Chien-Shiung Wu was an expert in nuclear physics, making many significant contributions to not only the field, but our understanding of the Universe.
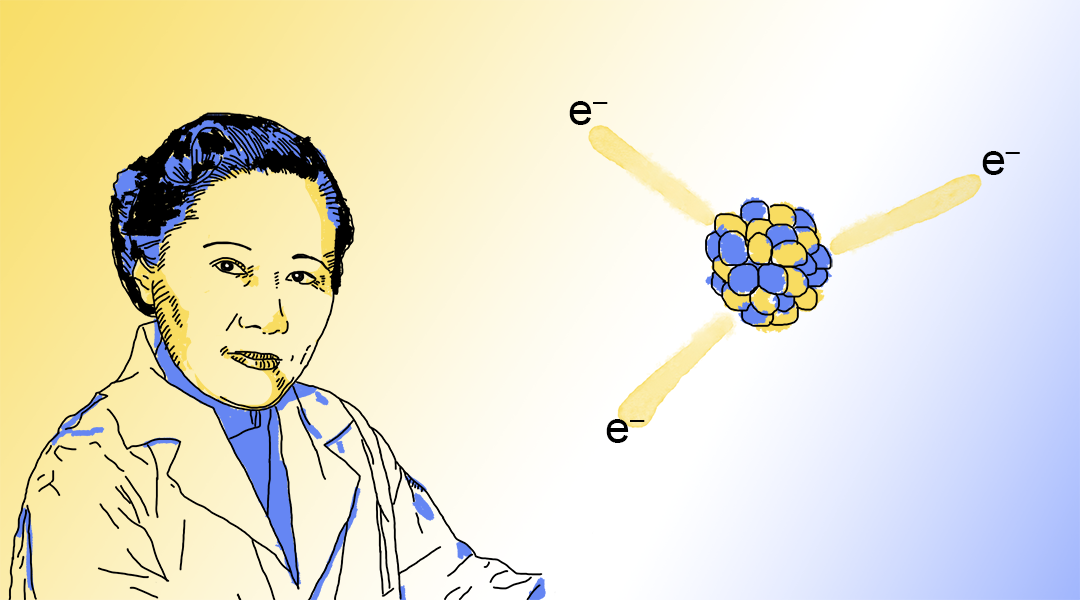

Chien-Shiung Wu was an expert in nuclear physics, making many significant contributions to not only the field, but our understanding of the Universe.
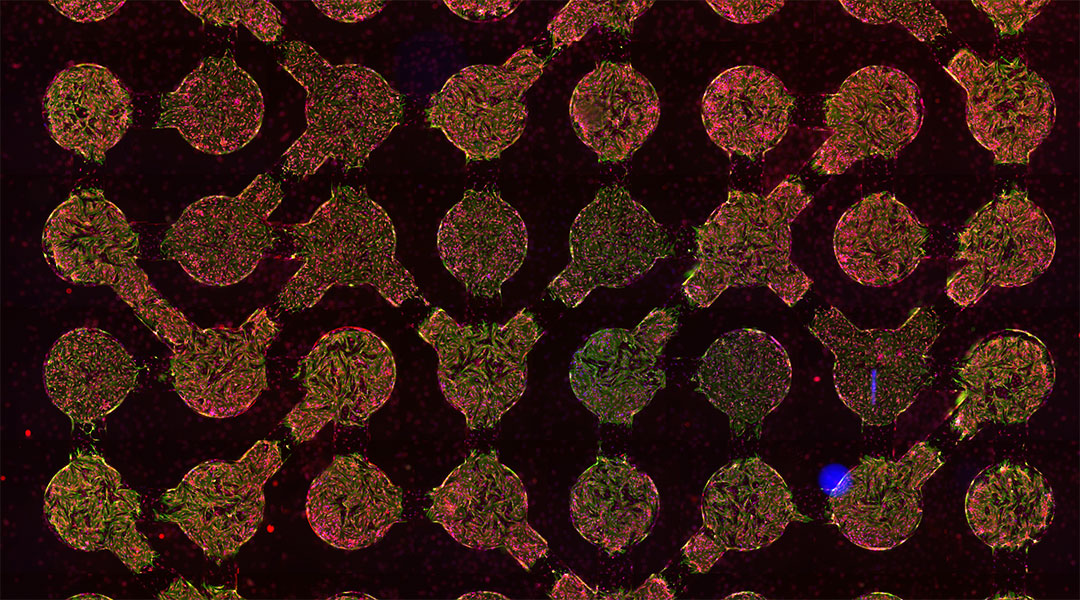
A biocomputer built from connected heart cells solves computational problems with high accuracy and at a low computational cost.
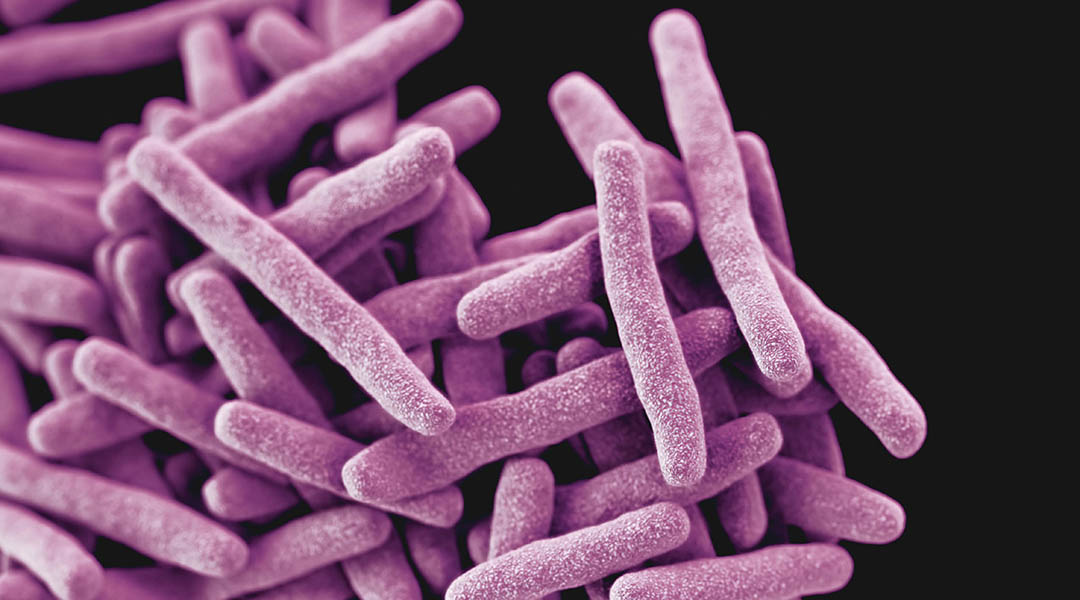
The genetic variant that causes Gaucher disease may have helped breakdown tuberculosis-causing bacteria in cells through lipid buildup.
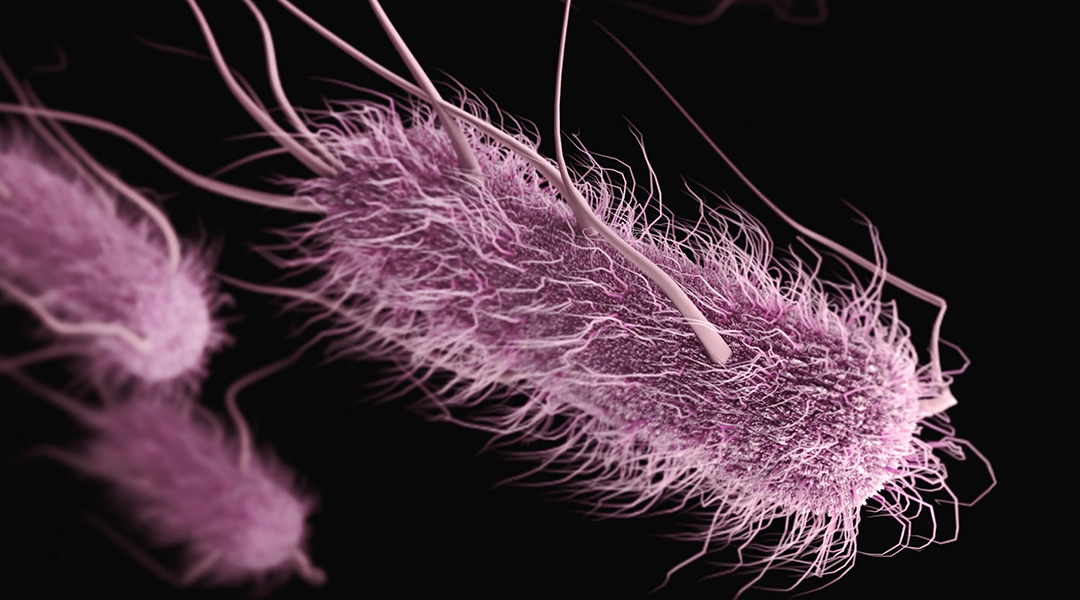
Incorporating polymer skeletons inside bacteria stops them from replicating and results in cyborg cells that are half living, half artificial.
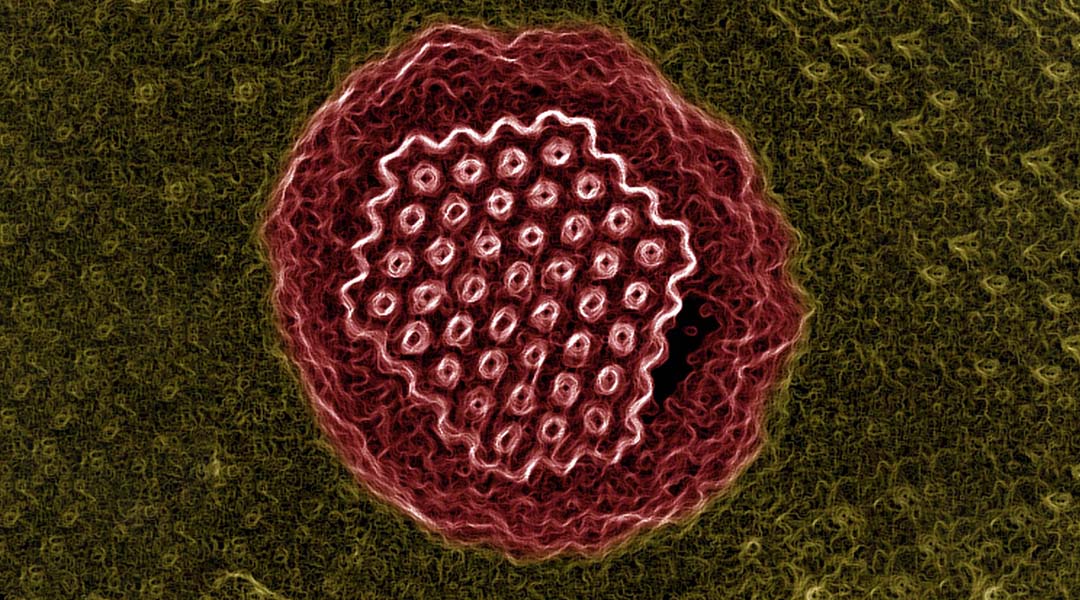
How seven ancient viruses ranging in age from 27,000 to 48,500 years were recovered from the Siberian permafrost, and what researchers hope to learn from them.
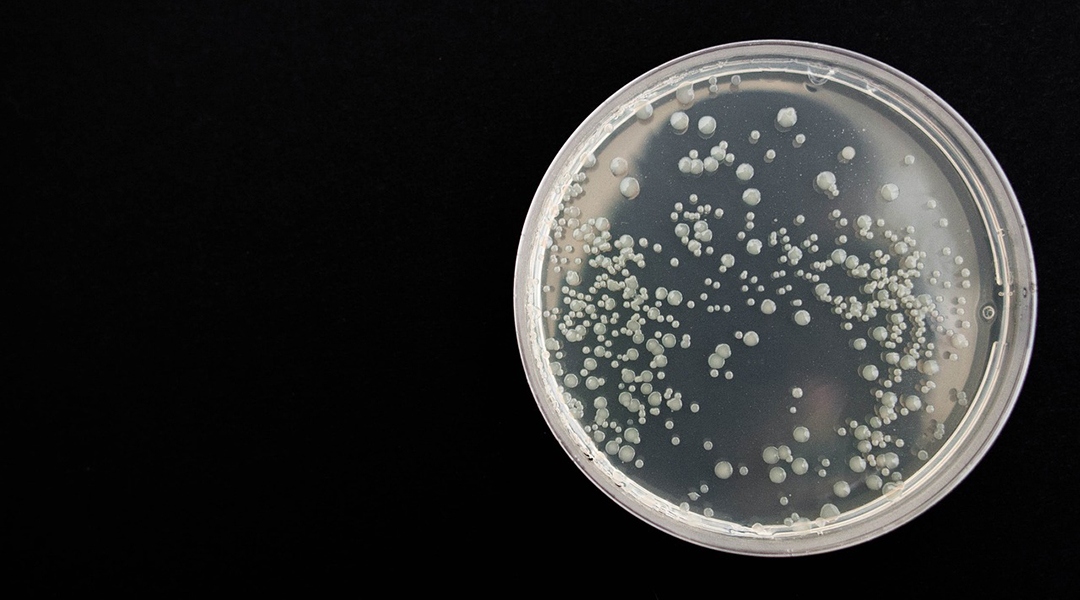
It is generally accepted that a community of beneficial bacteria make up the lung microbiome, but their origin and formation have remained unclear — until now.
New research finds that more genetic features appear to be linked to sudden unexplained deaths in infants and toddlers.
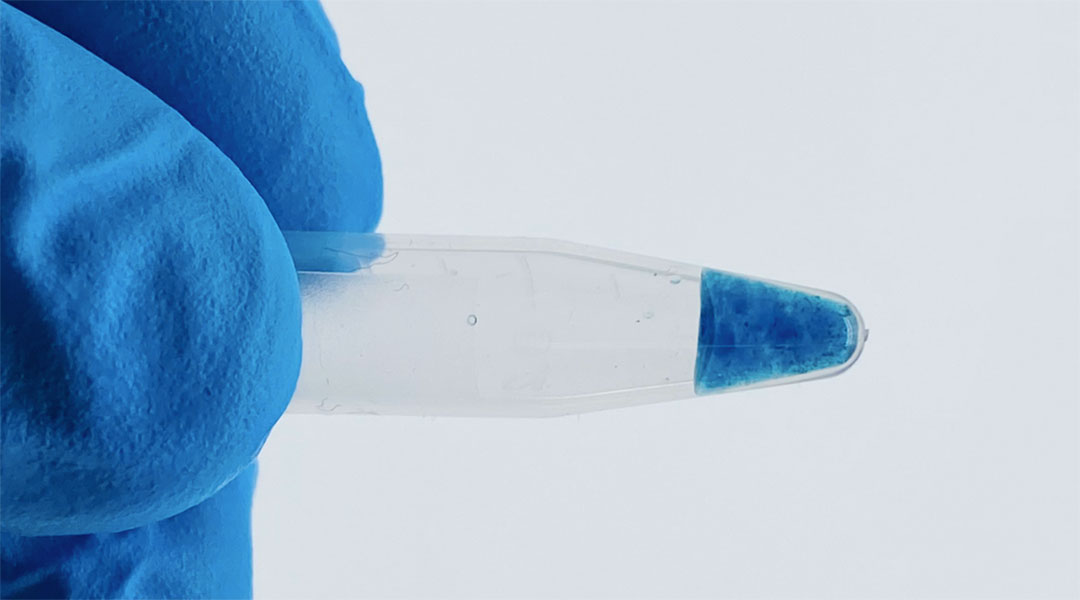
A new hydrogel platform helps monitor chemotherapies in the body in real-time, allowing their side effects and potency to be better understood.
Check out atomic glimpses of graphene ribbons, double bubble microspheres, and a solar evaporator made from bone.
Swimming cellbots capable of autonomous motion and drug encapsulation can deliver their payload at desired sites.