Synthesis of a rare metal complex of nitrous oxide opens new vistas for the degradation of a potent greenhouse gas.
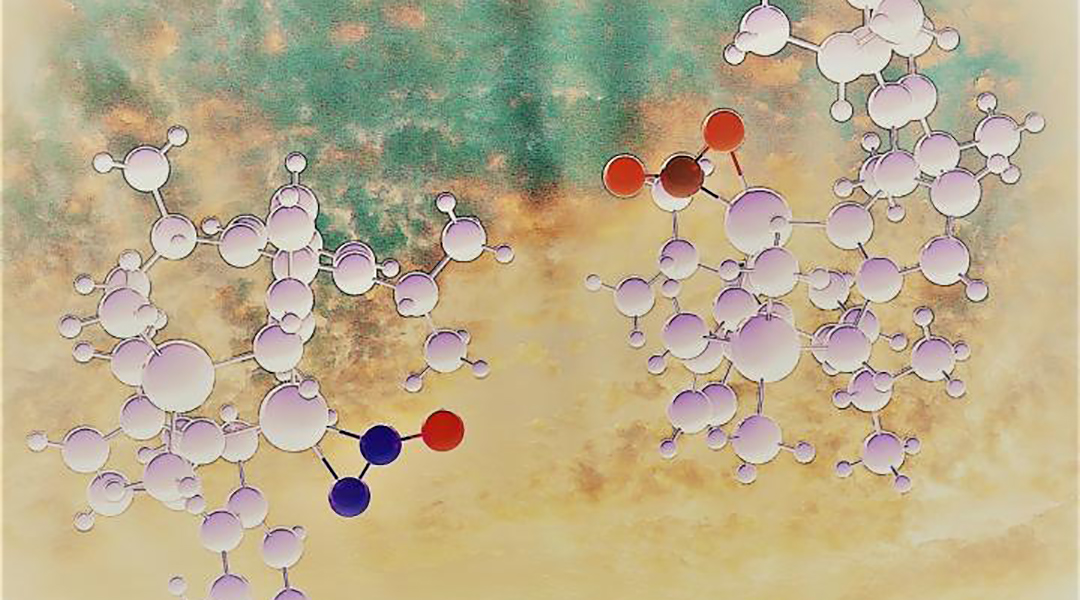

Synthesis of a rare metal complex of nitrous oxide opens new vistas for the degradation of a potent greenhouse gas.
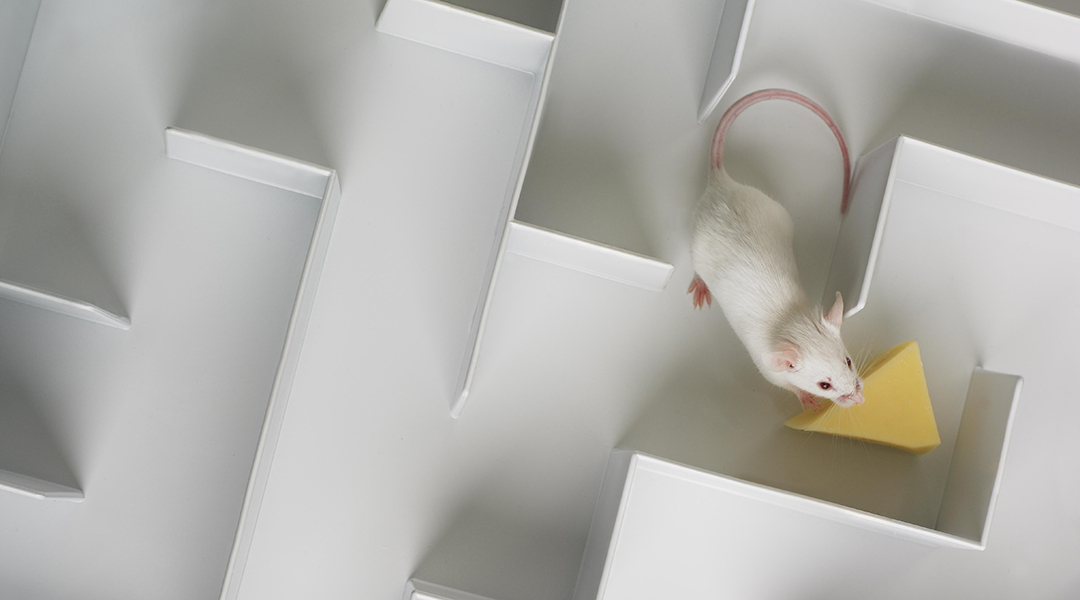

Replacing animal testing with the ever-growing capabilities of AI and deep learning could help minimize the need for animals in scientific discovery.

The Dyatlov Pass incident is an intriguing unsolved mystery. Now, researchers from EPFL and ETH Zürich use science to put forth a plausible explanation for the mysterious death of nine hikers.

Nvel tuberculosis vaccine demonstrated strong immune response in mice.
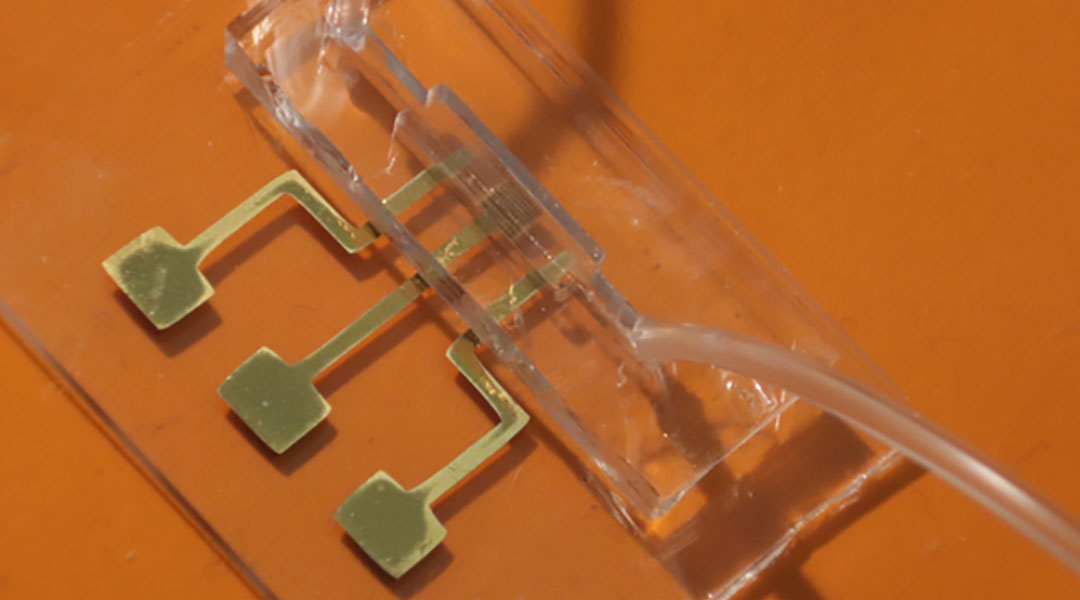
The testing platform identifies the presence of two antibodies in microliter samples of blood.
Models that can predict and help us to understand the body’s thermal state could help optimize temperature management strategies in a clinical setting.
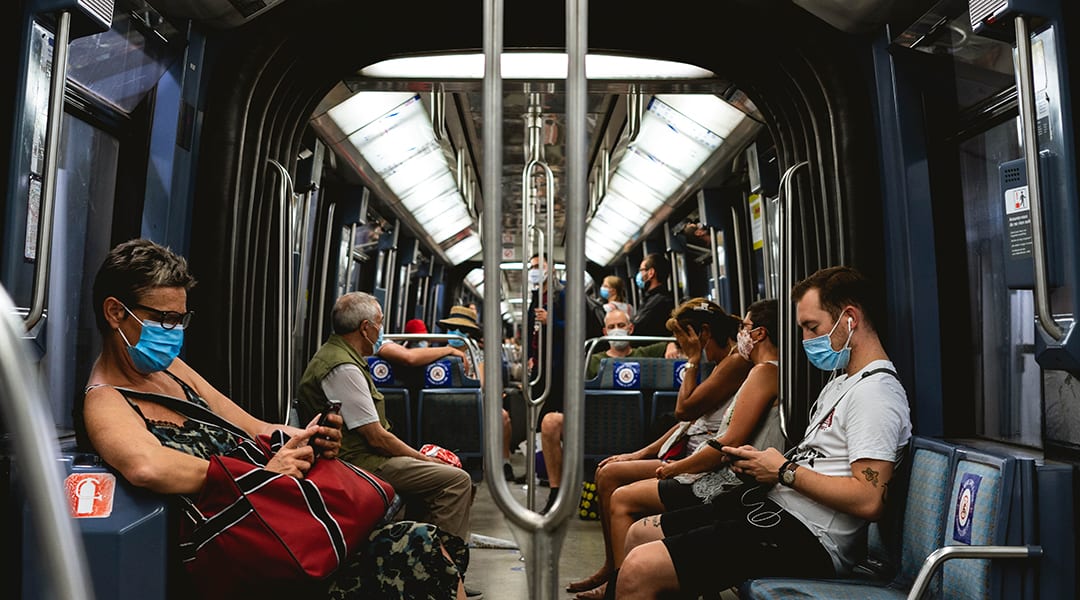

Developments in pathogen-detecting materials could provide an easy means of detecting viruses within public places.
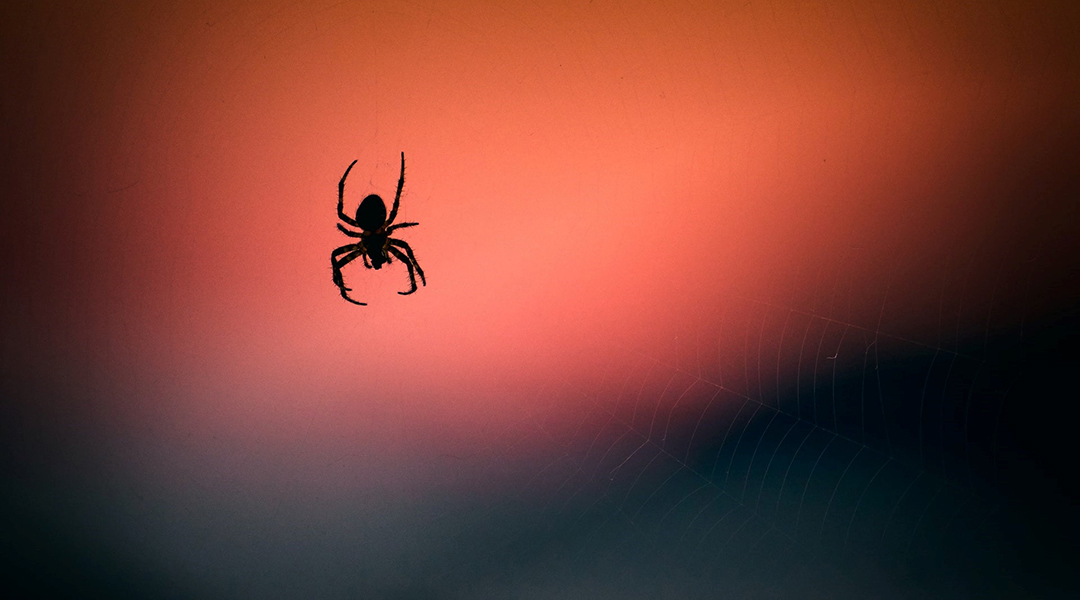

New research is uncovering the importance of small predatory species in shaping ecosystems and managing threatened populations.

This year’s Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine recognizes the achievements made in identifying and treating hepatitis C.
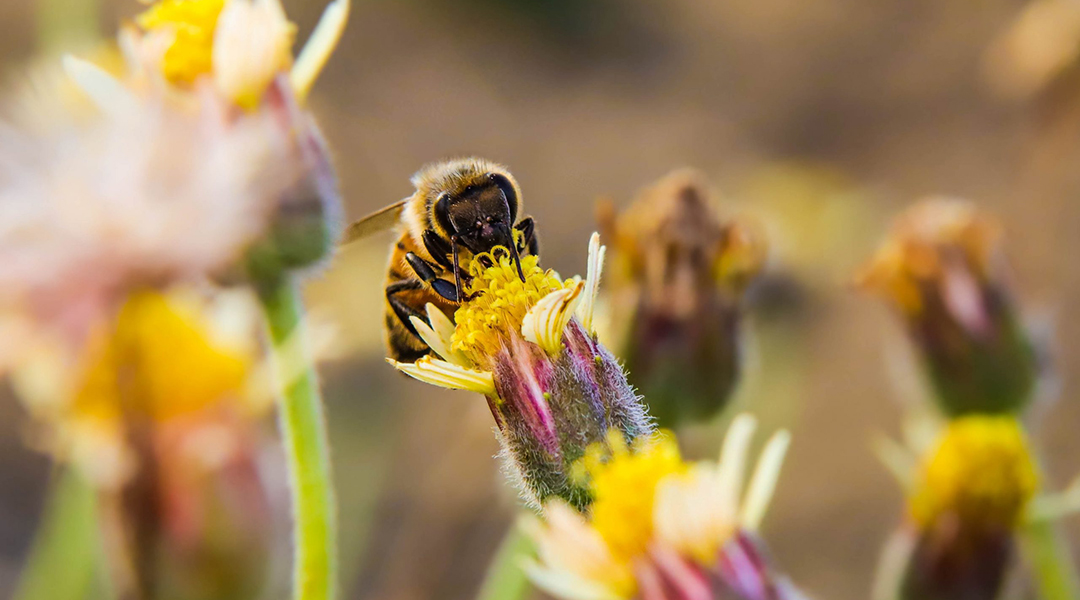

Spread of the giant Asian hornet (Vespa mandarinia) in the USA threatens honeybee colonies, and new analysis assesses the possible impact.