Latest
Turning Periods into Power: Menstrual Blood a Valuable Resource for Medical Diagnostics
Wearable sensors help women analyse menstrual blood for affordable, non-invasive health monitoring.

Behavioral Fever Helps Fight Parasitic Infections
Infected fruit flies use behavioral fever against deadly parasitoid wasps.

Fermilab Confirms Muon g-2 Measurements
Fermilab releases its final results, testing the Standard Model of particle physics.
Methods Perspectives: Magnetic Force Microscope Calibration Explored by Héctor Corte-León
Héctor Corte-León explores the advantages and disadvantages of the different techniques used to calibrate a magnetic force microscope.

Immune resilience gene signature could hold the key to healthy aging
High levels of a certain biomarker gives people a survival advantage, study finds.
Using 3D printing to treat bone infections
A new biomaterial shows unprecedented success at eliminating bacteria that cause bone infections and promote the regrowth of injured bones.

A Big Ring in the sky challenges modern cosmology
The discovery of colossal structures like the Big Ring is reshaping established theories about the physics of the Universe.

Routine test misses 70% of gestational diabetes cases
A new study urges doctors to turn to more dependable tests to prevent the development of type II diabetes in mothers and children.
Decorated nanospheres boost chemotherapy and cut side effects
Scientists are using decorated nanoparticles to precisely target tumors with chemotherapy, effectively reducing side effects.

Anti-aging for lasers: Gallium nitride lasers get a longevity boost
Scientists have uncovered the cause of rapid degradation in powerful gallium nitride lasers and develop a solution to extend their lifespan.
ASN Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter and receive the latest science news directly to your inbox.

A working quantum battery may be just around the corner
Scientists create designs for quantum batteries, which harness the potential of quantum mechanics to enhance energy storage.
How can we spur plastic upcycling? Turn it into something valuable
Scientists convert harmful microplastics into valuable graphene using plasma, offering a promising solution for this type of pollution.

AI and robotics join forces to revamp how medications are made
Scientists are speeding up drug formulation to breath new life into old medications and reduce risk of clinical trial failure.

Could adding extra dimensions help solve the quantum gravity puzzle?
Adding extra dimensions to a theory known as “fuzzy gravity” may help bridge the gap between quantum mechanics and relativity.

Misinformation spreads like a nuclear reaction on the internet
The new model simulating nuclear fission replicates the start and spread of rumors founded in misinformation.
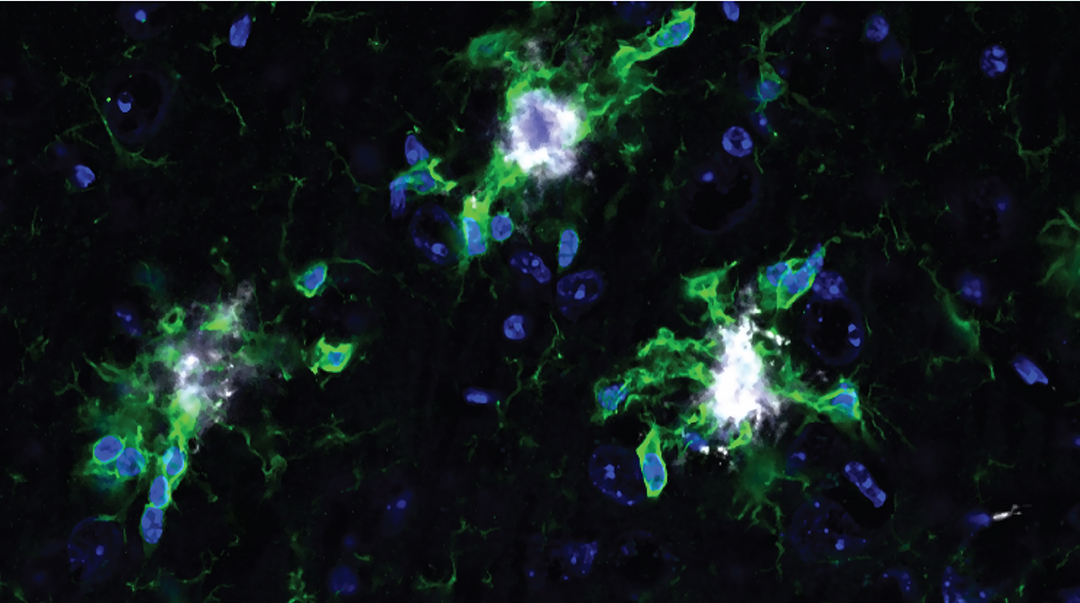
Xenon gas protects brain cells against Alzheimer’s disease, clinical trial underway
Inhaled xenon gas reduced neuroinflammation, brain atrophy, and boosted protective neurons in mouse models of Alzheimer’s.
Chirality could be the key to successful bone repair
Bone implants integrate better with the body when they mimic the natural handiness of molecules that make up our bones.

Computer system helps scientists understand how cancer could be reversed
BENEIN is a computer network that can identify the master regulators that cause normal cells to go cancerous.
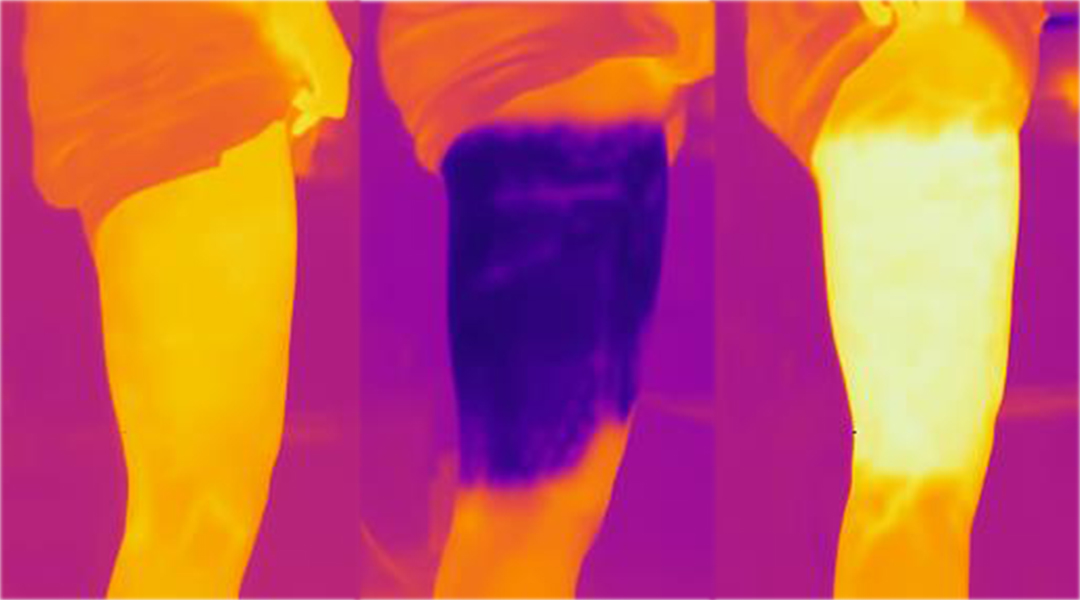

COOLWEAR: Water immersion therapy without waste
The fluidic wearable device is less wasteful when it comes to water, but equally effective alternative to water immersion therapy.
Xenon gas protects brain cells against Alzheimer’s disease, clinical trial underway
Inhaled xenon gas reduced neuroinflammation, brain atrophy, and boosted protective neurons in mouse models of Alzheimer’s.
Chirality could be the key to successful bone repair
Bone implants integrate better with the body when they mimic the natural handiness of molecules that make up our bones.
Computer system helps scientists understand how cancer could be reversed
BENEIN is a computer network that can identify the master regulators that cause normal cells to go cancerous.
COOLWEAR: Water immersion therapy without waste
The fluidic wearable device is less wasteful when it comes to water, but equally effective alternative to water immersion therapy.

Newly discovered quantum object could usher in new era of technology
Once relegated to theory, a newly discovered quantum object could be used to create new devices that will outpace modern electronics.

Quantum entanglement allows scientists to track time more accurately
Scientists have built atomic clocks with unprecedented levels of precision by harnessing quantum entanglement.
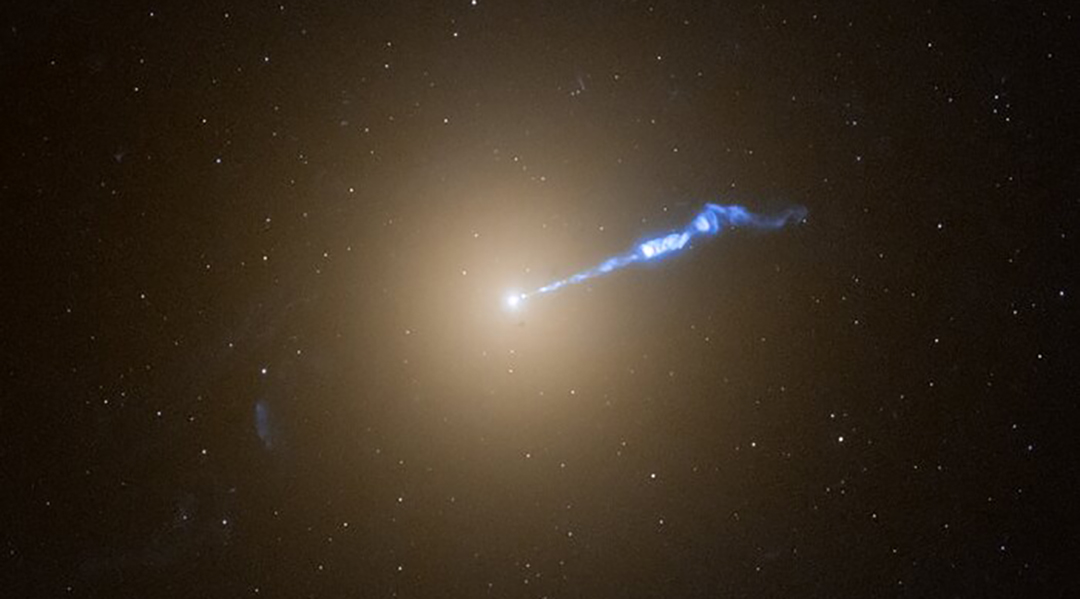

Black hole jet lights up dead stars like a cosmic blowtorch
Using the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers discovered the jet from a black hole, triggering nova explosions along its path.

Could dark matter particles be colliding?
New research on dwarf galaxies challenges the idea that dark matter is collisionless, suggesting it may interact in unexpected ways
Newly discovered quantum object could usher in new era of technology
Once relegated to theory, a newly discovered quantum object could be used to create new devices that will outpace modern electronics.
Quantum entanglement allows scientists to track time more accurately
Scientists have built atomic clocks with unprecedented levels of precision by harnessing quantum entanglement.
Black hole jet lights up dead stars like a cosmic blowtorch
Using the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers discovered the jet from a black hole, triggering nova explosions along its path.
Could dark matter particles be colliding?
New research on dwarf galaxies challenges the idea that dark matter is collisionless, suggesting it may interact in unexpected ways
Securing data with bright entangled photons
Secure data sharing methods using quantum key distribution via satellites promise advancements in long-distance quantum communication.

Quantum communication could be integrated into existing fiber optic networks, new study shows
Quantum communication doesn’t necessarily need to be delayed; it might be possible to integrate it into existing fiber optic networks.

Calculating the true environmental costs of AI
The rapid growth of AI brings hope of unprecedented advancements in many sectors but what is its real carbon footprint?

Butterflies inspire magnetic robots that fly more efficiently
Monarch butterflies have inspired the design of 3D-printed robotic wings that rely on magnetic fields to generate their delicate movements.
Securing data with bright entangled photons
Secure data sharing methods using quantum key distribution via satellites promise advancements in long-distance quantum communication.
Quantum communication could be integrated into existing fiber optic networks, new study shows
Quantum communication doesn’t necessarily need to be delayed; it might be possible to integrate it into existing fiber optic networks.
Calculating the true environmental costs of AI
The rapid growth of AI brings hope of unprecedented advancements in many sectors but what is its real carbon footprint?
Butterflies inspire magnetic robots that fly more efficiently
Monarch butterflies have inspired the design of 3D-printed robotic wings that rely on magnetic fields to generate their delicate movements.

A rockslide in Greenland caused the Earth to vibrate for nine days
A mega-tsunami in Greenland surged through a fjord for days, creating seismic waves that caused seismometers across the globe to hum.

How can we spur plastic upcycling? Turn it into something valuable
Scientists convert harmful microplastics into valuable graphene using plasma, offering a promising solution for this type of pollution.

The threat beneath our feet: How soil microbes are losing the battle against crop disease
Just like our gut has helpful microbes, so too does the soil around plant roots. But what happens when antibiotics disrupt this balance?
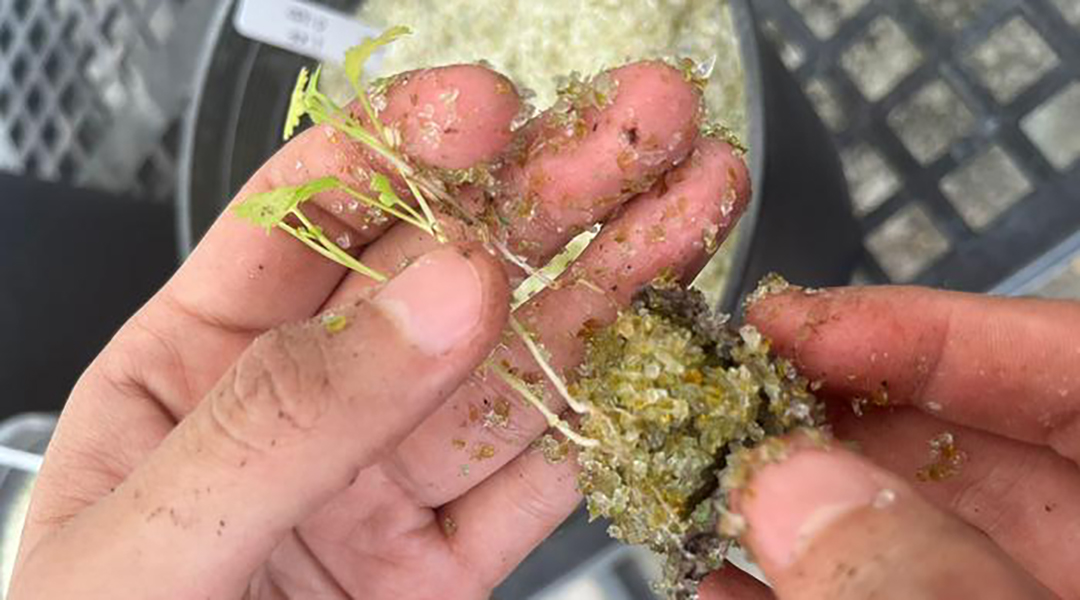

Crushed glass replaces soil in this innovative approach to sustainable agriculture
Pilot study explores how recycled glass is being used to grow salsa ingredients, protect coastlines, and safeguard the future of farming.
A rockslide in Greenland caused the Earth to vibrate for nine days
A mega-tsunami in Greenland surged through a fjord for days, creating seismic waves that caused seismometers across the globe to hum.
How can we spur plastic upcycling? Turn it into something valuable
Scientists convert harmful microplastics into valuable graphene using plasma, offering a promising solution for this type of pollution.
The threat beneath our feet: How soil microbes are losing the battle against crop disease
Just like our gut has helpful microbes, so too does the soil around plant roots. But what happens when antibiotics disrupt this balance?
Crushed glass replaces soil in this innovative approach to sustainable agriculture
Pilot study explores how recycled glass is being used to grow salsa ingredients, protect coastlines, and safeguard the future of farming.

André Isaacs: “Be okay with making mistakes”
Through teamwork and respect, Isaacs is forming lasting relationships with his students and building a community around dance.
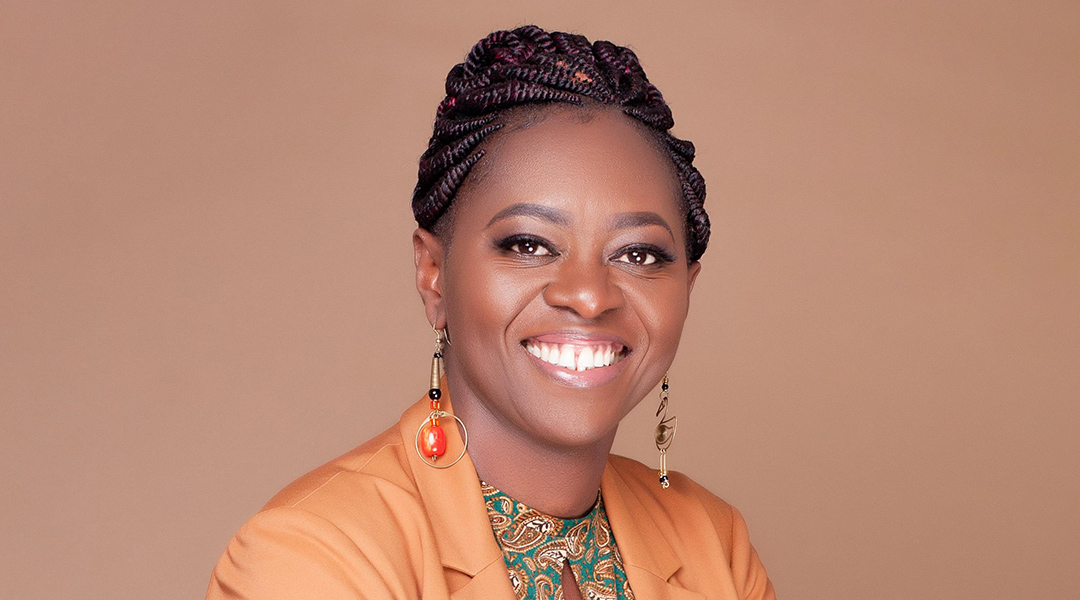

Faith Osier: “Throw yourself wholeheartedly into what you do”
With research groups spread over two continents, Osier is striving to eliminate malaria through her groundbreaking work in immunology, advocacy and awareness.
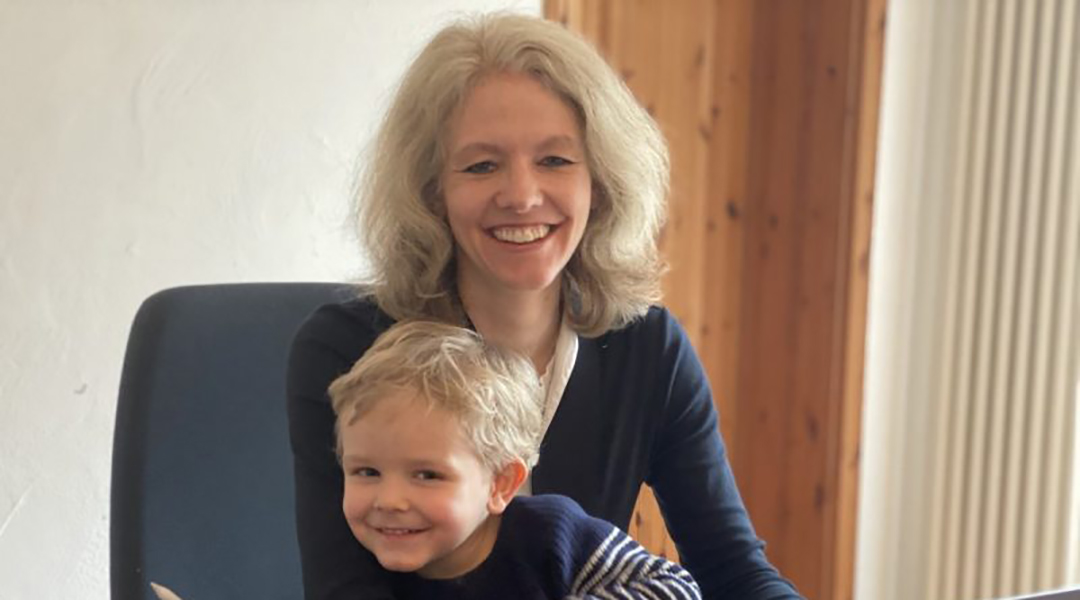

Bettina Lotsch: “I am excited by the prospect that our research can actually make a difference”
The materials chemist discusses her research, new innovations in tackling the energy crisis, and how her son helps with “zoom fatigue”.
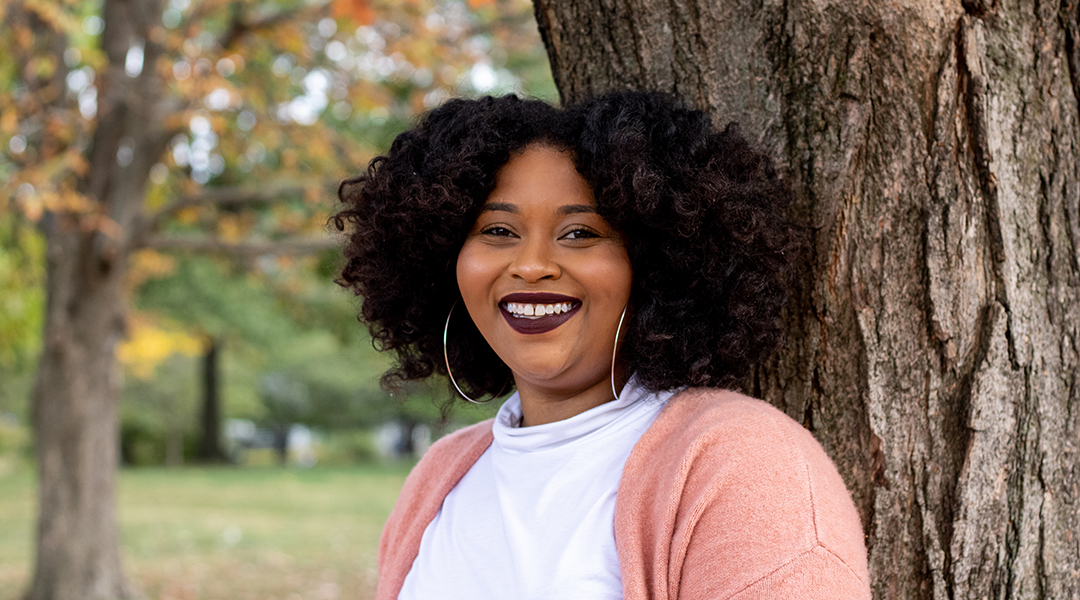

Devin Swiner: “At the heart of what I do, I want my science to help people”
The up-and-coming analytical chemist talks social media, engaging the next generation of women in STEM, and her journey through a Ph.D.

André Isaacs: “Be okay with making mistakes”
Through teamwork and respect, Isaacs is forming lasting relationships with his students and building a community around dance.

Faith Osier: “Throw yourself wholeheartedly into what you do”
With research groups spread over two continents, Osier is striving to eliminate malaria through her groundbreaking work in immunology, advocacy and awareness.

Bettina Lotsch: “I am excited by the prospect that our research can actually make a difference”
The materials chemist discusses her research, new innovations in tackling the energy crisis, and how her son helps with “zoom fatigue”.

Devin Swiner: “At the heart of what I do, I want my science to help people”
The up-and-coming analytical chemist talks social media, engaging the next generation of women in STEM, and her journey through a Ph.D.