Making lab-grown meat with a new 3D-printing strategy that combines fat and muscle cells to make the perfect, artificial steak.
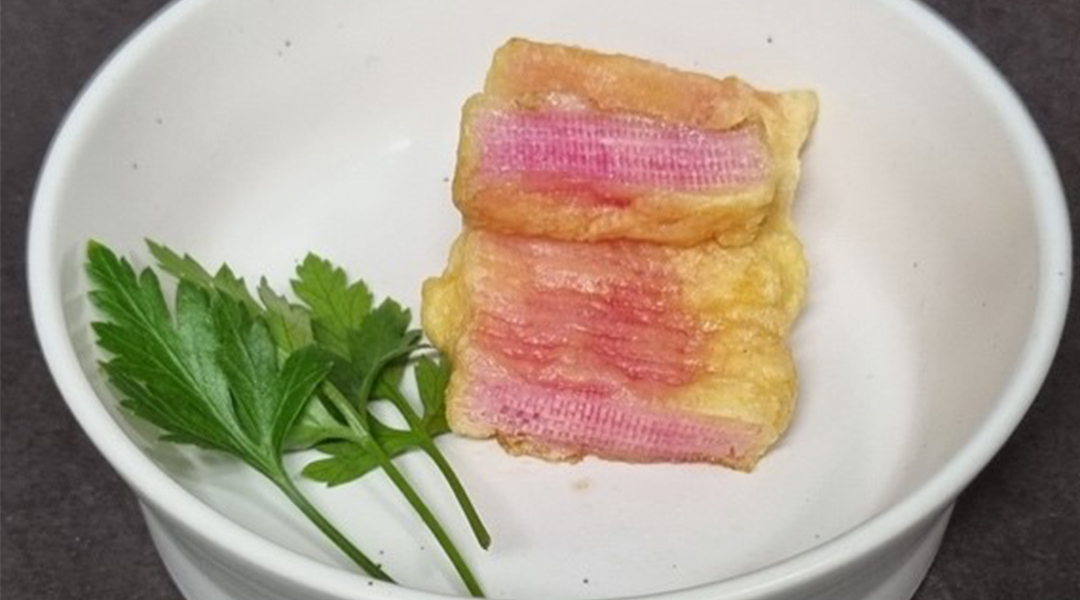


Making lab-grown meat with a new 3D-printing strategy that combines fat and muscle cells to make the perfect, artificial steak.

Made of self-assembling nanoparticles and a microgel, this new material could overcome limitations in 3D bioprinting.
Self-sensing materials will find a range of applications from tissue engineering to building lightweight aircraft.
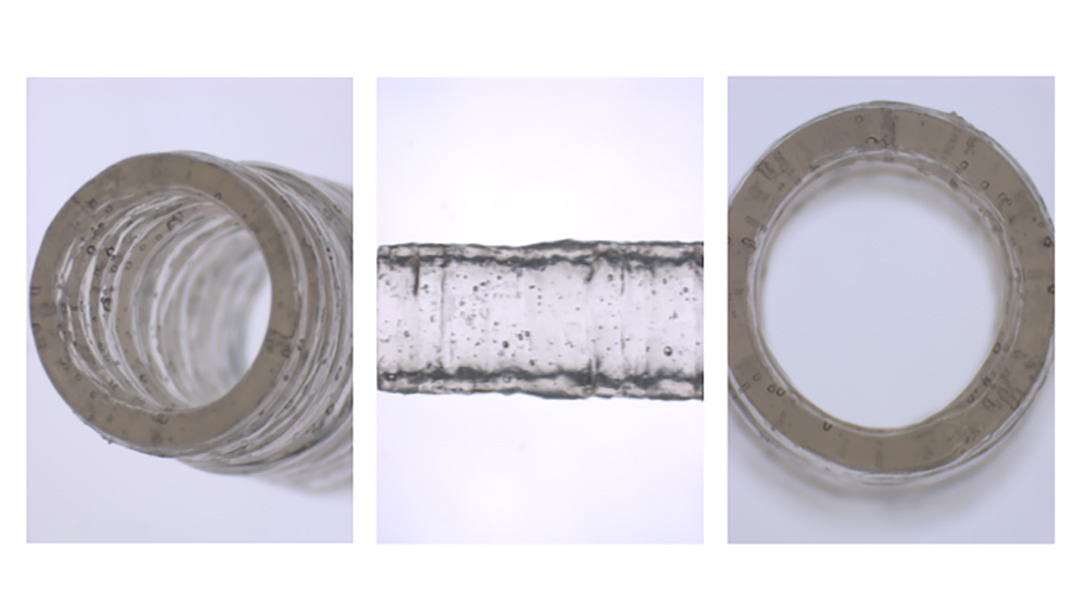
A new nanoengineered bioink allows scientists to print 3D, anatomically accurate, multicellular blood vessels.
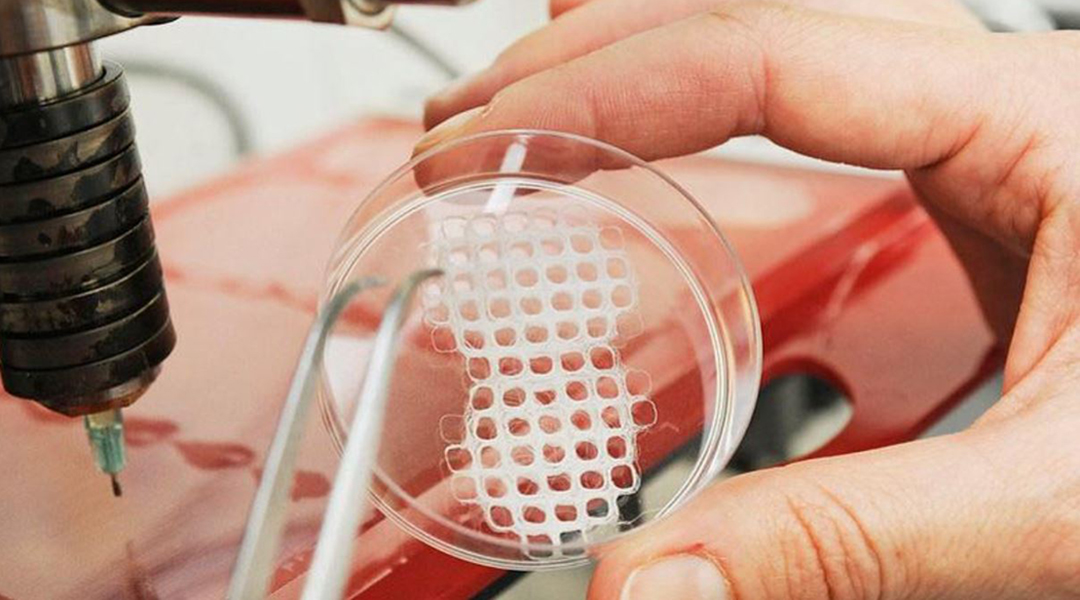
Machine vision and artificial intelligence can fine tune medical 3D printers to enable custom made tissue implants to suit the individual patient.
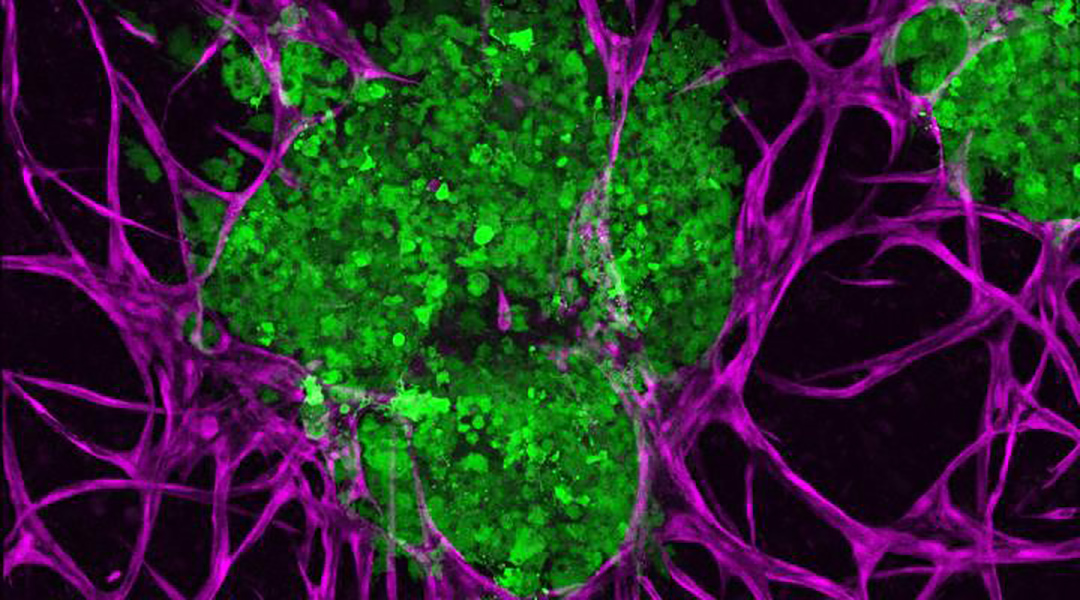
A prototype platform allows researchers to culture and study tumor growth in new detail.
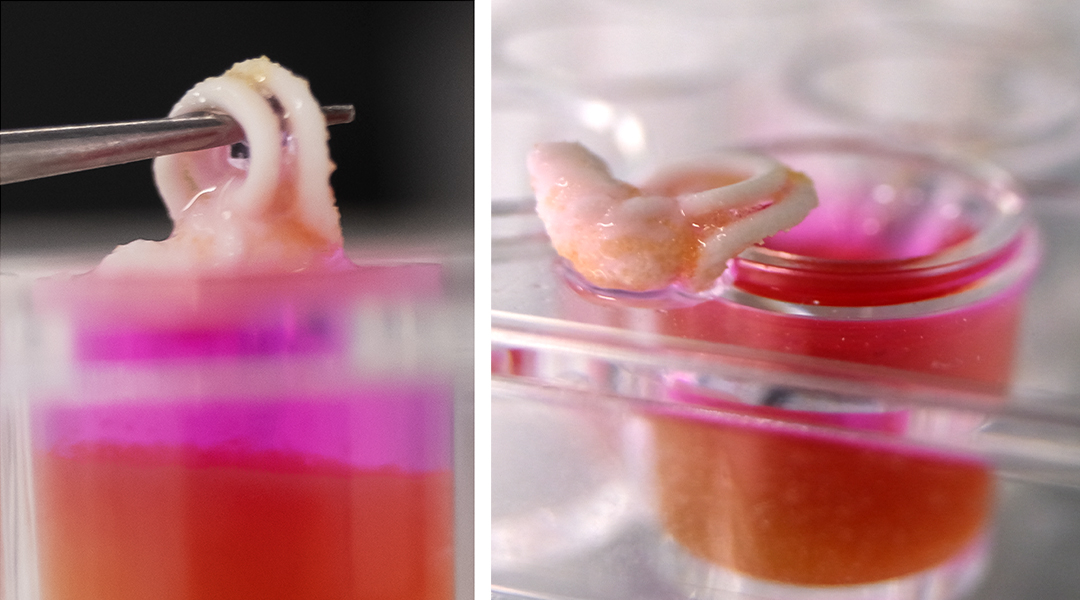
Researchers develop a new strategy to 3D print bone-mimicking structures at room temperature incorporating live, bone-forming cells.
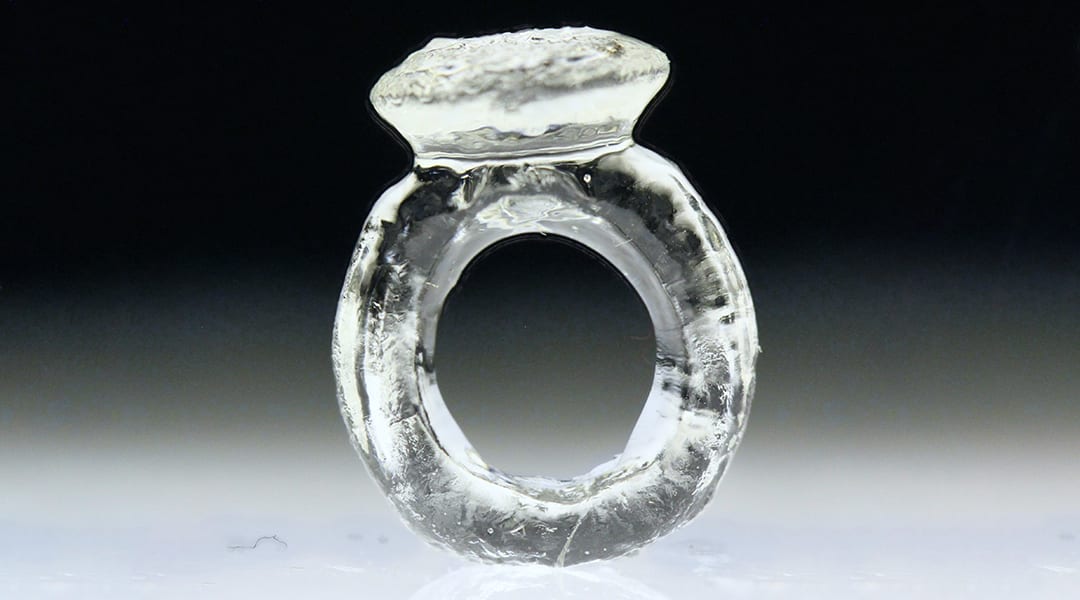

A new light-sensitive polymer resin gives researchers more control over 3D-printed objects.
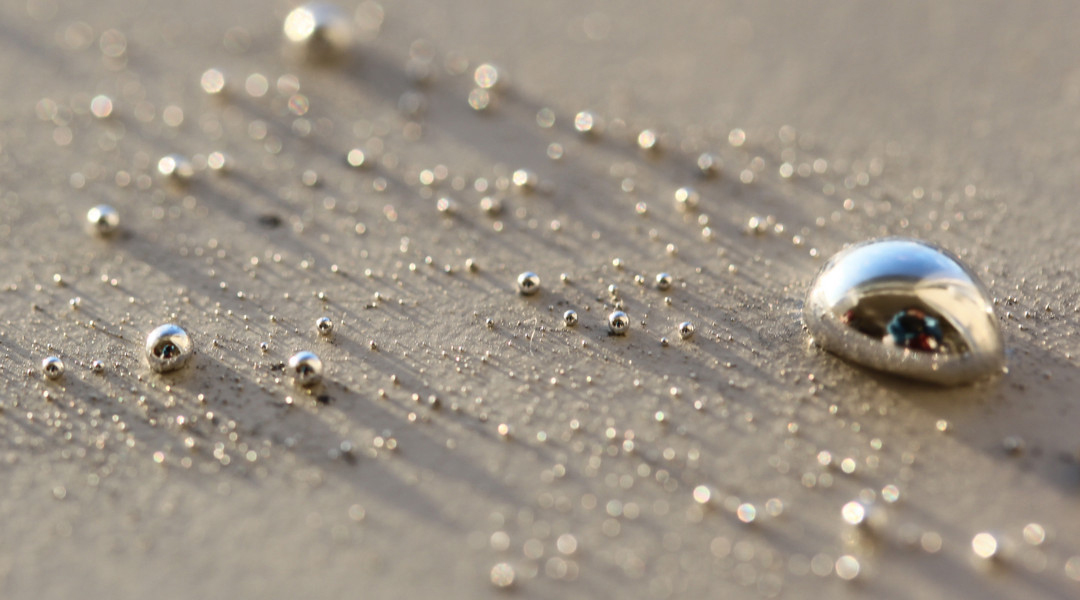

Direct‐write and 3D printing using liquids metals provides an interesting alternative for wiring in circuitry.
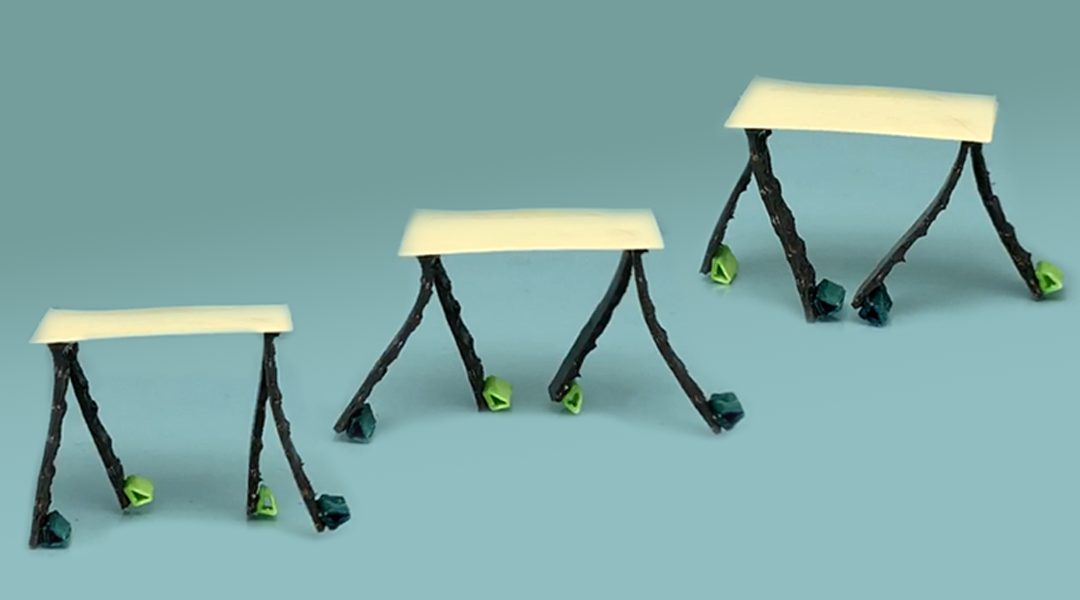

An automatic design approach with a new 3D-printing method is established to fabricate soft composites that can change to predetermined shapes and generate controllable robotic motions under a magnetic field.