The active structure of an oral macrocyclic drug has eluded scientists for years despite its widespread clinical use—that is, until now.
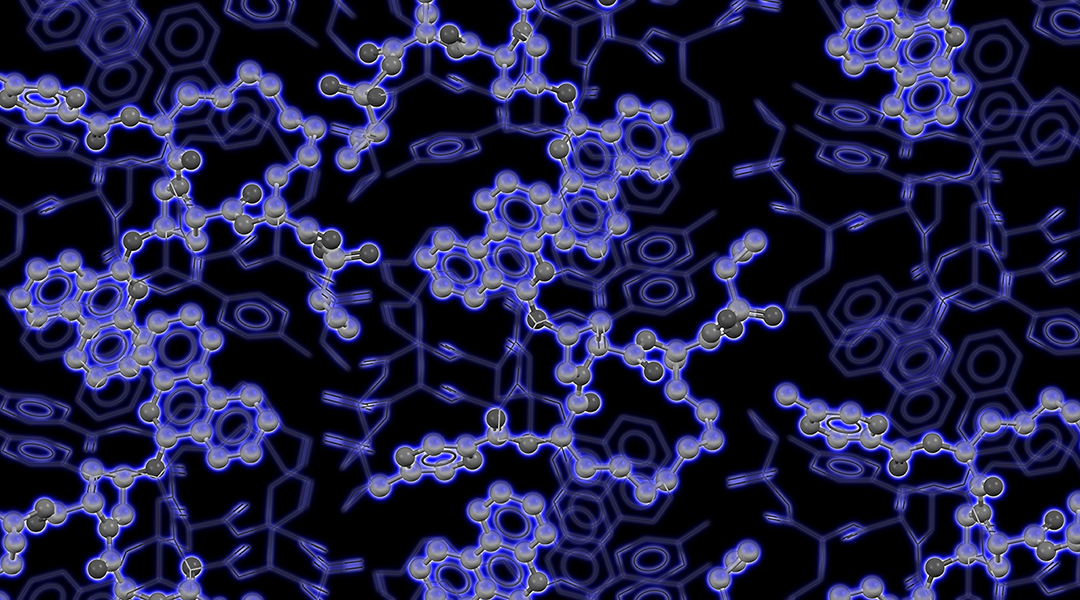

The active structure of an oral macrocyclic drug has eluded scientists for years despite its widespread clinical use—that is, until now.

Analyzing human hair from remains recovered in Menorca, researchers say they have provided the earliest direct evidence of drug use.

A pathway in the brain that forms its natural stress response could be used to make new treatments for anxiety.
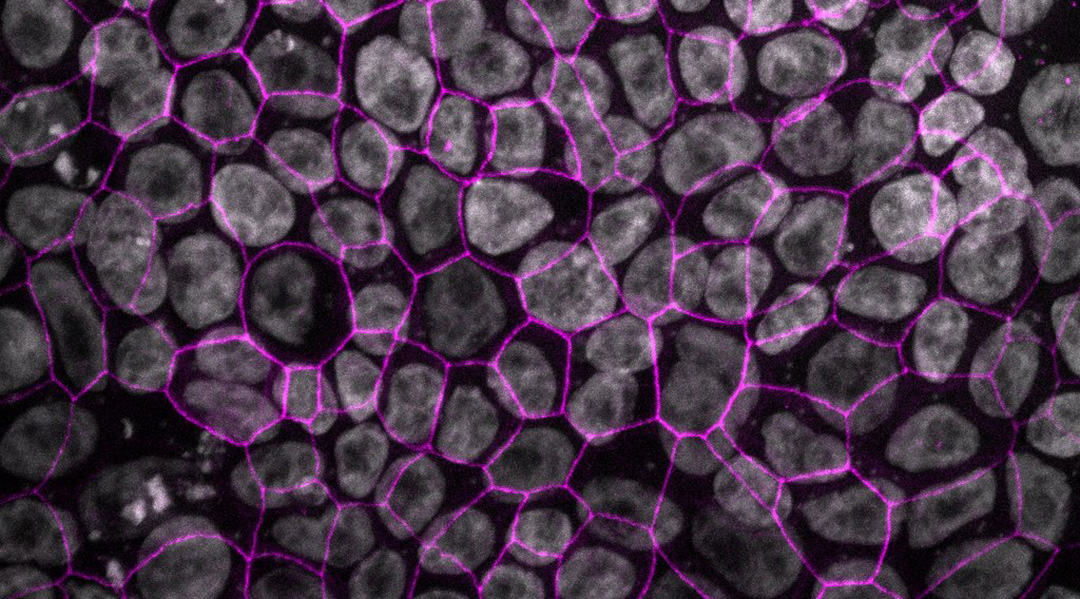
New lung model raises hopes for more realistic modeling of new drugs and therapies.
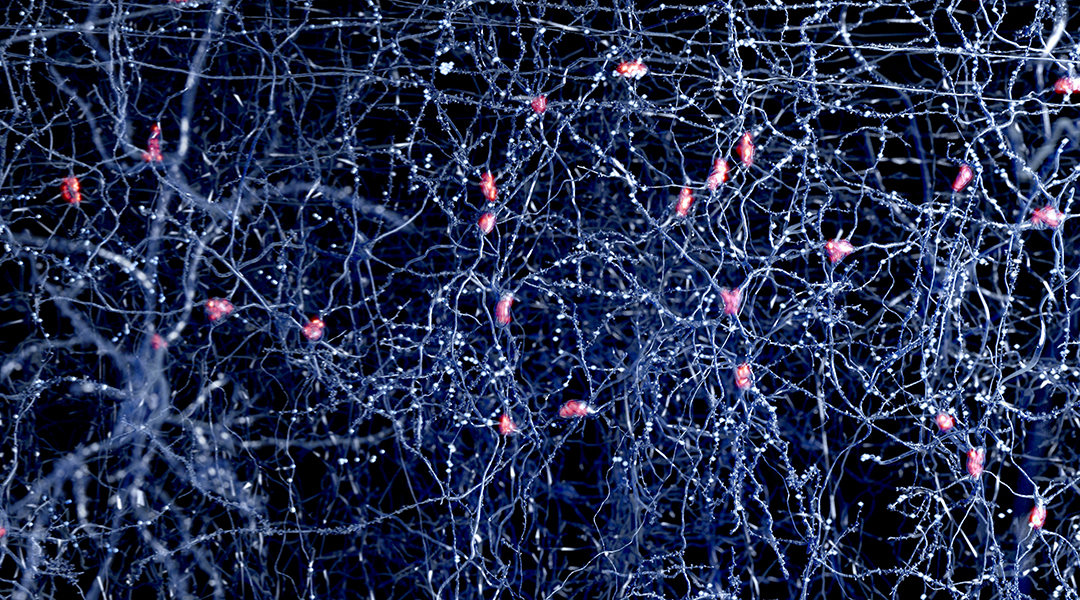
Researchers identify a protein that stops the brain from connecting memories, and regulating it could help improve memory loss treatment.

Viruses are so varied and evolve so quickly that creating effective treatments against them becomes a daunting task.
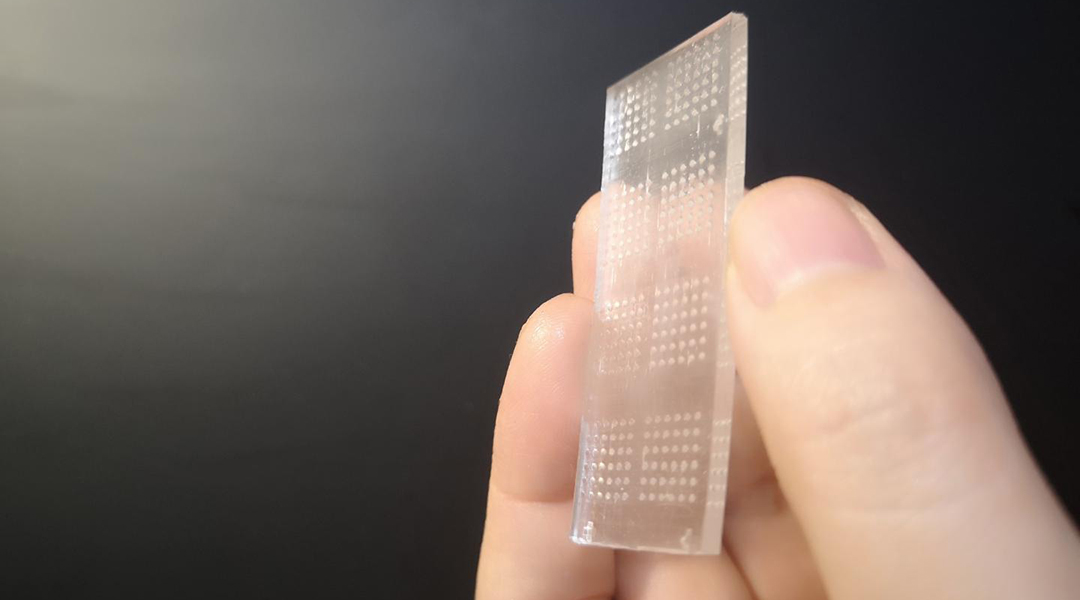
A new microwell chip holds promise for screening immunotherapy drugs with the added bonus that it can include a patient’s own cells for optimized treatment planning.
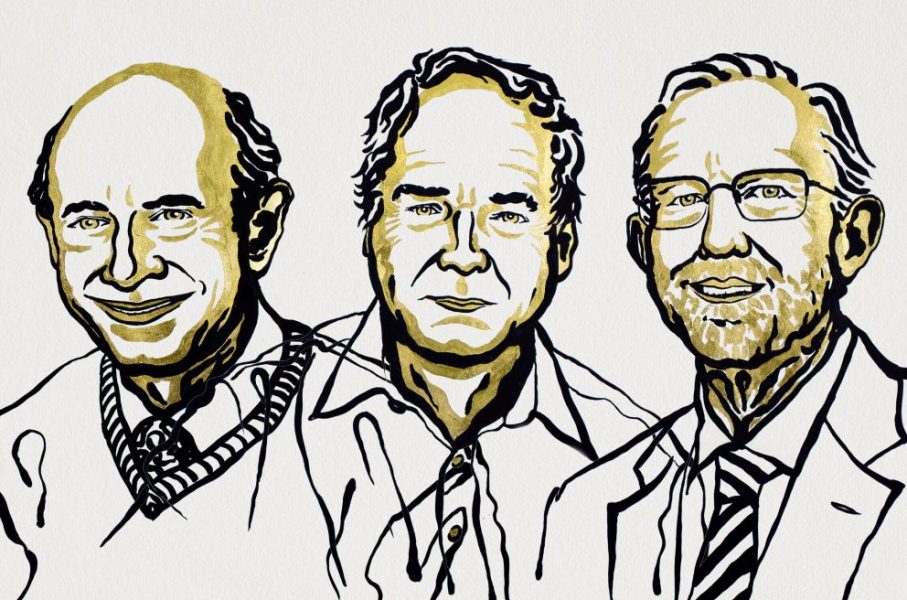

This year’s Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine recognizes the achievements made in identifying and treating hepatitis C.
New quantum algorithms will have dramatic impact in computational molecular biology and bioinformatics and promise to impact a number of life science applications.
RNA elements that are found in the genomes of numerous representatives within the same virus family provide new opportunities to expand the repertoire of targets for the development of antiviral therapy.