The mechanisms for how bacteria break down phosphonates in order to overcome times of phosphate limitation.
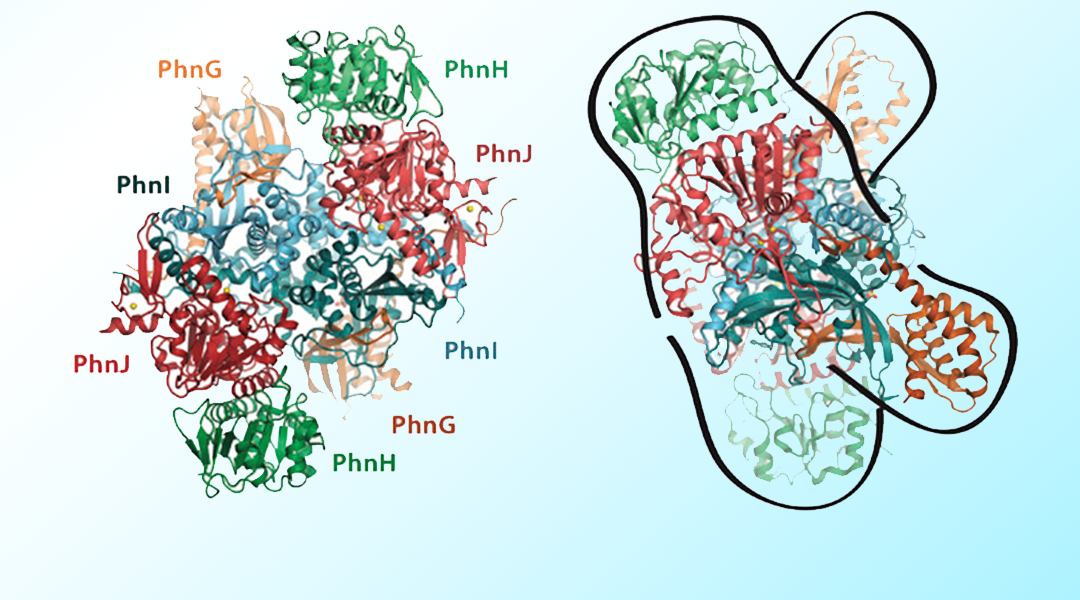

The mechanisms for how bacteria break down phosphonates in order to overcome times of phosphate limitation.
A special issue of Macromolecular Bioscience highlights progress in supramolecular hydrogel biomaterials.
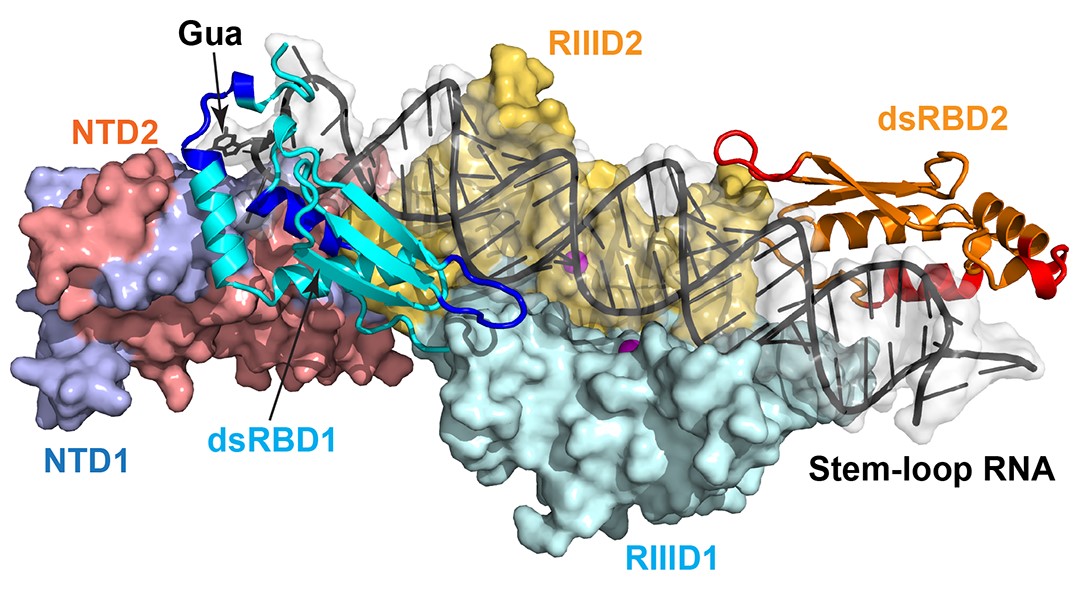
The double‐stranded RNA‐binding protein family controls RNA editing, stability, and function in all eukaryotes.

Spatial and temporal control of drug production is achieved by optogenetical triggering a hydrogel-encapsulated bacterial system.

Chemists developed a new biocatalytic material for green production of value-added chemicals.

A team of Polish scientists discovered how antimicrobial blue light can fight against infections caused by the P. aeruginosa bacterium, that occur often in burn victims.
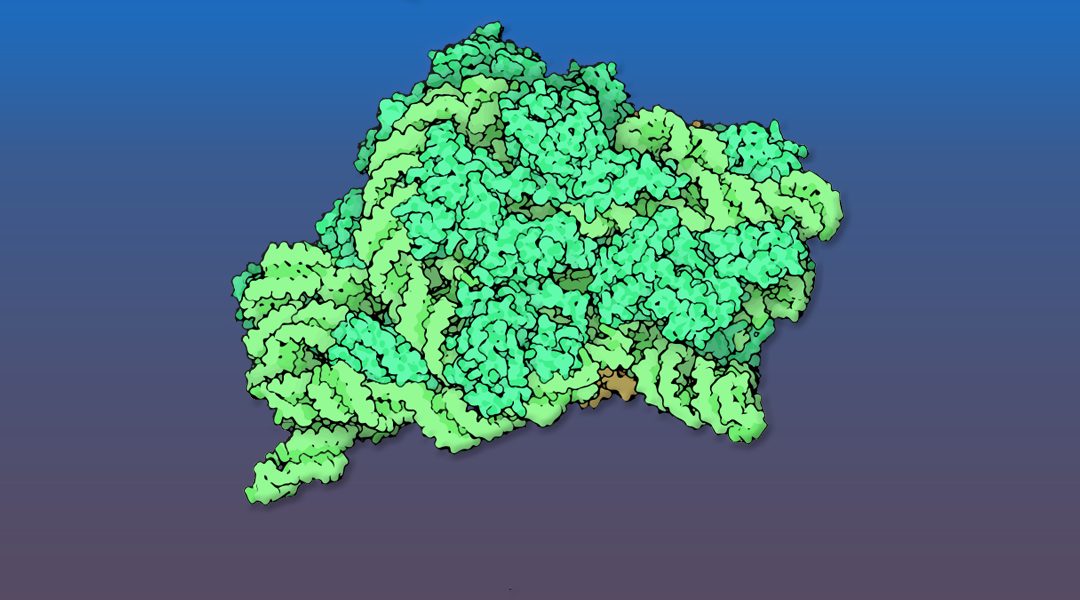
The intricate nuclear and cytoplasmic maturation steps of pre‐40S particles, the precursors to the small ribosomal subunits, in both yeast and human cells, are reviewed.
All organisms are subject to large amounts of genetic and environmental variation and have evolved mechanisms that allow them to function well in spite of these challenges. This property is generally referred to as robustness.
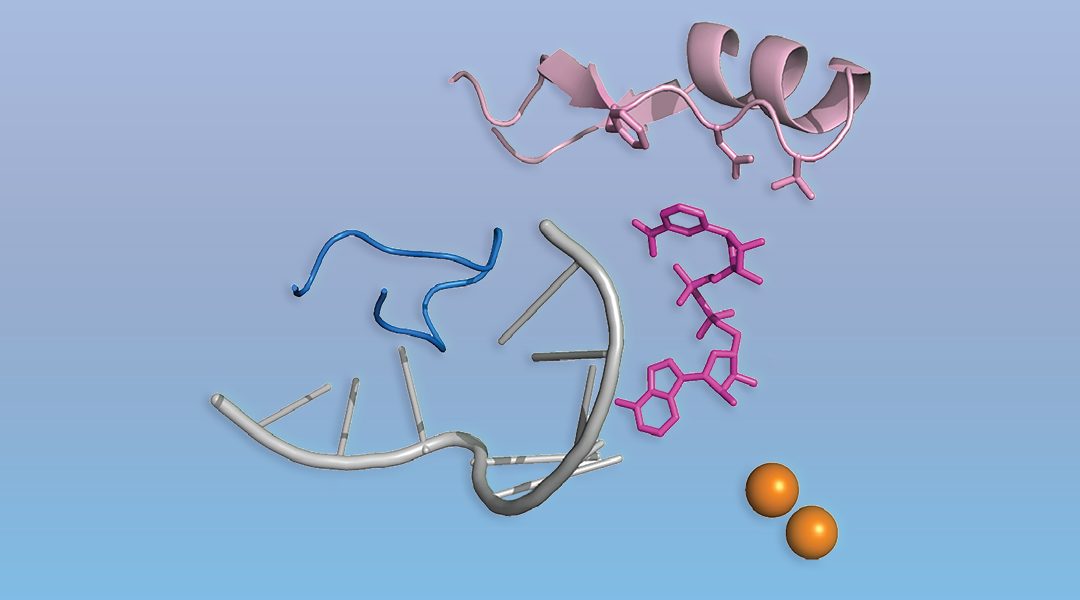
A new type of 5′‐RNA cap was discovered, and in contrast to the specialized eukaryotic m7G cap, the novel caps are abundant cellular cofactors like NAD+.
Single stranded RNAs with a free 5′ monophosphate end are susceptible to rapid degradation. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) are stabilized by hairpin structures and by “hiding” their 5′ ends within complex protein structures.