Accurately measuring brain signals is critical to determining what actions a user wants to perform.
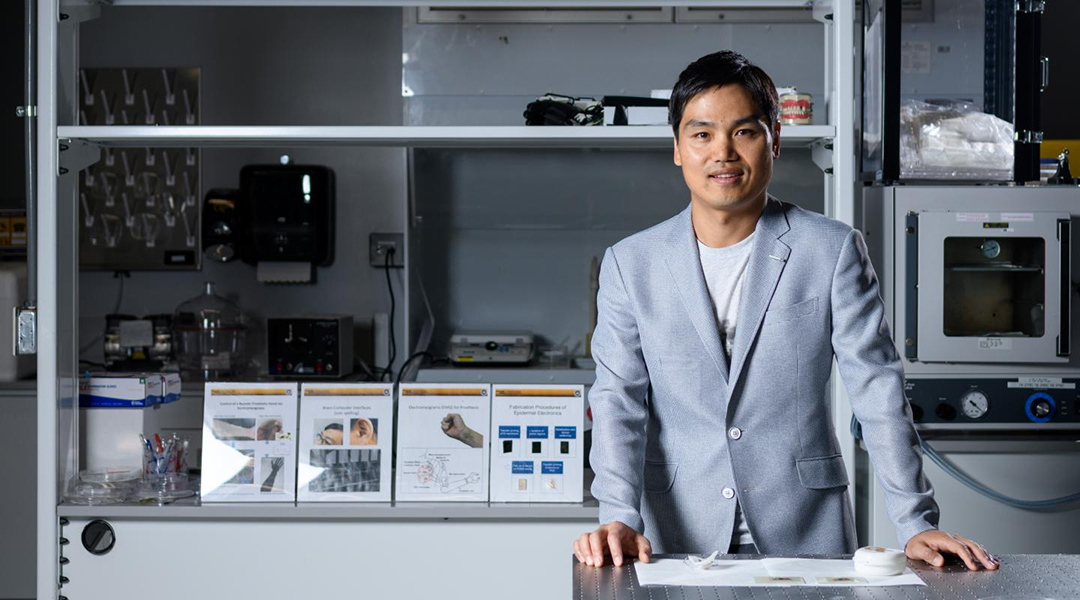

Accurately measuring brain signals is critical to determining what actions a user wants to perform.

A drug that changes conformation in response to light allows researchers to manipulate neural activity and investigate the link between brain states and behavior.

“Brain-on-a-chip” shows minute-by-minute how the blood–brain barrier reacts to high levels of inflammation.
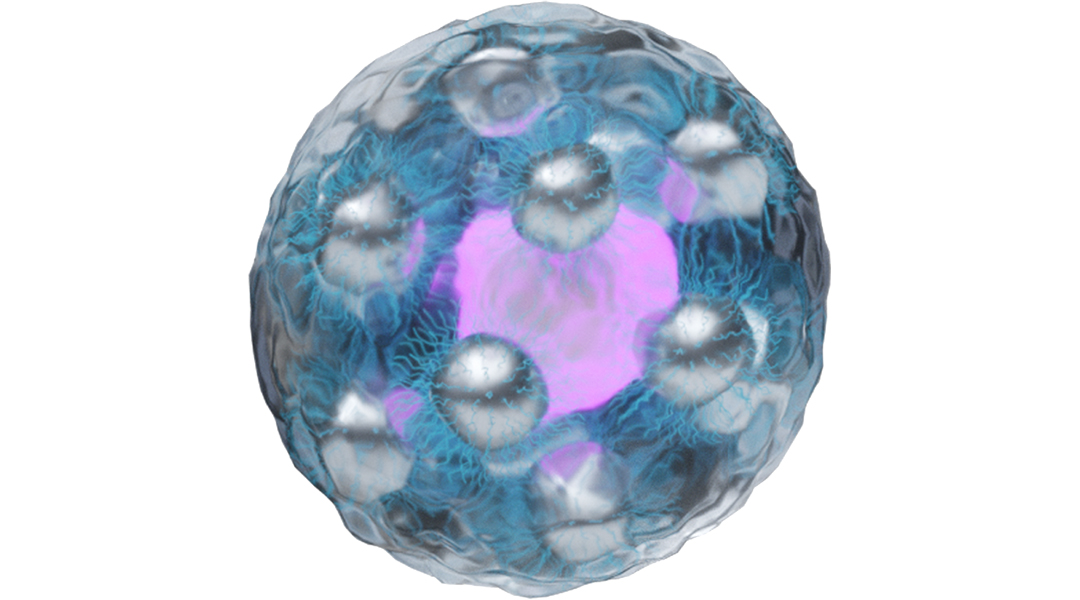
A minimally invasive method holds promise for the treatment of neurological disorders and injury.
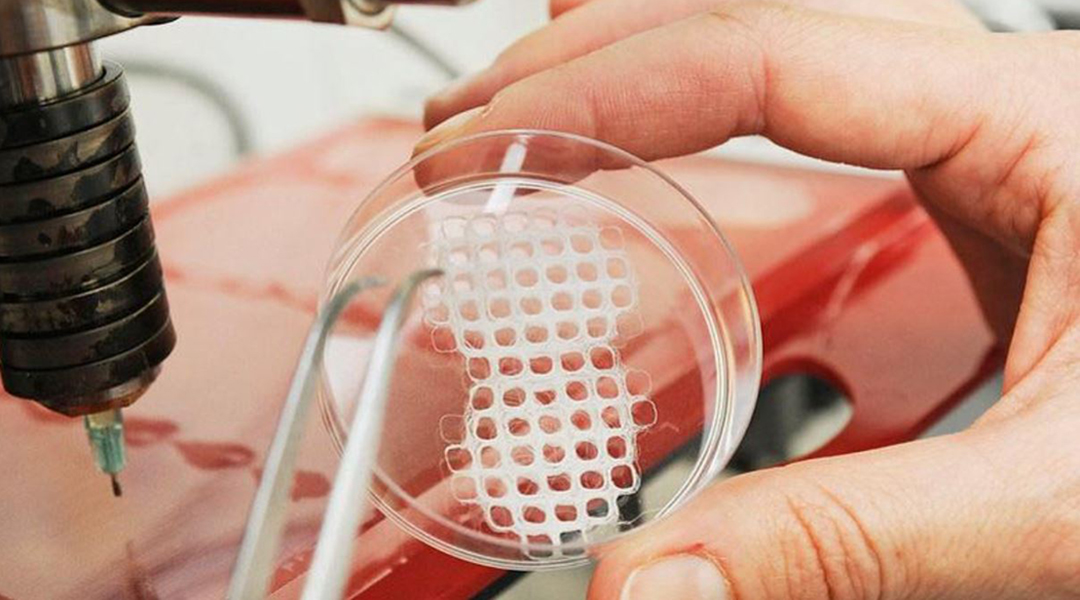
Machine vision and artificial intelligence can fine tune medical 3D printers to enable custom made tissue implants to suit the individual patient.
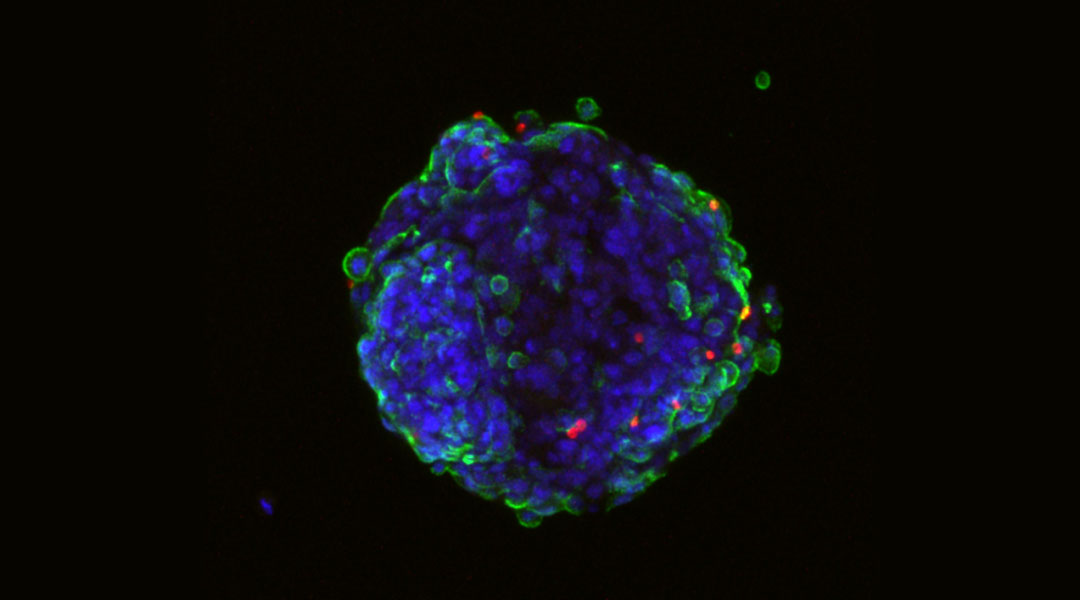
Researchers uncover how malaria infiltrates the blood–brain barrier and contributes to disease severity.
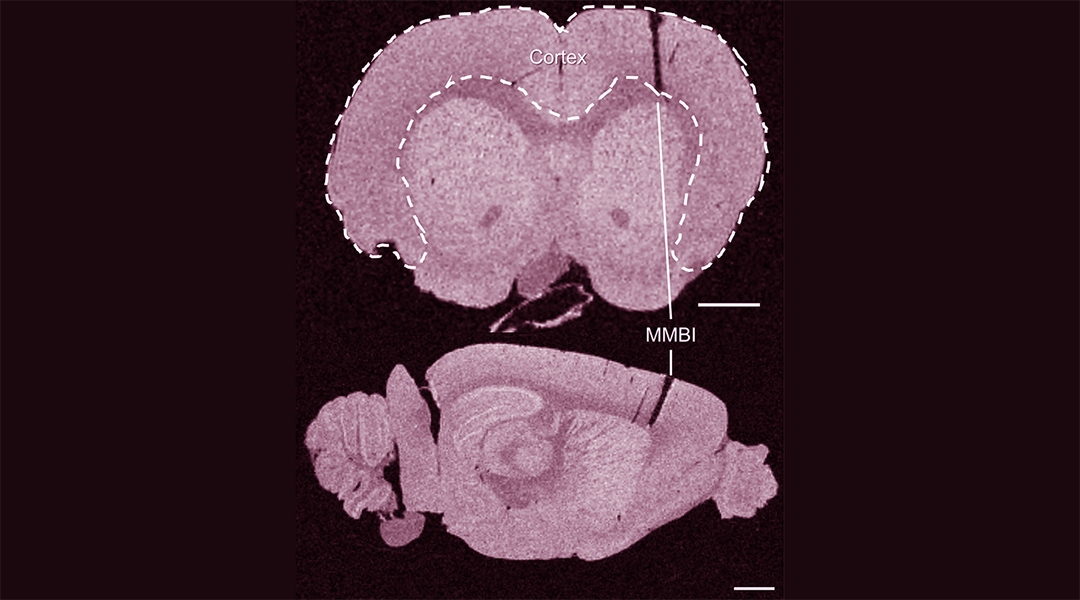
Pudding-like implants with a sugar-based delivery system show promise in reducing the foreign body response against brain implants.
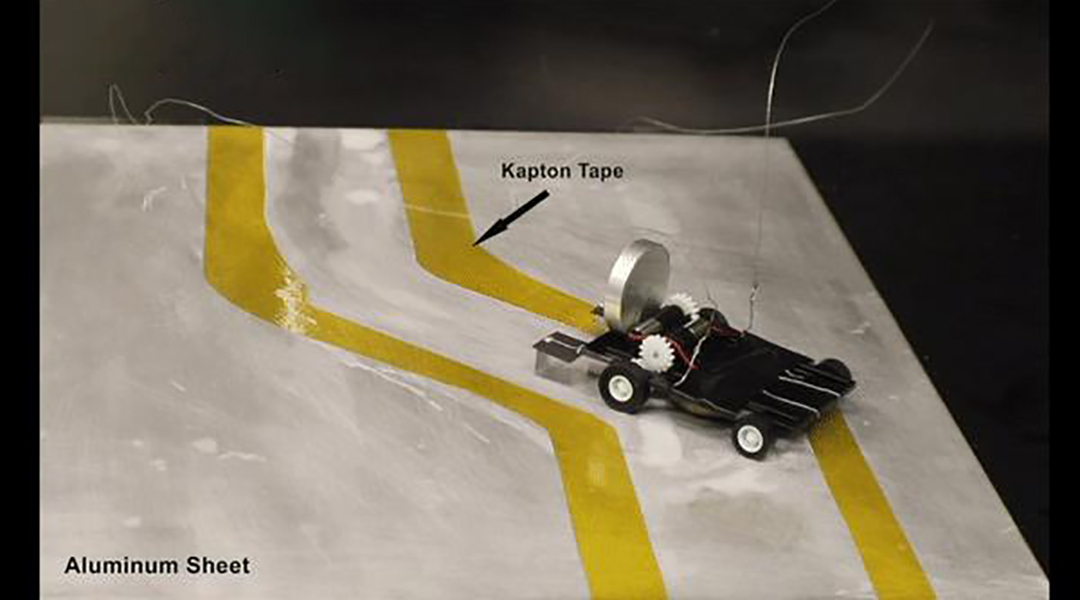
The “metal-eating” robot can follow a metal path without using a computer or needing a battery.
A new study provides hope for Parkinson’s disease, showing that neuron grafts using patients’ own cells have the potential to manage and even reverse symptoms.
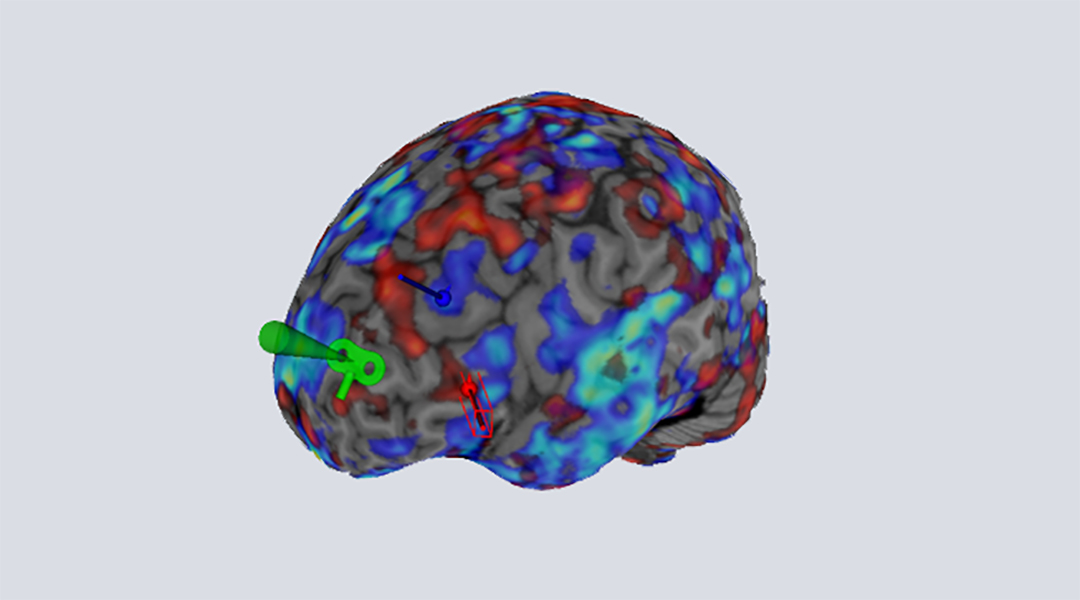
Taking advantage of progress made in neuroimaging, researchers hope that personalized treatments for mental disorders using brain stimulation therapies will be the way forward.