The weathering of the Earth’s surface serves as a geological thermostat and new research says that the breakdown of rocks at volcanic sites could help consume some of the world’s atmospheric carbon.
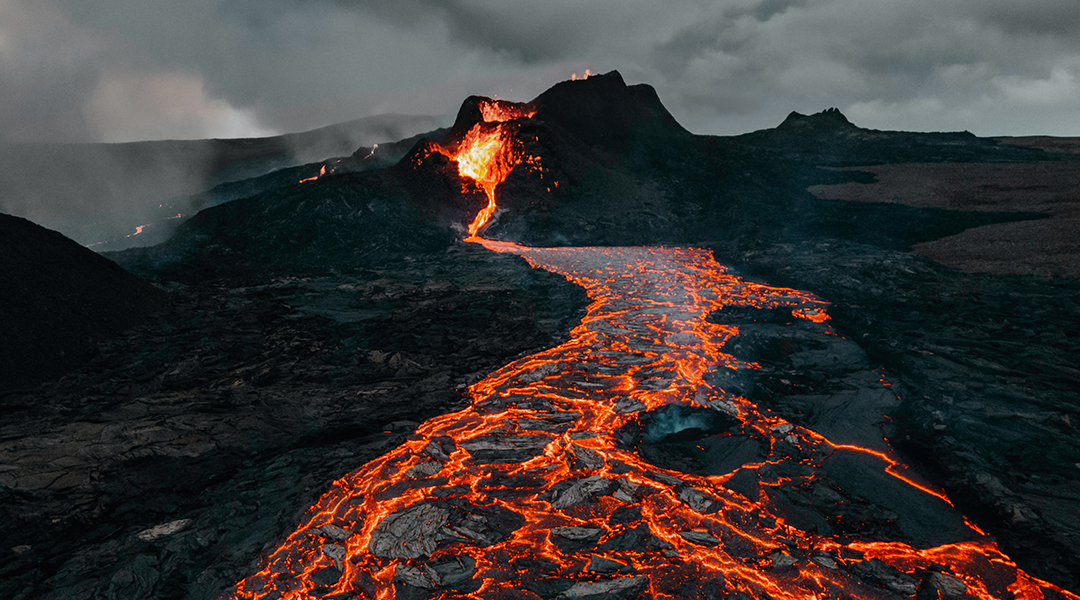


The weathering of the Earth’s surface serves as a geological thermostat and new research says that the breakdown of rocks at volcanic sites could help consume some of the world’s atmospheric carbon.
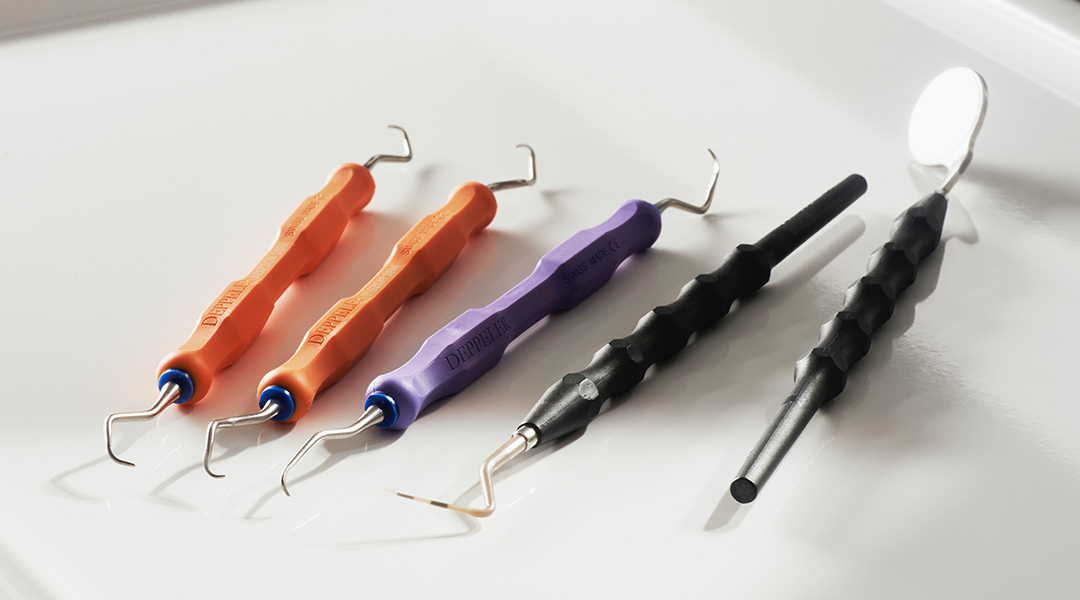

A charged microneedle patch for pain-free delivery of anesthetics could replace anxiety-inducing needles in dental work.

The Anthropocene has been defined by its carbon emissions, but modern technological advancements may hold the key to breaking this habit.
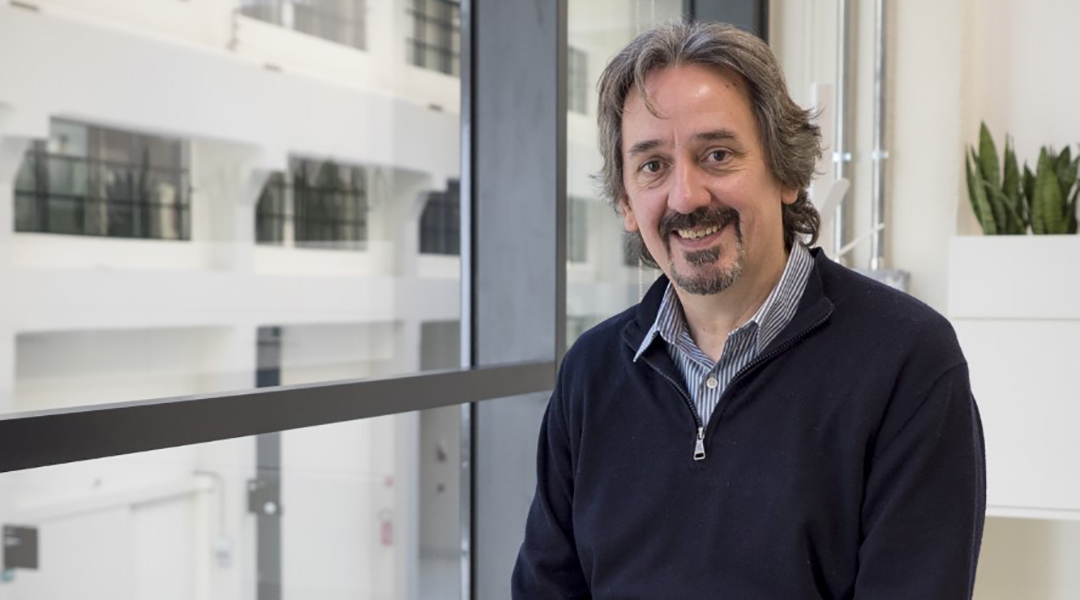

Albert Zink, director at the Institute for Mummy Studies, investigates remains from the past to bring ancient stories to life.
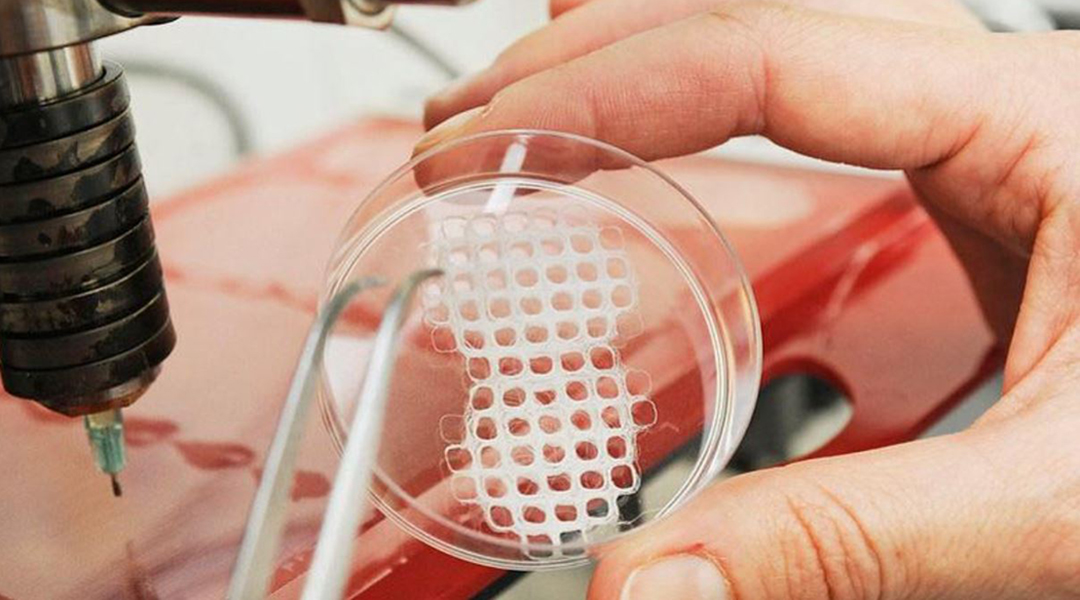
Machine vision and artificial intelligence can fine tune medical 3D printers to enable custom made tissue implants to suit the individual patient.

Changing the shape of soft matter using circuits made from DNA.
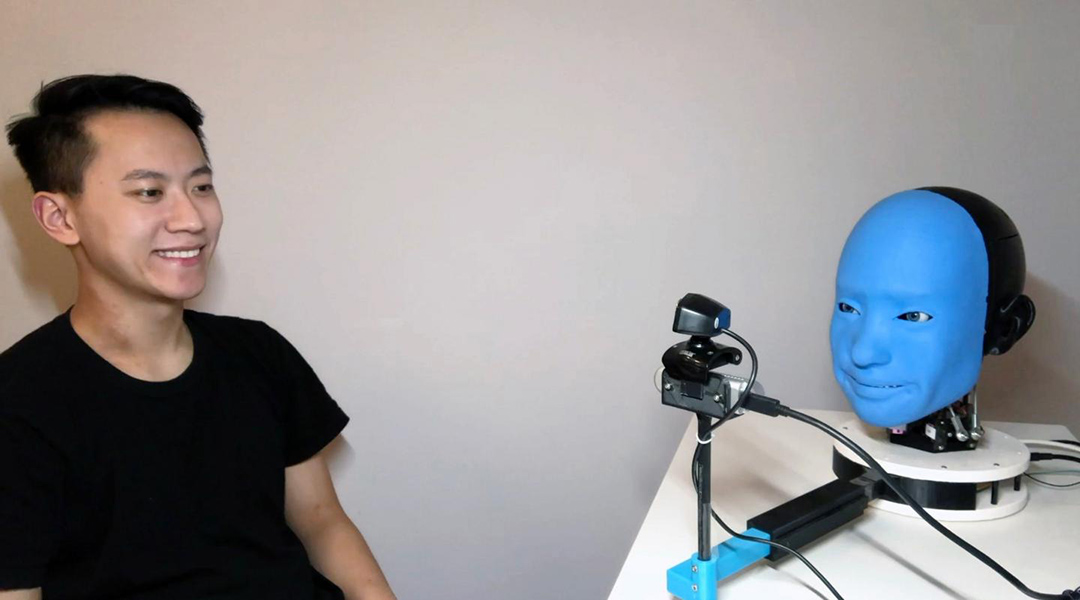

Researchers teach robots to make appropriate reactive human facial expressions, an ability that could build trust between humans and their robotic co-workers and care-givers.
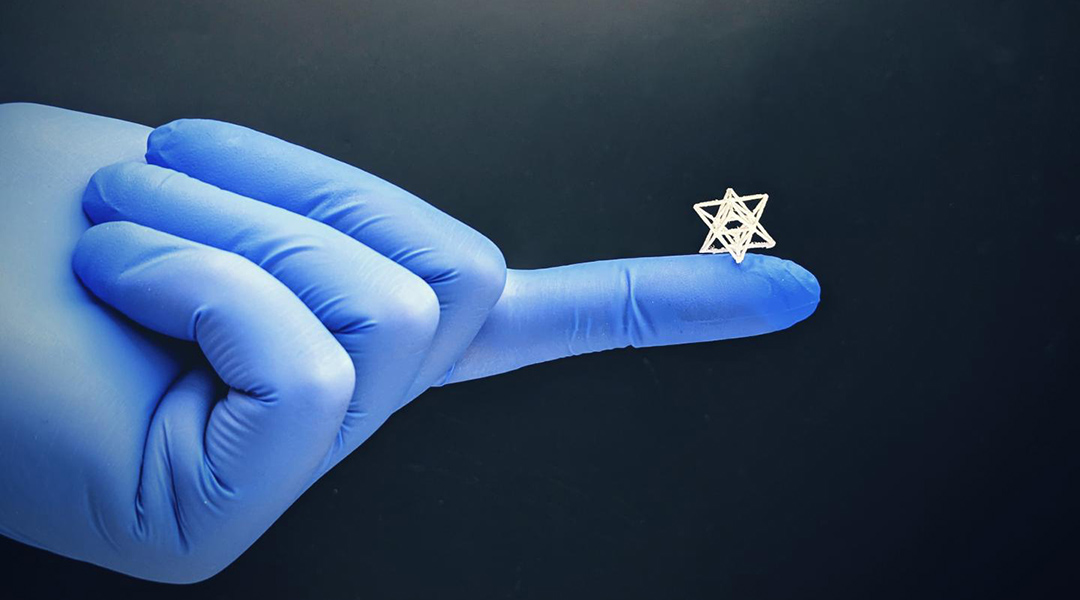

Researchers have flipped traditional 3D printing to create some of the most intricate biomedical structures yet.

Scientists in Japan have devised an efficient way to create the backbone to a whole family of natural products, thus unlocking potential new medicines.

A new approach to the synthesis of sustainable ammonia and urea uses food waste and brown water as feedstocks.