EPFL scientists have developed an innovative mathematical method to greatly improve computer modeling of metamaterials.

Composite laminates might replace metallic implants
Researchers from Universities in Germany, Brazil, and Israel designed promising multilayer composites applicable as bone fracture fixation devices but also for other orthopedic applications.
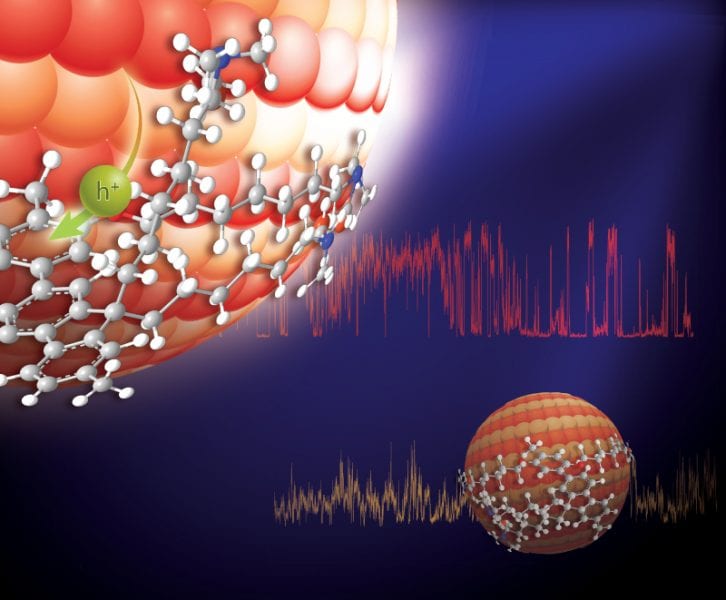
Shrinking quantum dots improves charge transfer
Single-particle study identifies possible path to improved conversion of sunlight to electricity in photovoltaic devices.
Most accessed papers in physica status solidi for October 2013
We present the most downloaded papers from the pss family of journals from October.
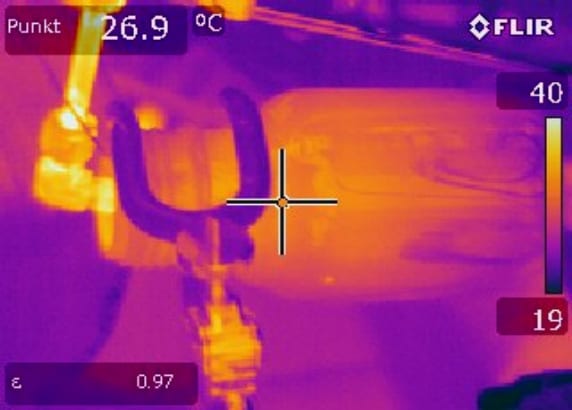

A better way to decontaminate medical supplies
Research investigates the antimicrobial efficiency of microwave plasma processed air with manifold RNS against vegetative bacteria and bacterial endospores.
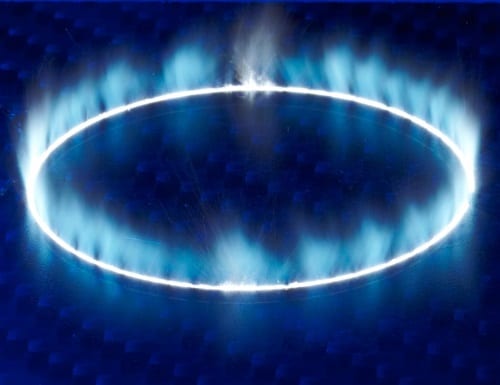
Cutting CFRP for future car generation
Volkswagen AG and partners are developing an innovative laser process for automated cutting of CFRP components for mass production.
September highlights from physica status solidi
Nanowires, solar cells, and silicene – these and more in September’s physics highlights.
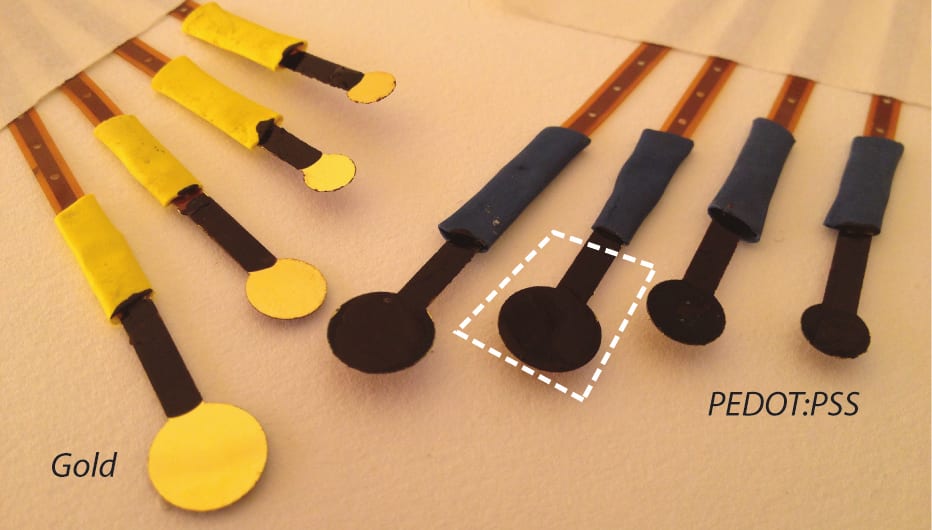
Better conducting gel for better EEG readings
Researchers suggest using conducting polymers as a new type of dry (gel-free) electrode for EEG.

Lynn Loo joins Advanced Materials' advisory board
Lynn Loo of Princeton University joins the editorial advisory board of Advanced Materials from 2013.
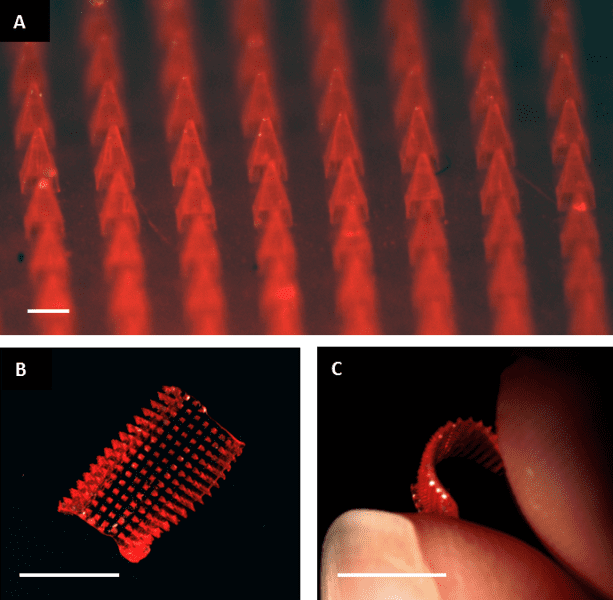
Dissolvable microneedle patches for transdermal drug delivery
The application of biocompatible polymeric microneedle patches is discussed as a promising and straightforward method of transdermal drug delivery.










