Scientists from the University of La Rioja in Spain showed how polyoxymethylene (POM) can be an excellent engineering material for 3D printing when an atmospheric pressure air plasma treatment is applied on a polycarbonate (PC)‐printing base.
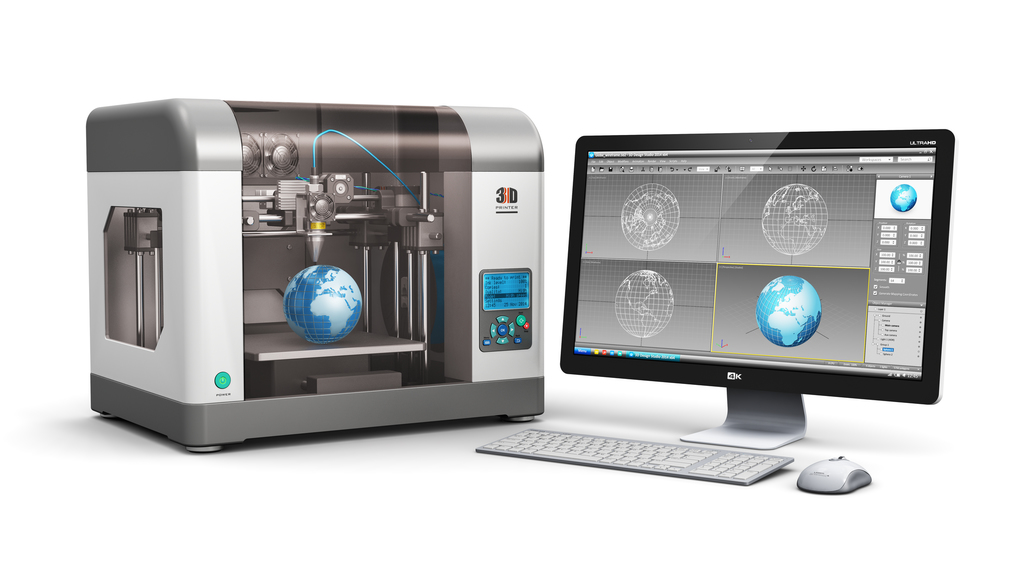


Scientists from the University of La Rioja in Spain showed how polyoxymethylene (POM) can be an excellent engineering material for 3D printing when an atmospheric pressure air plasma treatment is applied on a polycarbonate (PC)‐printing base.
Modelling can now confidently include accurate energy coupling parameters, leaving less to guess work.

Designing a low-cost human-machine interface with specific function and desirable performance characteristics.
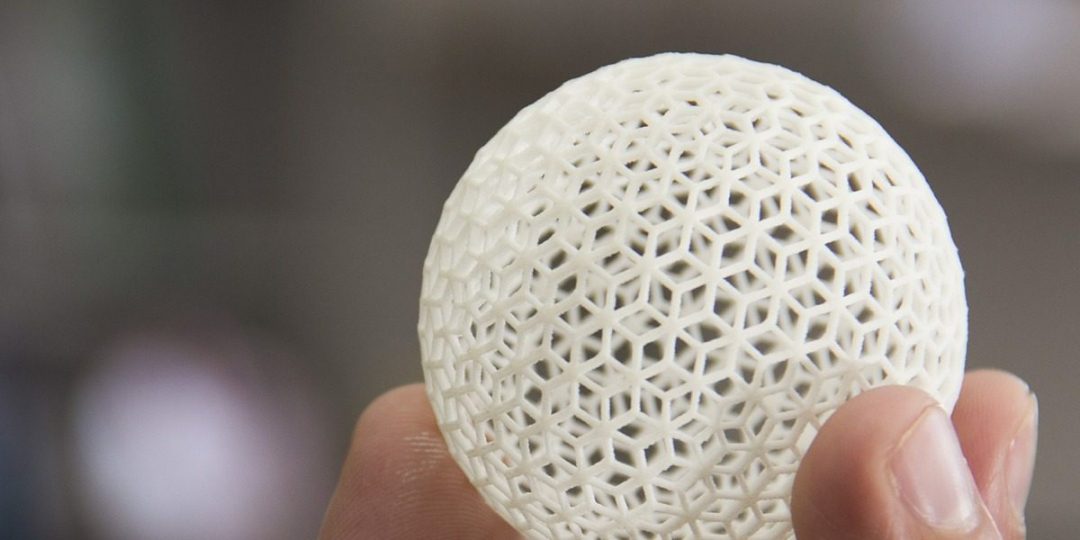

This month’s Advanced Engineering Materials covers and top papers!
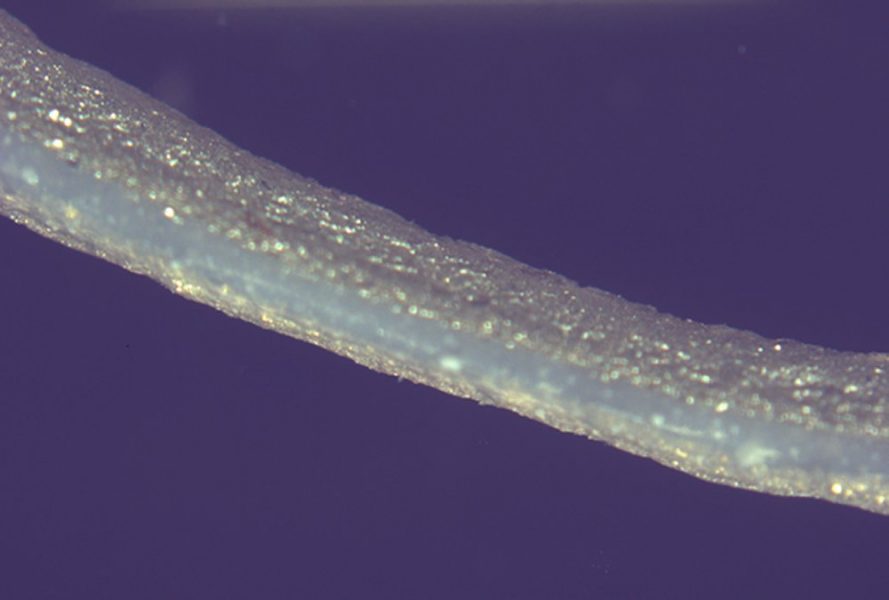
Researchers 3D printed piezoelectric sensors in a single step at room temperature by extruding a piezoelectric nanocomposite sandwiched between two layers of silver paste acting as electrodes.

New findings have the potential to vastly increase the functional capabilities of 3D-printed devices for industries such as electronics, healthcare and quantum computing.
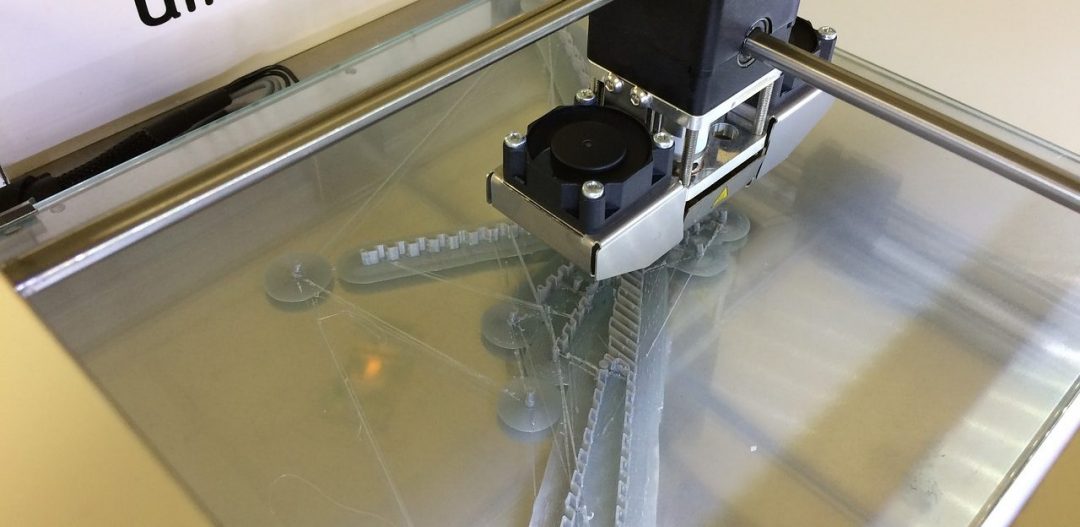

A team or Irish researchers evaluated the use of a barrel atmospheric plasma system for the treatment of the polymers acrylonitrile butadiene styrene and polylactic acid polymer particles used in 3D printing.

This month’s Advanced Engineering Materials covers and top papers!

Precision micromanufacturing of electrospun microfibers can create 3D scaffold structures which support the growth of tessellated microtissues.
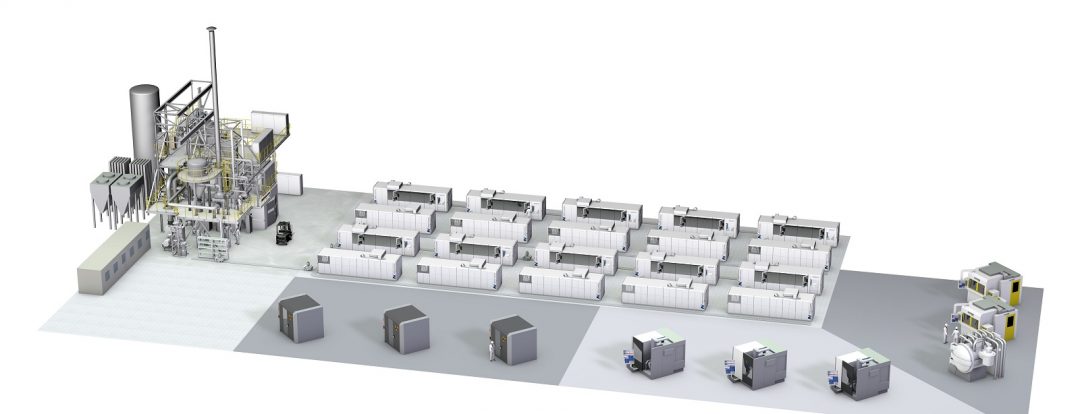

Additive Industries and SMS group jointly develop a production system for additive manufacturing of metals in industrial scale.