Latest

Farming under solar panels: The promise of agrivoltaics in the fight for net-zero
Combining agriculture with solar energy, agrivoltaics offers a promising solution to reduce carbon emissions while boosting food production.

Molecules secreted by parasitic worms found to reduce scarring during wound healing
Researchers have discovered that a protein produced by parasitic worms in the gut enhances wound healing in mice.
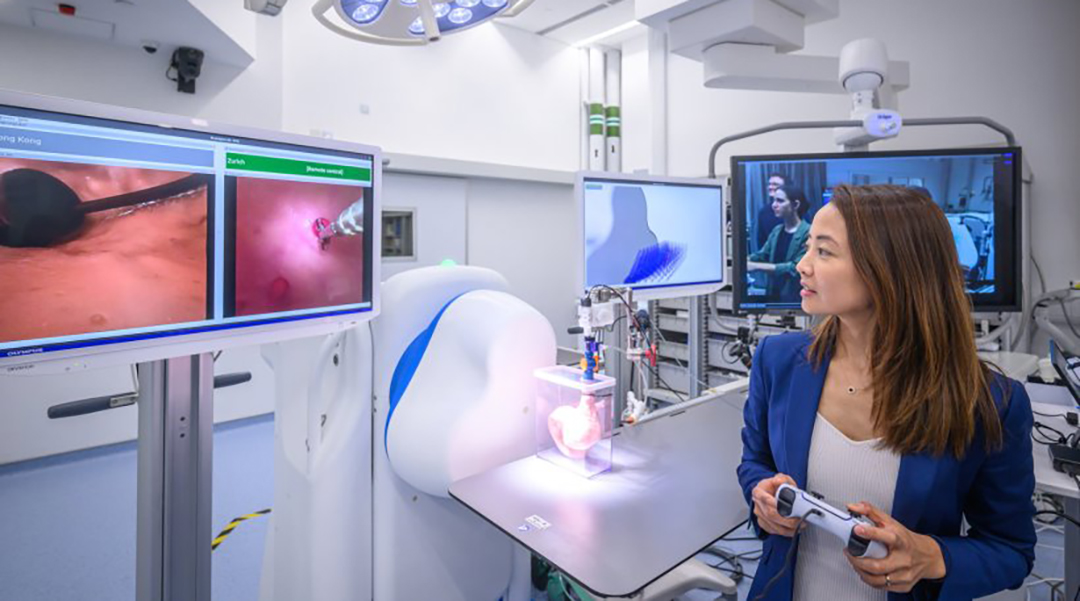
Remote-controlled robot is changing the game for endoscopes
A new teleoperated robot makes it possible to perform endoscopes remotely, making the procedure available in underserviced regions.

Gigantic cosmic strings may have spawned supermassive black holes and galaxies
Scientists theorize that cosmic strings interacting with dense matter in the early universe provided the seeds for galaxies and black holes.

How flickering lights cause hallucinations in our brains
Scientists have solved a centuries-old mystery that could help develop new forms of non-invasive brain therapy.
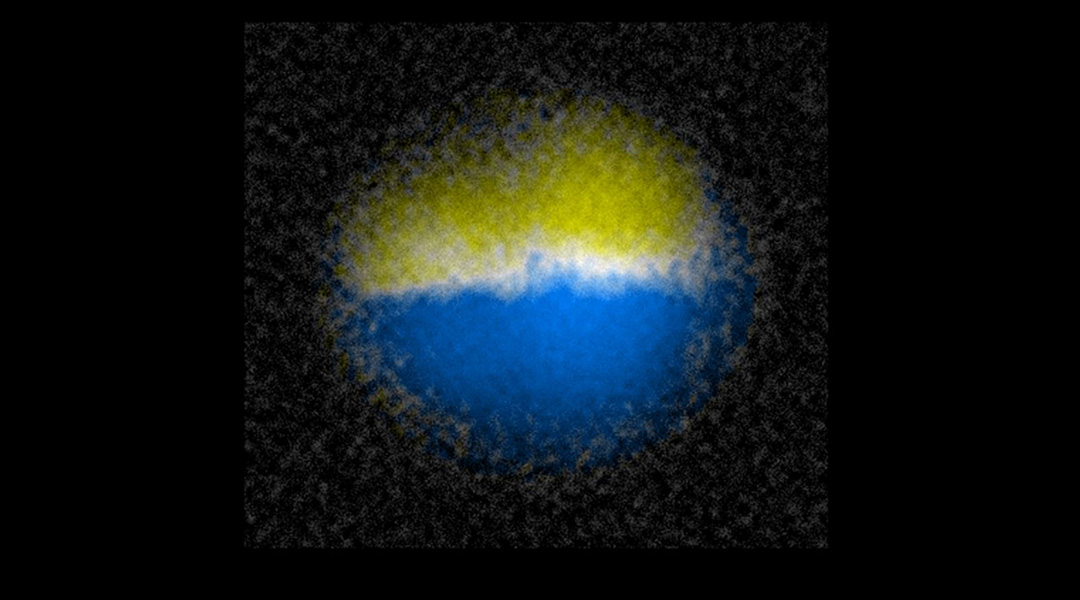
Physicists create a quantum domain wall in the lab
Researchers have discovered how to create and manipulate a quantum object called a “domain wall”, which exhibits particle-like properties.

Waning immunity and COVID-19 boosters modeled in digital town
The debate around COVID-19 boosters is highly nuanced, but a new computational model could help better inform policy around such measures in an evolving pandemic.
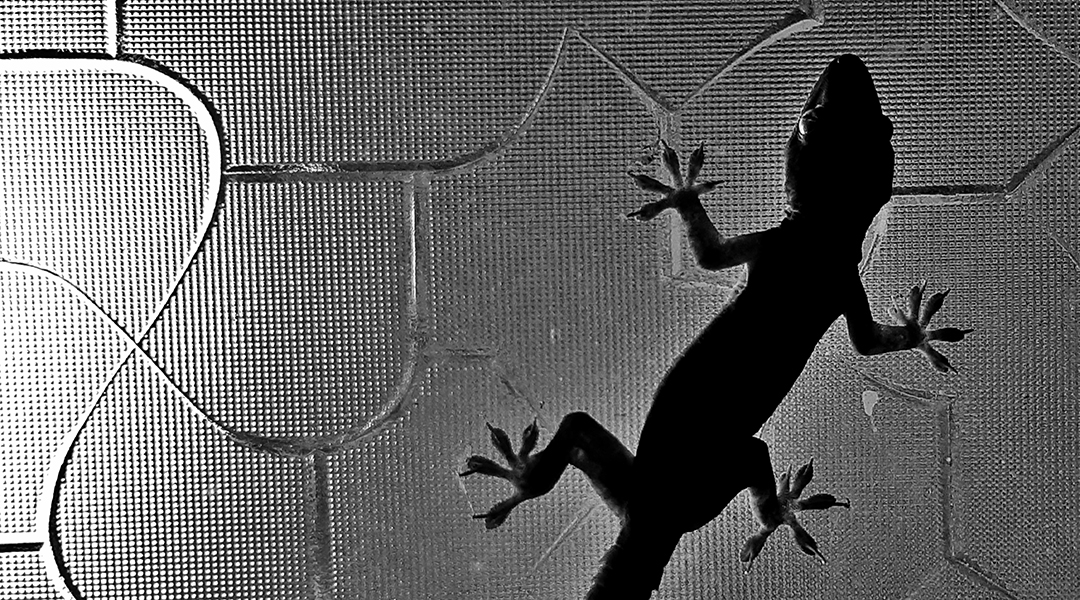

Gecko feet-inspired dry adhesive could stick around
Inspired by microscopic hairs on gecko feet, scientists in South Korea have developed a shape-memory polymer that acts as a dry adhesive.
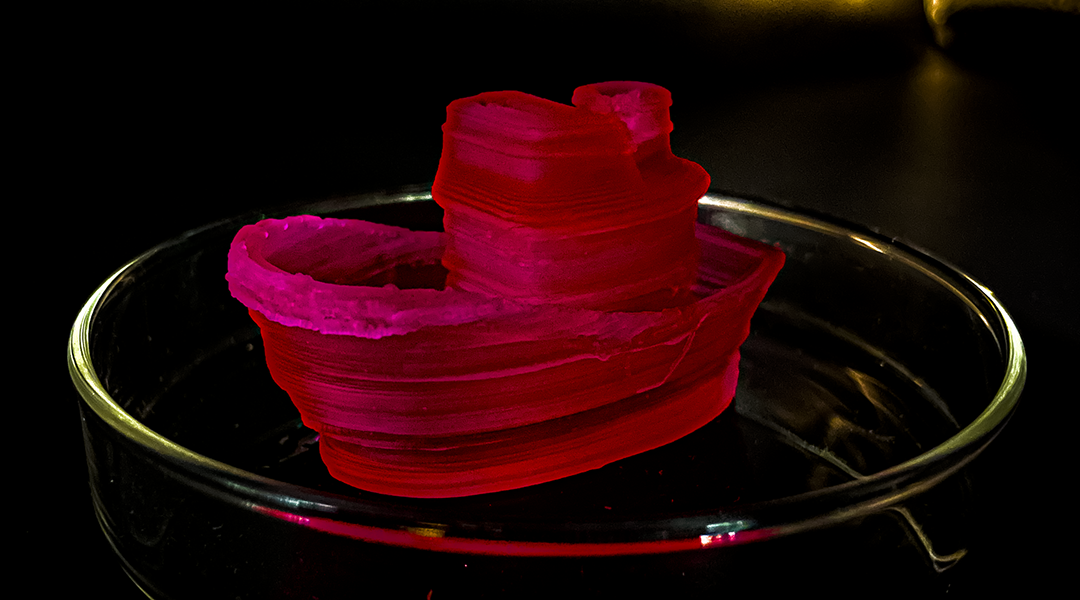
Recyclable hydrogels for fast prototyping
Researchers have created stiff, recyclable hydrogels that can be broken down into their base components and reshaped on demand.
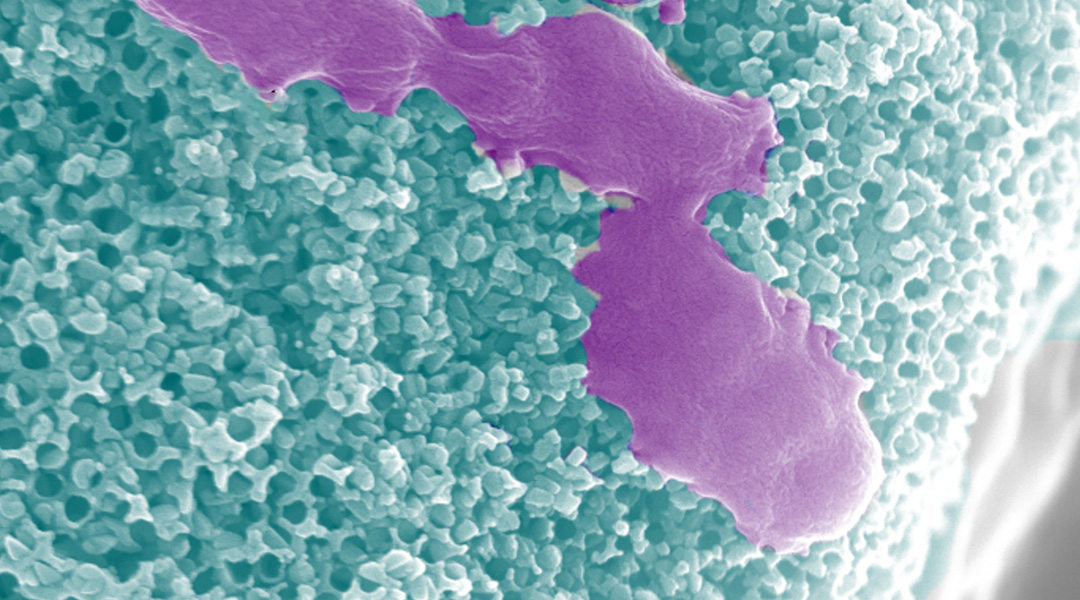
Urea-powered microrobots bust up bacterial films
Hybrid microrobots harvest chemical energy from their environment for self-propulsion while releasing reactive species to kill bacteria.
ASN Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter and receive the latest science news directly to your inbox.

A wearable air sampler to detect SARS-CoV-2
A wearable air sampler to help monitor personal exposure to SARS-Cov-2 and identify high-risk areas for indoor exposure.
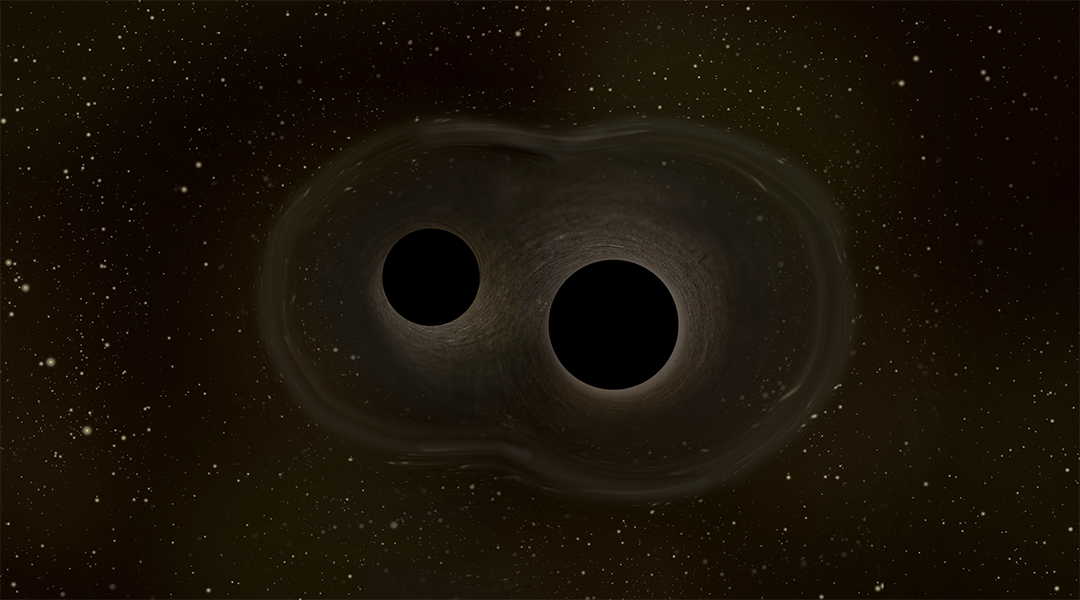

Physicists identify a quantum membrane in merging black holes
The existence of a quantum membrane is predicted by some theories of gravity, and scientists might be one step closer to identifying one.

Microplastics are taking flight
New research with samples from Pic du Midi Observatory reveal that microplastics are traversing the globe through the atmosphere.

Self-repairing electronics on the horizon
Through a happy accident, researchers have identified a new self-repairing electronic material that could make sci-fi dreams a reality.
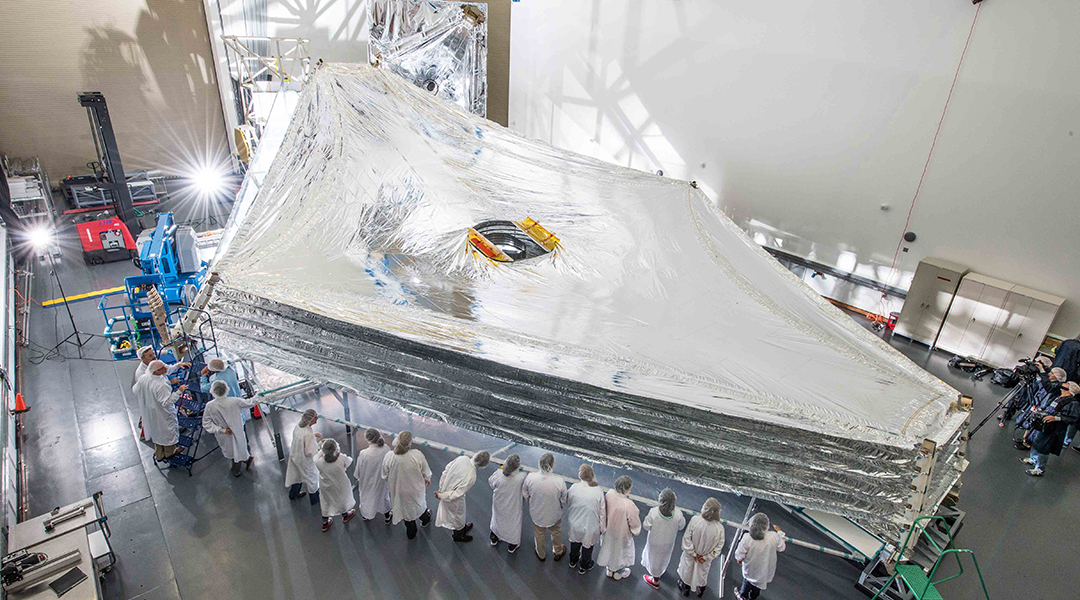

NASA’s James Webb Telescope successfully deploys sunshield
Webb team successfully deploys 70ft sunshield in key launch milestone for the spacecraft’s operations.

Exploring effective treatments for hereditary hair loss
Scientists are delving into the future of hair loss treatments, from macromolecules to laser therapies and CRISPR gene editing.
Sniffing out lung diseases with a portable E-Nose
Revolutionizing respiratory disease detection with a portable E-Nose for non-invasive breath analysis.
A synthetic nanoenzyme helps combat IBD
To minimize inflammation in IBD, scientists have developed a synthetic enzyme that targets multiple problematic pathways.

How bioinks could help astronauts survive long space missions
Scientists are exploring how to store and transport ready-to-use bioink cartridges to treat injuries on the International Space Station.
Exploring effective treatments for hereditary hair loss
Scientists are delving into the future of hair loss treatments, from macromolecules to laser therapies and CRISPR gene editing.
Sniffing out lung diseases with a portable E-Nose
Revolutionizing respiratory disease detection with a portable E-Nose for non-invasive breath analysis.
A synthetic nanoenzyme helps combat IBD
To minimize inflammation in IBD, scientists have developed a synthetic enzyme that targets multiple problematic pathways.
How bioinks could help astronauts survive long space missions
Scientists are exploring how to store and transport ready-to-use bioink cartridges to treat injuries on the International Space Station.

Cooling particle beams to study the hottest topics in physics
A new experimental technique could push the capabilities of particle accelerators in exploring the subatomic world.
String theory used to describe the expanding universe
To address unknown quantum gravitational effects in the early universe, physicists have recruited string theory to help solve the problem.
Artificial physicist to unravel the laws of nature
Scientists hope that a new machine learning algorithm could one day be used to automate the discovery of new physical laws.

The dramatic story behind general relativity’s Nobel Prize snub
More than 100 years on after Einstein’s 1921 Nobel Prize, some confusion remains around the committee’s reasons for omitting relativity.
Cooling particle beams to study the hottest topics in physics
A new experimental technique could push the capabilities of particle accelerators in exploring the subatomic world.
String theory used to describe the expanding universe
To address unknown quantum gravitational effects in the early universe, physicists have recruited string theory to help solve the problem.
Artificial physicist to unravel the laws of nature
Scientists hope that a new machine learning algorithm could one day be used to automate the discovery of new physical laws.
The dramatic story behind general relativity’s Nobel Prize snub
More than 100 years on after Einstein’s 1921 Nobel Prize, some confusion remains around the committee’s reasons for omitting relativity.
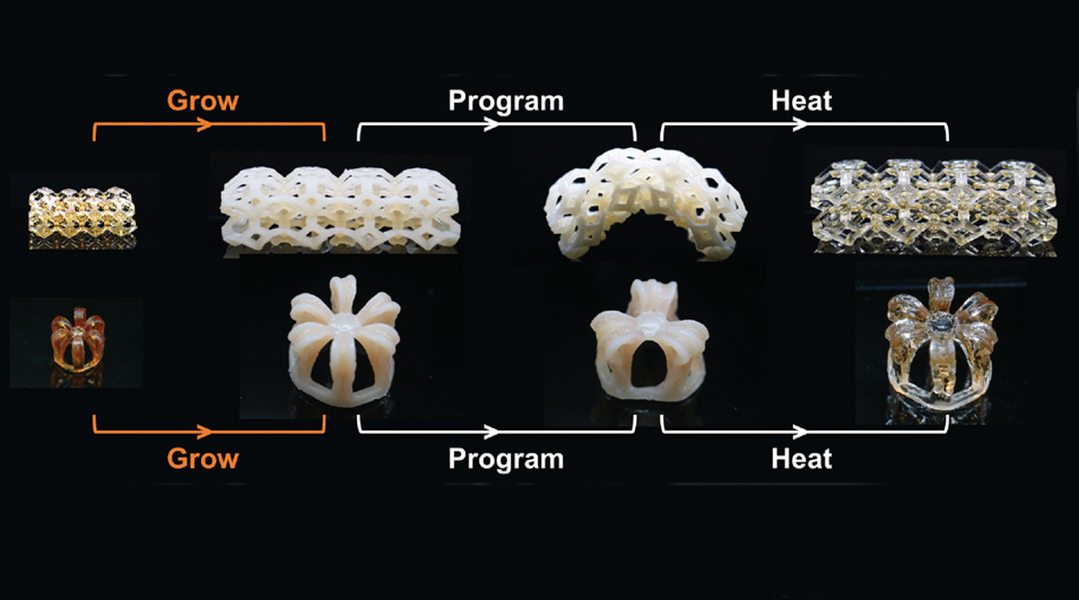
4D printing “living” structures inspired by immortal jellyfish
4D printing produces a living polymer network that can be printed into 3D shapes and then broken down into its monomer units for reuse.

A soft robotic hand takes a two-pronged approach to grasping
Resembling a balloon filled with coffee grounds, this gripper uses granular jamming and electrostatic interactions to manipulate objects.

Pathogen detection with nanotechnology
Researchers turn to nanotechnology to boost the detection of pathogens, including SARS-CoV-2.

Flexible zinc-air batteries for wearable electronics
A novel hydrogel component could increase the life cycle of cheap, safe, environmentally friendly, and energy-efficient batteries.
4D printing “living” structures inspired by immortal jellyfish
4D printing produces a living polymer network that can be printed into 3D shapes and then broken down into its monomer units for reuse.
A soft robotic hand takes a two-pronged approach to grasping
Resembling a balloon filled with coffee grounds, this gripper uses granular jamming and electrostatic interactions to manipulate objects.
Pathogen detection with nanotechnology
Researchers turn to nanotechnology to boost the detection of pathogens, including SARS-CoV-2.
Flexible zinc-air batteries for wearable electronics
A novel hydrogel component could increase the life cycle of cheap, safe, environmentally friendly, and energy-efficient batteries.

Decarbonizing the chemical industry with sustainable photons
Decarbonizing the chemical industry is possible, provided decreases in the cost of solar energy and increases in LED efficiency continue.
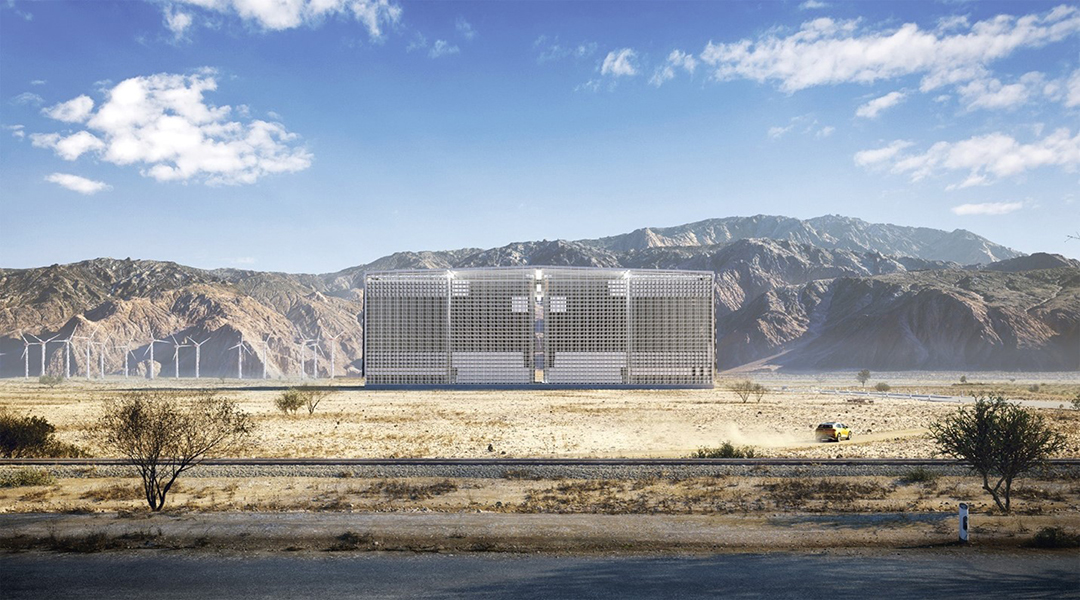

Gravity energy storage elevated to new heights
An innovative new gravity storage system with an “elevator” style building design is a viable solution to global grid-scale energy storage.
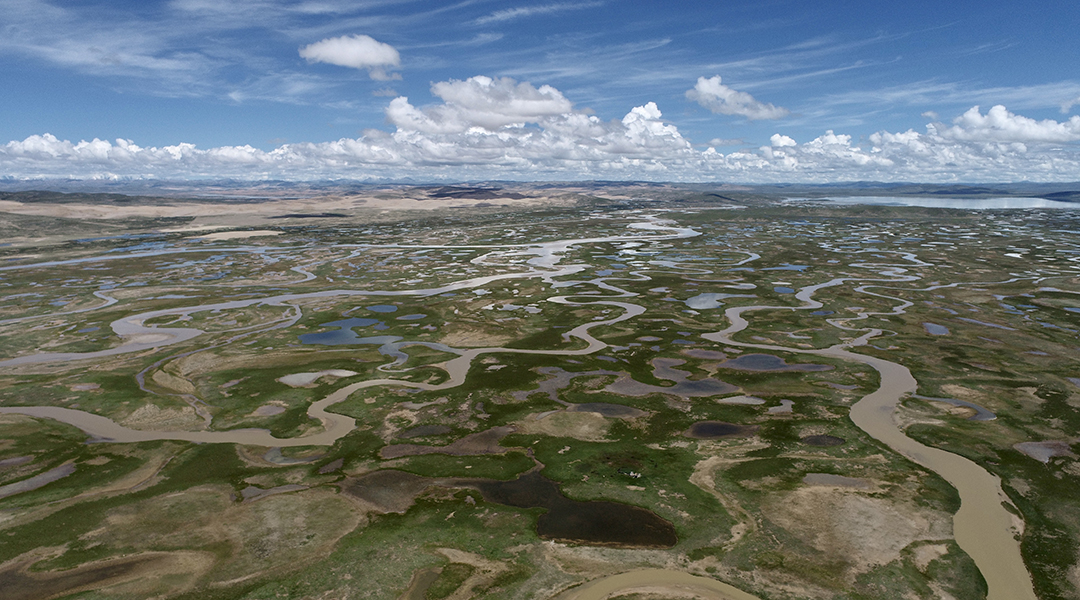

Improving the health of China’s Upper Yellow River
Environmental protection measures implemented in recent years have seen positive outcomes in improving the health of the Mother River of China.
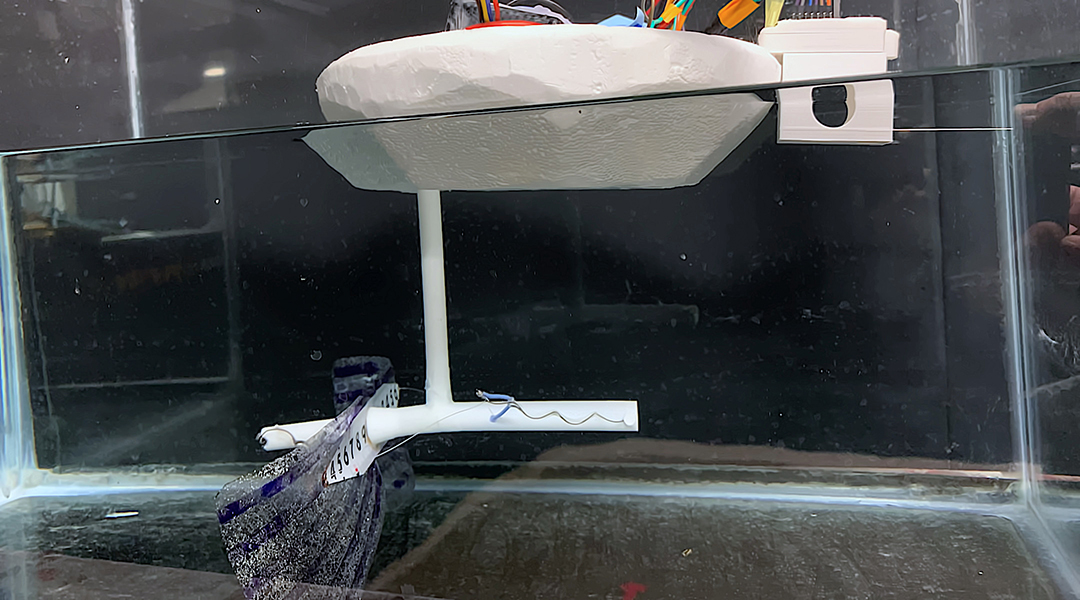

Learning from a robotic octopus swimmer
A robotic swimmer that mimics the movement of octopuses could help researchers better monitor aquatic environments remotely and in real time.
Decarbonizing the chemical industry with sustainable photons
Decarbonizing the chemical industry is possible, provided decreases in the cost of solar energy and increases in LED efficiency continue.
Gravity energy storage elevated to new heights
An innovative new gravity storage system with an “elevator” style building design is a viable solution to global grid-scale energy storage.
Improving the health of China’s Upper Yellow River
Environmental protection measures implemented in recent years have seen positive outcomes in improving the health of the Mother River of China.
Learning from a robotic octopus swimmer
A robotic swimmer that mimics the movement of octopuses could help researchers better monitor aquatic environments remotely and in real time.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.