A low temperature water-splitting protocol uses microwave power in lieu of concentrated solar energy.


A low temperature water-splitting protocol uses microwave power in lieu of concentrated solar energy.
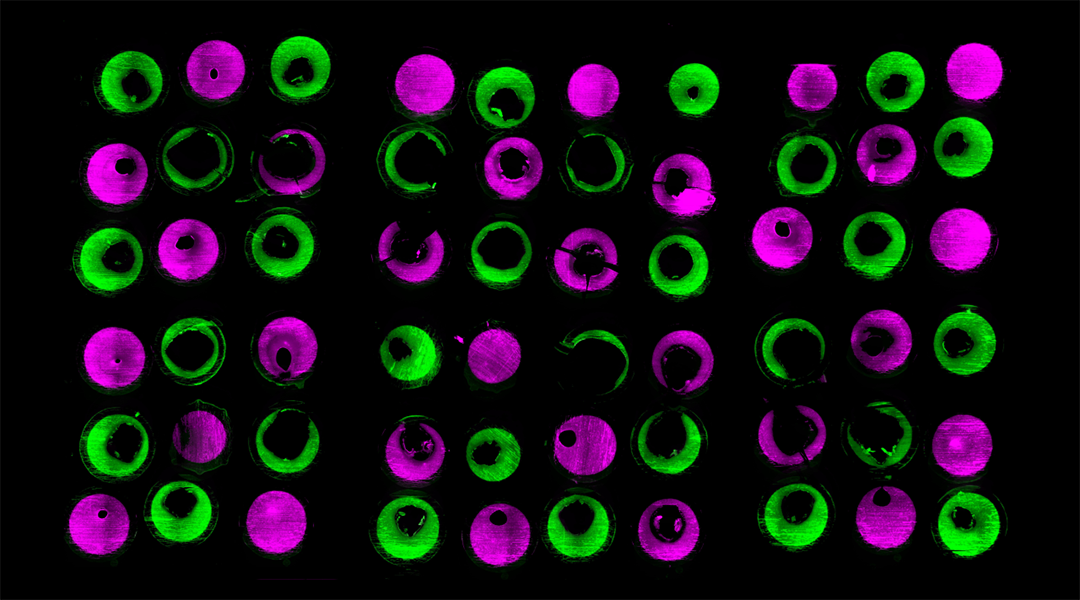
From micrometer-sized nanoflowers to hydrogel hearts, this edition of “This month in pictures” features more intriguing images from our journals and the science behind them.

While plastic waste is an issue, its prominence in the general public’s concern for the environment is overshadowing greater threats.

Researchers develop an efficient, low-energy method for upcycling polyethylene plastic waste into valuable molecules that can be repurposed for further use.
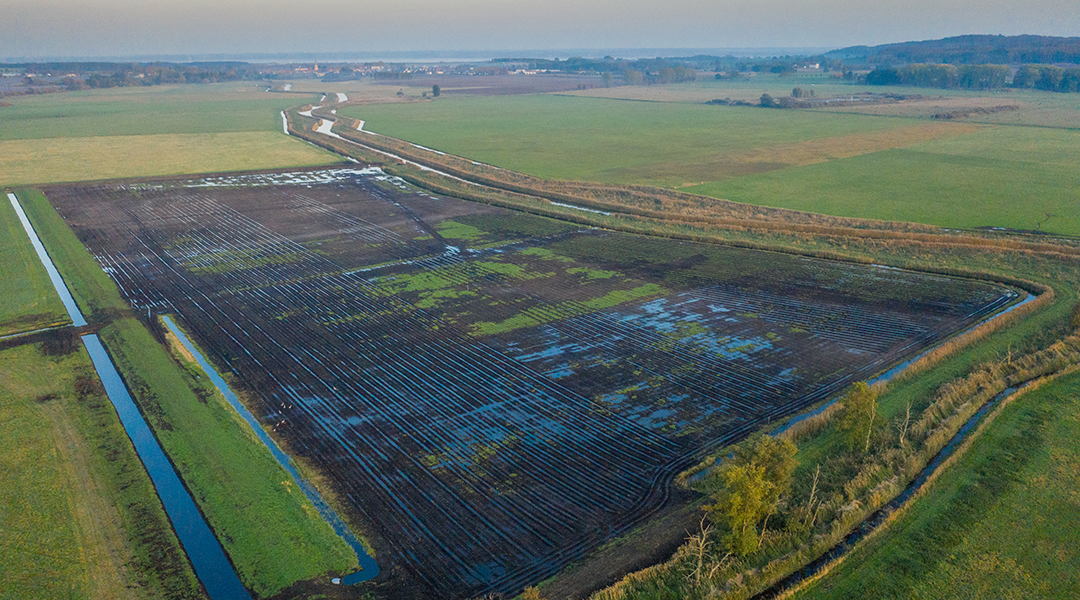

Peatlands are among the most valuable ecosystems on Earth but when damaged are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions.
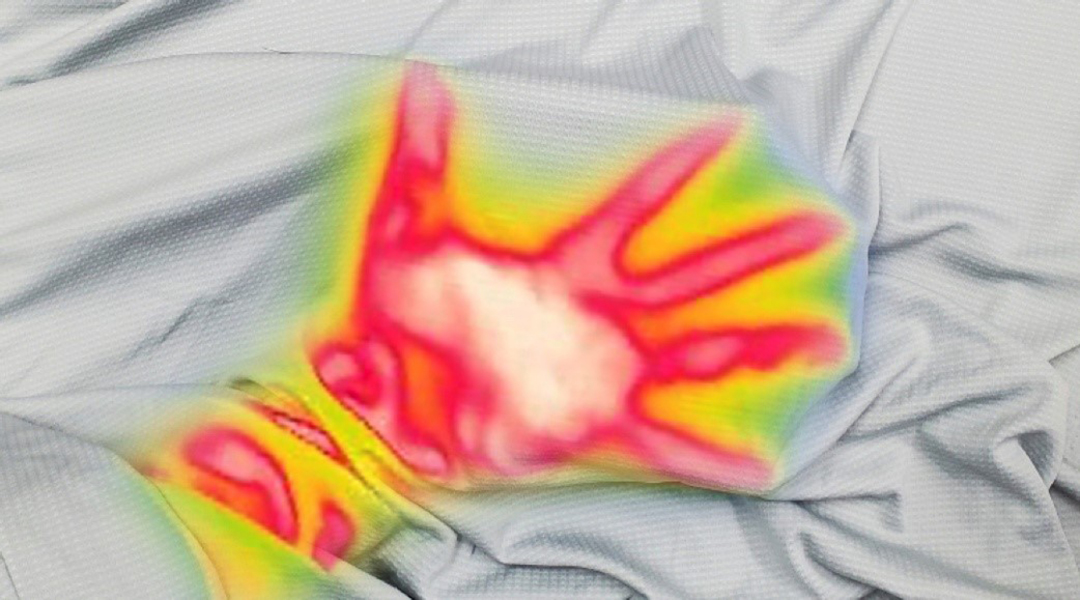
A simple alteration in the functionality of our clothing could surprisingly help lower energy consumption in buildings and homes.

The Swansea-based materials physicist talks about the role of energy materials in mitigating climate change, his love of sports, and how his passion for science helps it to blend seamlessly into his life.
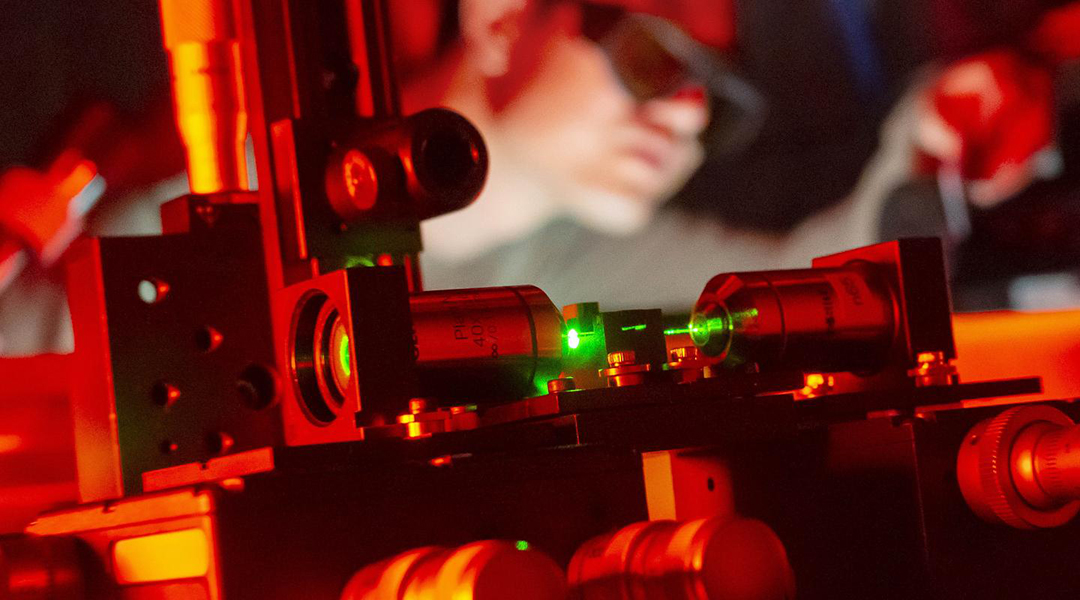

New hybrid optical fibers contain 2D materials that enhance light-matter interactions and open doors for a range of new technological advancements.
Could a new understanding of silicon surfaces someday revolutionize semiconductor technologies?

Lightweight but tough, bamboo is the hope for a more sustainable life and future for our planet.