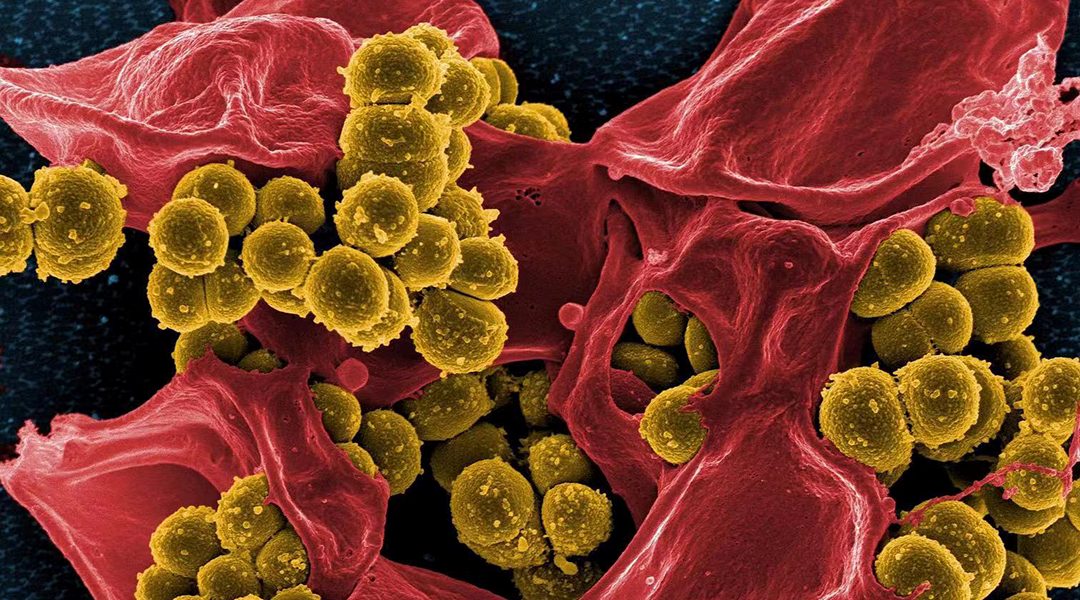
Multidrug-resistan (MDR) bacteria represent an ever-growing global crisis, with devastating consequences to public health care. We are now approaching a post-antibiotic era in which most of the existing antibiotics are no longer functional, and new drug discovery is essentially frozen.
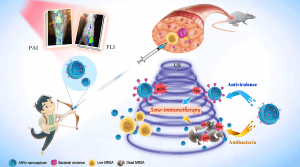
Schematic illustration of ANVs nanocapturer which combines antibacterial sonodynamic therapy and antivirulence immunotherapy. PAI: Photoacoustic imaging, FLI: Fluorescence imaging, US: Ultrasound.
In the quest for alternatives, antibiotic-free methods hold particular promise for preventing and controlling MDR bacterial infections due to their decreased potential to induce resistance. Antimicrobial sonodynamic therapy is a particularly novel technology, which relies on the interaction between low frequency ultrasound and a sonosensitizer to generate reactive oxygen species. Although highly lethal to virtually all bacteria while simultaneously removing concerns of future resistance, in its current state, this treatment strategy is not always sufficient for timely and effective infection eradication due to limited efficiency in the production of radical oxygen species.
Instead of applying direct bacteriostatic (preventing bacteria from reproducing) or bactericidal tactics, antivirulence therapy selectively disarms pathogenic bacteria by neutralizing virulence factors secreted at various stages of the infection process. This “disarm – don’t kill” approach aims to combat immunosuppression and protect the host immune system from virulence subversion. When combined with antibacterial therapy, even difficult-to-treat bacteria, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), are expected to be tractable by such dual-track regimen.
A research team led by Professor Gang Liu of Xiamen University has reported a facile and bioinspired strategy for bridging antibacterial sonodynamic therapy with antivirulence immunotherapy.
“The presented work is the first combination of antibacterial sonodynamic therapy and antivirulence immunotherapy, which promises a new way for antibiotic-free nanotheranostics to robustly combat MDR bacterial infections”, says Dr. Xin Pang, the lead author of this study.
As a proof-of-concept, a neutralizing monoclonal antibody was genetically displayed on cell membrane nanovesicles (ANVs) to capture alpha-toxin, a key virulence factor of MRSA bacteria. Upon ultrasound activation, the sonosensitizers in ANVs nanocapturer efficiently generate reactive oxygen species to kill bacteria and accelerate the virulence clearance by the neutralizing monoclonal antibody. In addition to the “one-arrow-two-hawks” approach, antibody-piloting ANVs was also shown to allow for precise optical diagnosis of MRSA infection.
Kindly contributed by the author.