Researchers applying optomechnical systems to help unlock vibrational secrets of chemical and biological samples at the nanoscale.
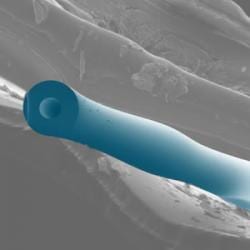

Researchers applying optomechnical systems to help unlock vibrational secrets of chemical and biological samples at the nanoscale.
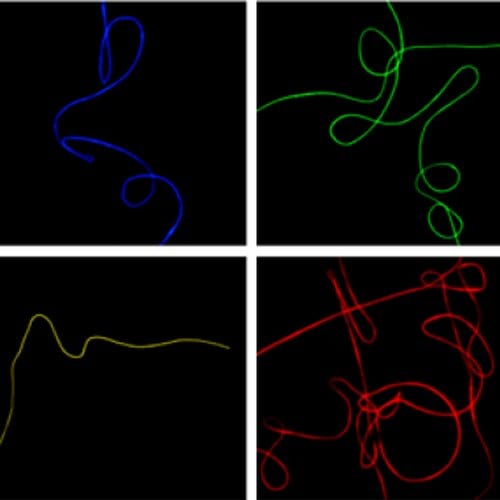
Italian researchers review the properties of electrospun light-emitting nanofibers.

New material could be perfect for tactile sensors for robot hands
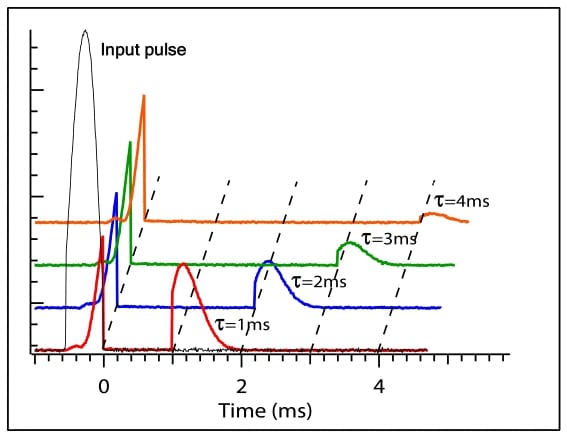
One of the exciting potential applications of electromagnetically induced transparency and slow and stored light is for practical realization of quantum memory, and, ultimately, quantum computing. Recent advances using ensembles of warm atoms in vapor cells have been made.
The main properties that make carbon nanotubes (CNTs) a promising technology for many future applications are: extremely high strength, low mass density, linear elastic behavior, almost perfect geometrical structure, and nanometer scale structure. Also, CNTs...
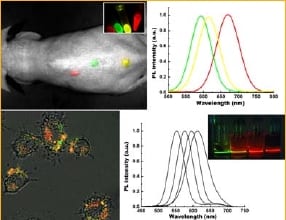
An international team of researchers review a useful tool for three dimensional multi-photon microscopy and imaging

Sending atomic and nuclear clocks into the inner reaches of our solar system could help scientists find proof of elusive dark matter.

When the light absorbers are made very small, almost all the device performance metrics improve—but doing this is easier said than done.
This new brain–computer interface detects weakened brain signals and boosts them to healthy levels, potentially reversing cognitive aging in the brain.
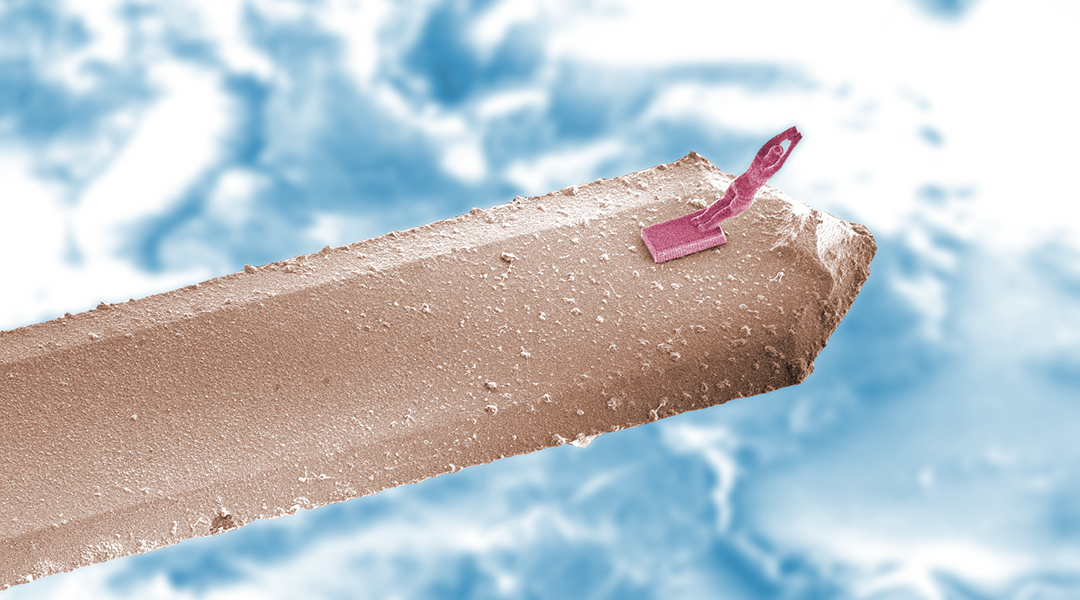

From holographic sound waves to nanobelt haystacks, this gallery gives a renewed appreciation for scientific exploration.