Three-dimensional (3D) printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a family of several flexible manufacturing methods that enable creation of structures usually in a layer-by-layer manner. There is a common belief in the 3D printing community that this approach will be able to soon revolutionize the manufacturing approaches in a wide range of industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction and dentistry. Rapid progress in the development of techniques has made 3D printing affordable to research communities, industries, and hobbyists.
For instance, thanks to open source designs, the price of an FDM 3D printer can be as low as $500. Ease of use, growing reliability, cost-effectiveness (e.g., inexpensive tools), design freedom and diversity of compatible materials (e.g., metals, polymers, ceramics) are amongst numerous benefits provided by 3D printing. Multimaterial printing is another capability of 3D printing to manufacture structures that require locally varying properties in order to be light and economic.
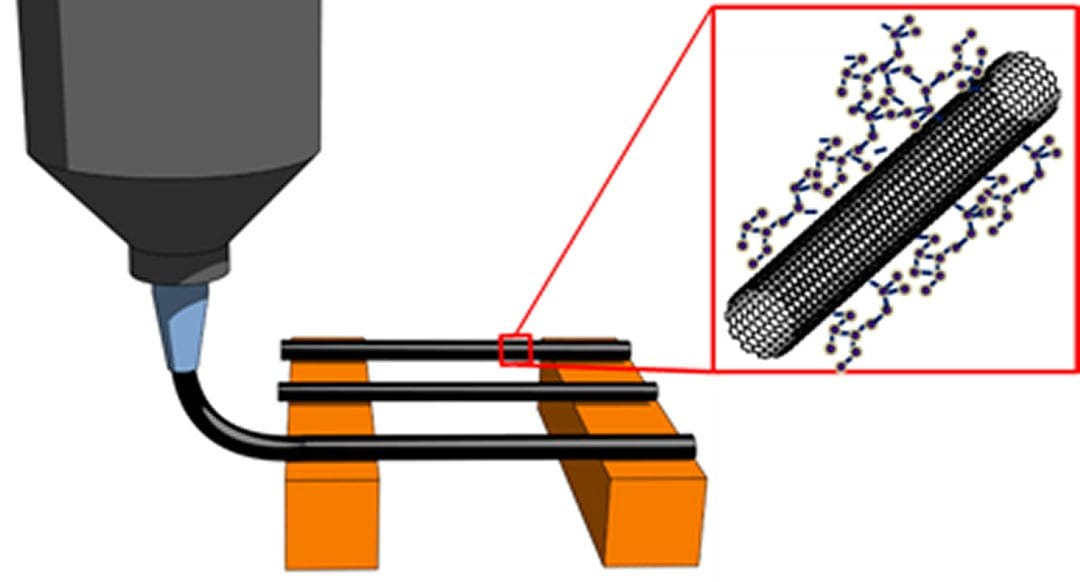
In addition to the development of 3D printing processes, new materials need to be developed in order to fabricate high-end products as the parts fabricated using typical printing materials (e.g., photopolymers or thermoplastics) have low mechanical strength and no functionality. The incorporation of nano- and micro-scale reinforcements to these pure printing materials improve mechanical performance and add various functionalities (e.g., electrical, thermal, magnetic) to the printed parts. The capability of 3D printing for customized geometries combined with improved materials’ properties using reinforcements enable tailoring final properties of the parts. These characteristics push 3D printing from prototyping to fabrication of high-end products for a wide variety of applications ranging from relatively small devices such as microelectronics, dental implants, biomedical (e.g., ligaments and organs), to large composite structures for aerospace and automotive industries. In this article, a brief overview is presented mainly over the latest progresses in 3D printing of multifunctional polymer nanocomposites and microfiber einforced composites including the benefits, limitations and potential applications.