Researchers use molecular imprinting to develop a highly sensitive and selective nanorod biosensor with artificial antibodies.
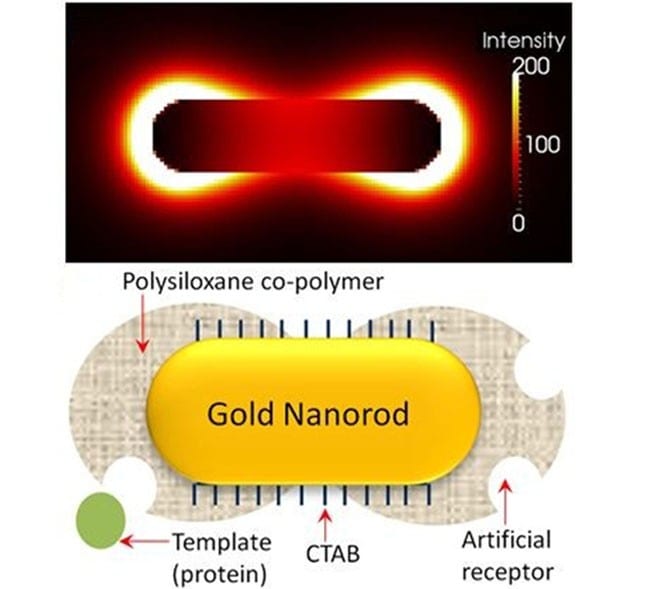

Researchers use molecular imprinting to develop a highly sensitive and selective nanorod biosensor with artificial antibodies.
Researchers use enzymes to link antigens and adjuvants, creating safer and more effective vaccines by lowering the required adjuvant dosage.
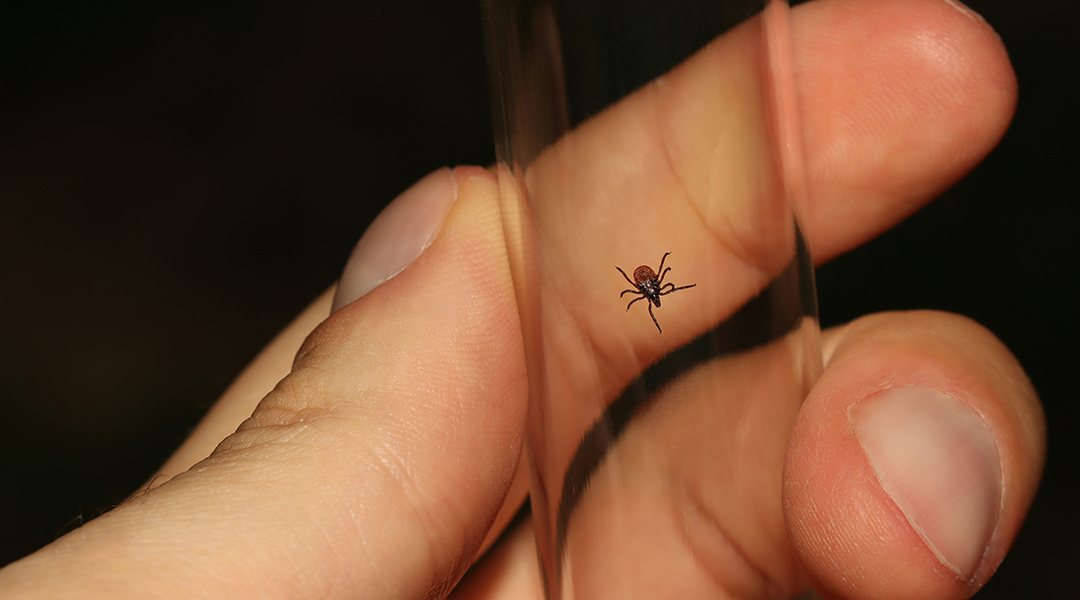

An allergy to red meat known as alpha-gal syndrome is brought on by tick bites and is becoming a global issue.
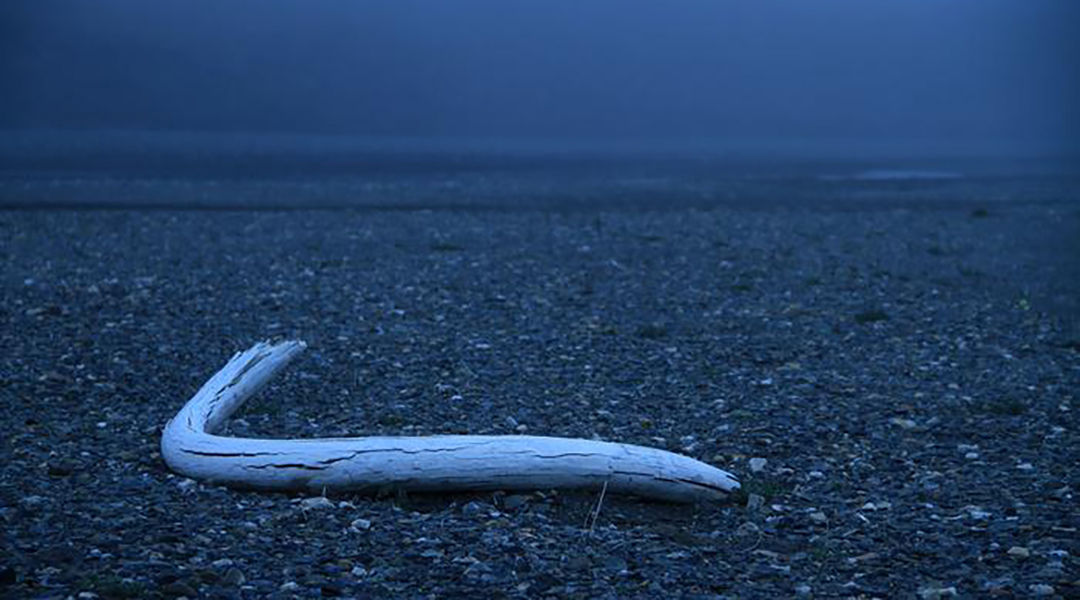

A bottleneck event caused inbreeding in the last woolly mammoths, but scientists find this was not responsible for their demise on Wrangel Island.
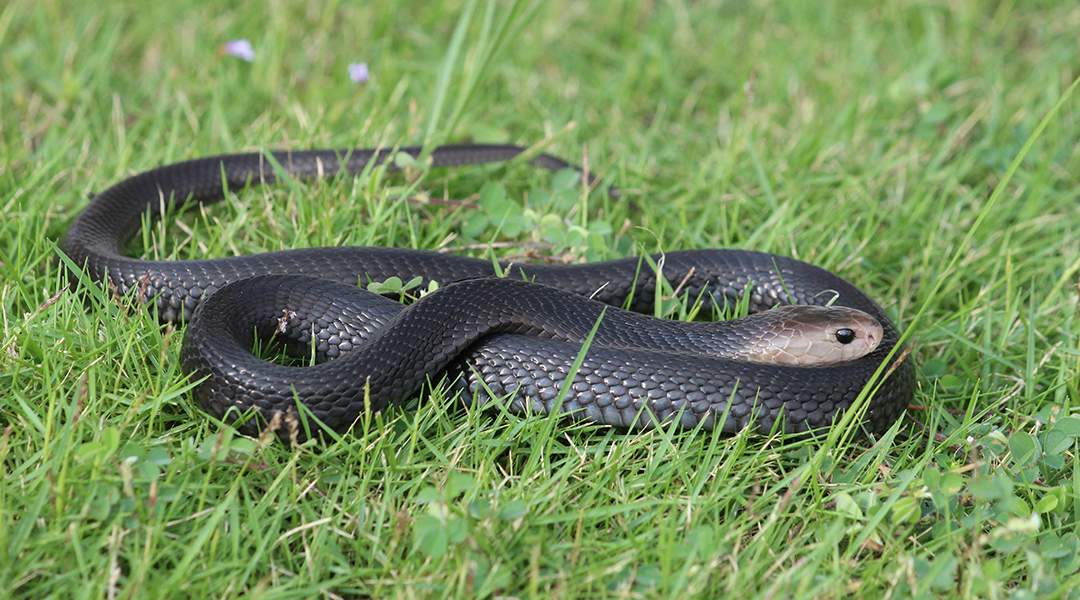

Lab-made model of human blood vessels provides accurate insights into effects of snake venom and could help develop new antivenoms.
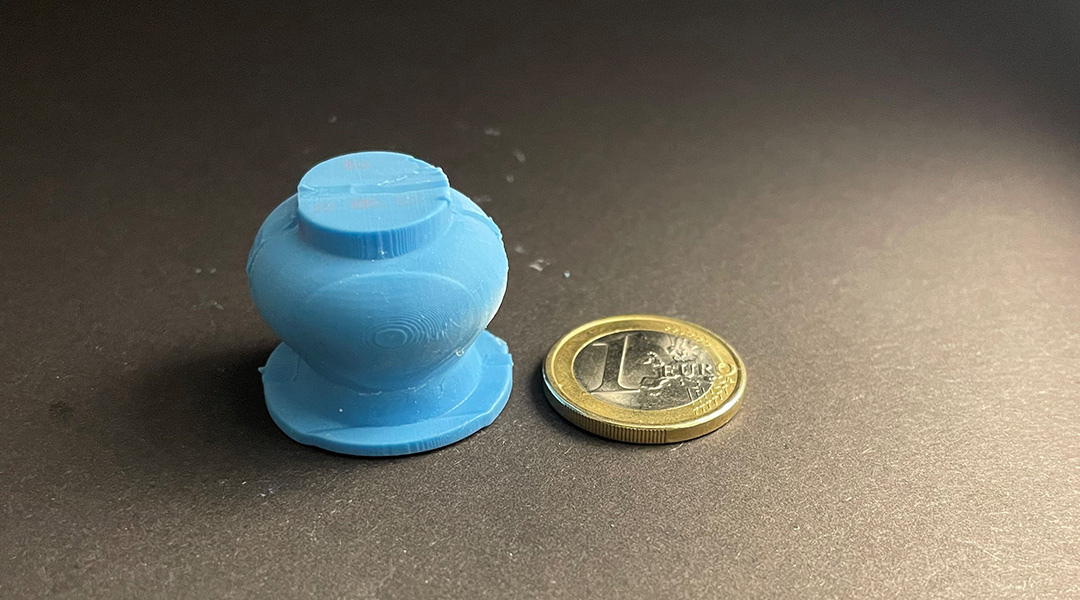

Collecting blood in a painless and minimally-invasive way may soon be possible with this prototype suction cup device.
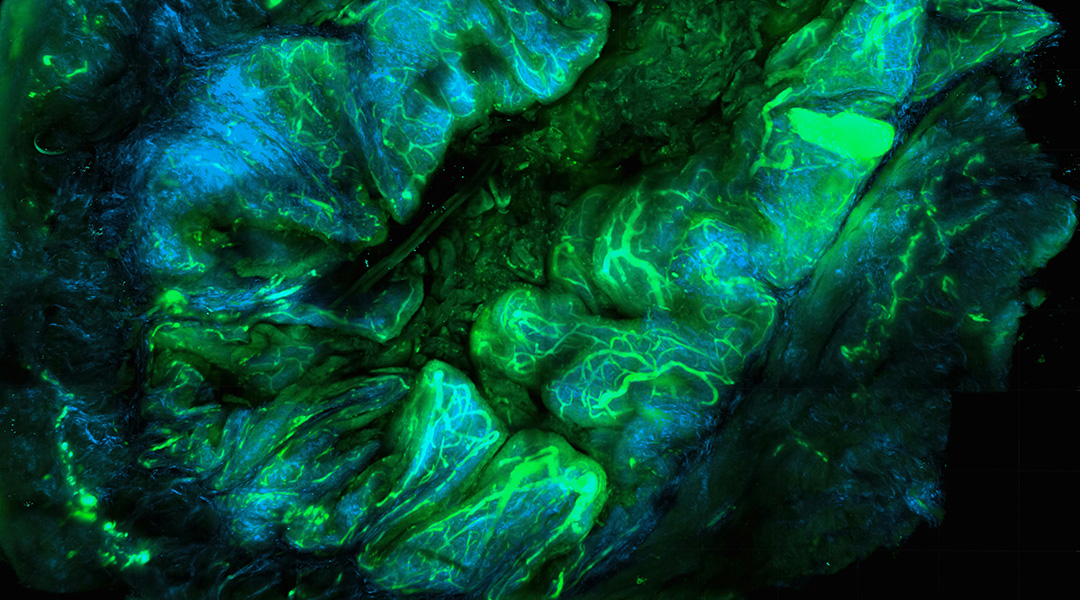
New probe system offers real-time protein mapping within living cells, unlocking insights into cellular function and disease mechanisms.
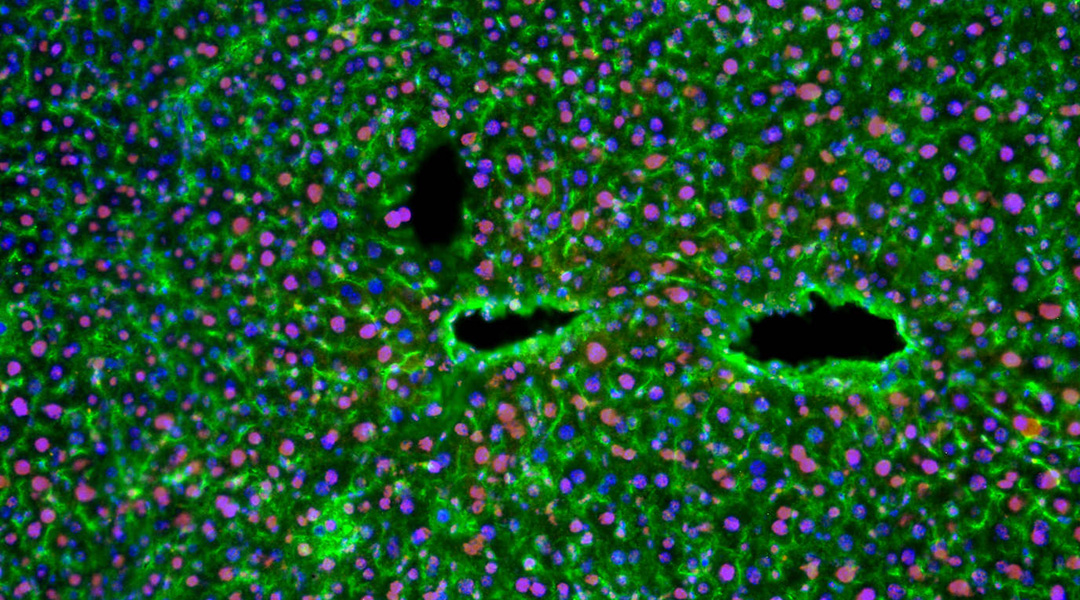
A new study finds that amyloid beta, a culprit in Alzheimer’s disease, is important for maintaining a healthy liver.

Microneedle skin patches combined with a safe electrical current help antigens cross the skin to trigger an immune response against tumors.
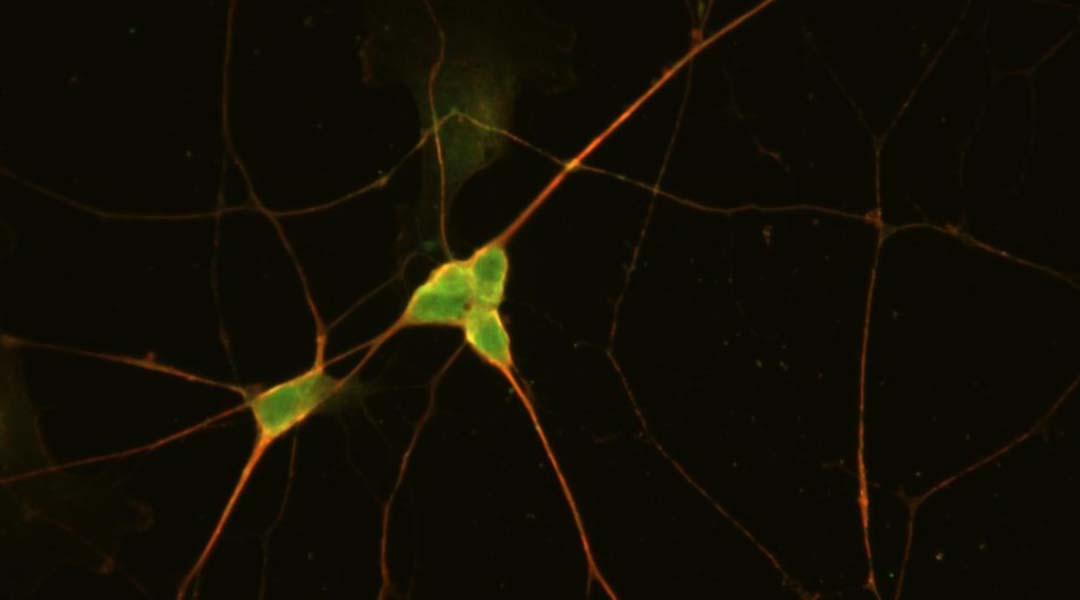
A model based on human stem cell–derived neurons is allowing researchers to understand opioid-induced respiratory failure to improve overdose treatment.