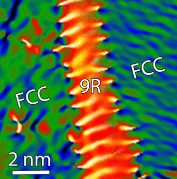 Nanocrystalline palladium thin films with nanoscale growth twins have been investigated using transmission electron microscopy in order to unravel the fundamental mechanisms controlling the formation and the evolution of twin boundaries under mechanical and hydrogen loading. The results provide insightful information to better understand the behaviour of growth twins in high stacking fault energy nanocrystalline metallic thin films.
Nanocrystalline palladium thin films with nanoscale growth twins have been investigated using transmission electron microscopy in order to unravel the fundamental mechanisms controlling the formation and the evolution of twin boundaries under mechanical and hydrogen loading. The results provide insightful information to better understand the behaviour of growth twins in high stacking fault energy nanocrystalline metallic thin films.
Phys. Status Solidi B (2014) DOI 10.1002/pssb.201350161
Spin mode locking in quantum dots revisited [Feature Article]
S. Varwig, A. Greilich, D. R. Yakovlev, and M. Bayer
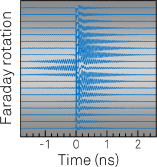 This Feature Article provides an overview of optical studies of electron and hole spin dynamics in an (In,Ga)As/GaAs quantum dot ensemble. A key feature in these experiments is the synchronization of particular modes of the spin precession in a perpendicular magnetic field to the periodic train of laser pulses that create the spin polarization. This mode-locking allows the measurement of single-spin coherence properties and coherent manipulations, such as rotations by short laser pulses.
This Feature Article provides an overview of optical studies of electron and hole spin dynamics in an (In,Ga)As/GaAs quantum dot ensemble. A key feature in these experiments is the synchronization of particular modes of the spin precession in a perpendicular magnetic field to the periodic train of laser pulses that create the spin polarization. This mode-locking allows the measurement of single-spin coherence properties and coherent manipulations, such as rotations by short laser pulses.
Phys. Status Solidi B (2014) DOI 10.1002/pssb.201350235