NC State researchers create develop an elastic material that is embedded with aligned, nanoscale needles.
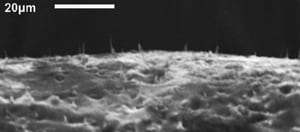

NC State researchers create develop an elastic material that is embedded with aligned, nanoscale needles.
Lab wins three Federal Laboratory Consortium awards for energy storage, cancer treatment, and next-gen microchip work.
A nanomaterial engineered by researchers at Duke can help regulate chloride levels in nerve cells that contribute to chronic pain, epilepsy, and traumatic brain injury.
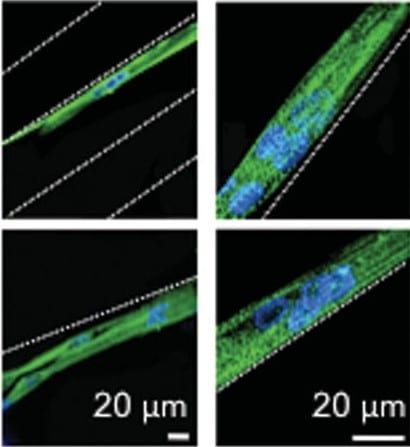
Researchers have engineered a protein biomaterial to generate mimics of human skeletal muscle to study the effect of injury and disease on this tissue.
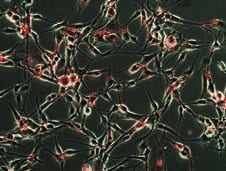
Researchers at Rutgers University have developed a method to generate an entire library of safe quantum dots quickly and efficiently.
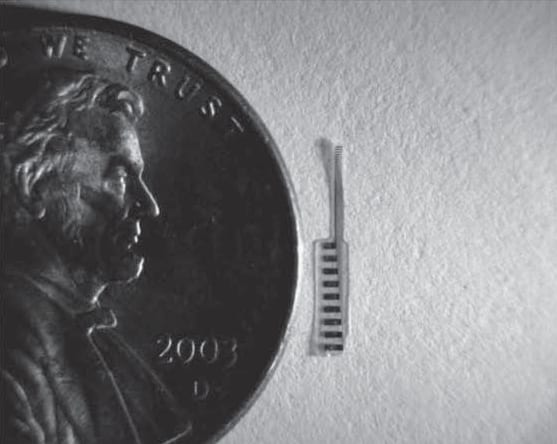

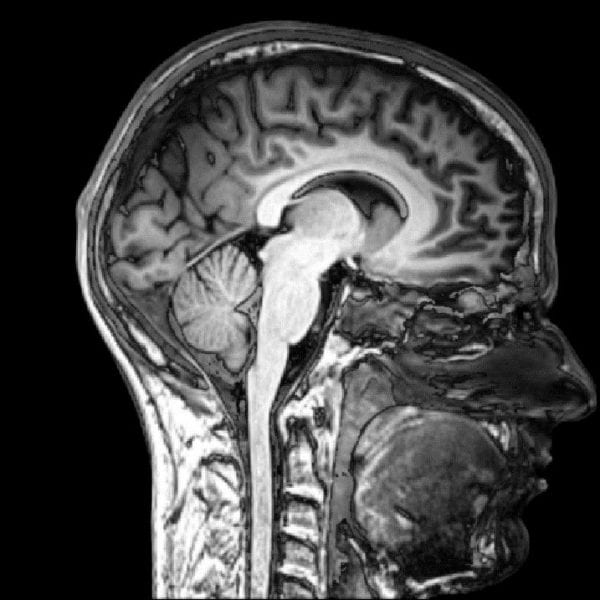
University of Texas researchers develop materials that are stiff for initial implantation, and then soften to better match the mechanical properties of brain tissue.
Gossuin, Sandre, et al. describe the design of magnetic nanoparticles with optimised relaxivity for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Researchers demonstrate learning in a memristive device.

The International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics (WPI-MANA) features in a new special issue from Advanced Materials.
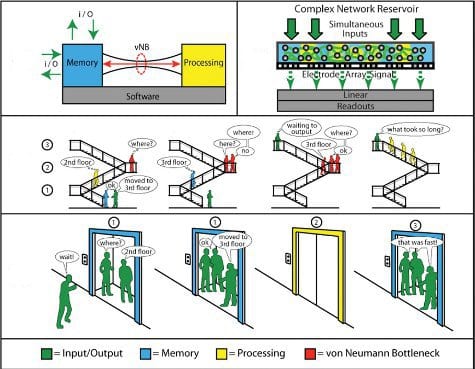
A computing network that exhibits emergent behavior similar to that in biological brains is hypothesized by Adam Z. Stieg of the California NanoSystems Institute