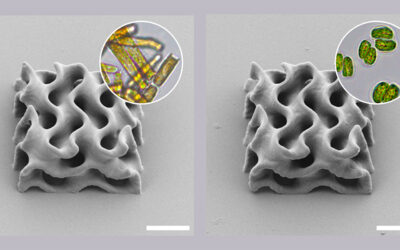
In 2014, the School of Footwear Design and Technology Politecnico Calzaturiero, in Capriccio di Vigonza near Padua, awarded a prize for its eighth design contest realized in cooperation with BASF. This time the task was to develop an innovative design of a sneaker using polyurethanes (PU). The winning project presents a sneaker suitable for cycling and street walking with an interesting design and a clever use of different PU and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) materials.
In 2014, the School of Footwear Design and Technology Politecnico Calzaturiero, in Capriccio di Vigonza near Padua, awarded a prize for its eighth design contest realized in cooperation with BASF. This time the task was to develop an innovative design of a sneaker using polyurethanes (PU). The winning project presents a sneaker suitable for cycling and street walking with an interesting design and a clever use of different PU and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) materials.
Especially for use in very cold weather conditions, BASF now offers a family of PU systems under the name Elastopan Extreme Frost. The most important feature here is the combination of flexural performance at extremely low temperatures with a very high slip resistance on wet and icy surfaces, low abrasion and good shock absorption. These properties make it suitable for even Arctic and Siberian working shoes. The chemical company told that in contrast to standard systems, soles made from this new material show a flexural strength at minus 45°C of more than 50,000 cycles in Canadian Ross flex test and over 8,000 cycles under Russian GOST conditions.
The second innovation is the polyester-based Hydrolysis Plus, a new Elastopan PU system as well. Shoemakers can use it for the higher-density outsoles as well as for the lower-density midsoles and for leisure as well as for safety shoes. However, it is specifically designed and shows its benefits mainly in single density soles for street and casual shoes. BASF reports that the relative loss of hardness was less than 15% after the standard hydrolysis test (100% relative humidity, 21 days at 70 °C). Under the same conditions, the tensile strength was reduced by less than 30%. These properties ensure high durability under extremely hot and humid conditions.
BASF now also offers Elastopan and Elastollan grades manufactured based on renewable resources. Here customers can choose between a bio-based TPU or PU system derived from sebacic acid or the new mass balance approach. In this approach the substitution of fossil raw materials by renewable ones takes place already during the manufacturing of basic chemicals. The bio-based amount of raw material is then allocated mathematically to the corresponding product. This allows to save fossil resources, to reduce greenhouse gases and guarantees the established chemical and mechanical properties of the existing systems.