In many fields, from health to food quality control, environmental monitoring and technical applications, there is a growing demand for responsive sensors, which show fast and simple changes in the presence of specific molecules. Water is among the most common chemicals to be monitored. “Understanding how much water is present in a certain environment or material is important,” explains DESY scientist Michael Wharmby.
The functional part of the scientists’ new sensor-material is a so-called copper-based coordination polymer, a compound with a water molecule bound to a central copper atom. “On heating the compound to 60 °C, it changes colour from blue to purple”, reports Pilar Amo-Ochoa from the Autonomous University of Madrid (UAM). “This change can be reversed by leaving it in air, putting it in water, or putting it in a solvent with trace amounts of water in it.” Using high-energy X-rays, the scientists were able to see that in the sample heated to 60 °C, the water molecule bound to the copper atoms had been removed. This leads to a reversible structural reorganisation of the material, which is the cause of the colour change.
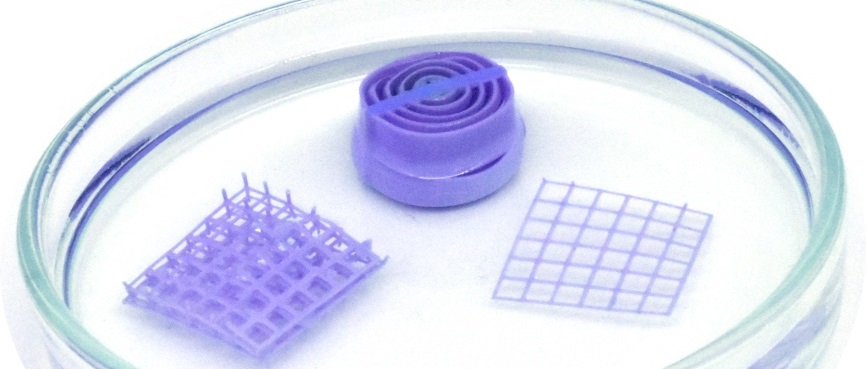
“Having understood this, we were able to model the physics of this change,” explains José Ignacio Martínez from the Institute for Materials Science in Madrid. The scientists were then able to mix the copper compound into a 3D printing ink and printed sensors in several different shapes which they tested in air and with solvents containing different amounts of water. These tests showed that the printed objects are even more sensitive to the presence of water than the compound by itself, thanks to their porous nature. In solvents, the printed sensors could already detect 0.3 to 4 %of water in less than two minutes. In air, they could detect a relative humidity of 7 %.
If it is dried, either in a water free solvent or by heating, the material turns back to purple. A detailed investigation showed that the material is stable even over many heating cycles, and the copper compounds are evenly distributed throughout the printed sensors. Also, the material is stable in air over at least one year and also at biological relevant pH ranges from 5 to 7. “Furthermore, the highly versatile nature of modern 3D printing means that these devices could be used in a huge range of different places,” emphasises Shlomo Magdassi from The Hebrew University of Jerusalem. He adds that the concept could be used to develop other functional materials as well.
“This work shows the first 3D printed composite objects created from a non-porous coordination polymer,” says Félix Zamora from the Autonomous University of Madrid. “It opens the door to the use of this large family of compounds that are easy to synthesize and exhibit interesting magnetic, conductive and optical properties, in the field of functional 3D printing.”