Researchers describe the experimental realization of an optical switch controlled by a single photon, allowing light to govern the transmission of light.


Researchers describe the experimental realization of an optical switch controlled by a single photon, allowing light to govern the transmission of light.

Bubble wrap is lighter, stronger and more flexible than sheet metal and more heat- and chemical-resistant than plastic or other polymer-based bubble wraps.
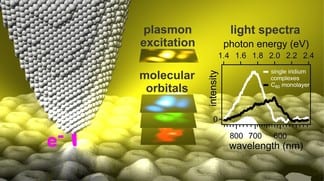
Scientists have discovered how optical signal transmission can be controlled, which could lead to integration of plasmonics with electronic circuits.

Mark G. Allen has been named the inaugural scientific director of the University of Pennsylvania’s Krishna P. Singh Center for Nanotechnology.
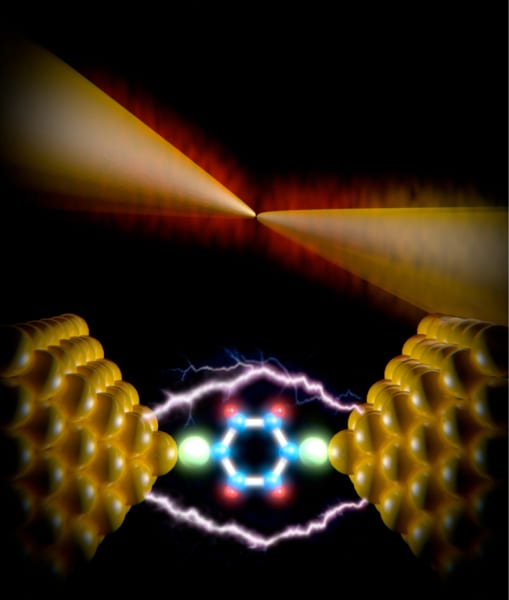
An international research team has shown the unique ways in which heat dissipates at the tiniest scales.

Leading nanotechnology scientist wins award for research inspired by nature and its ability to create materials.
Researchers at NIST have reported the first observation of the “spin Hall effect” in a Bose-Einstein condensate.

Dr. O. Anatole von Lilienfeld of Argonne has been awarded the 2013 Thomas Kuhn Paradigm Shift prize of the “Computers in Chemistry” division of the ACS.
Technology out-powers even the best supercapacitors and could drive new applications in radio communications and compact electronics.
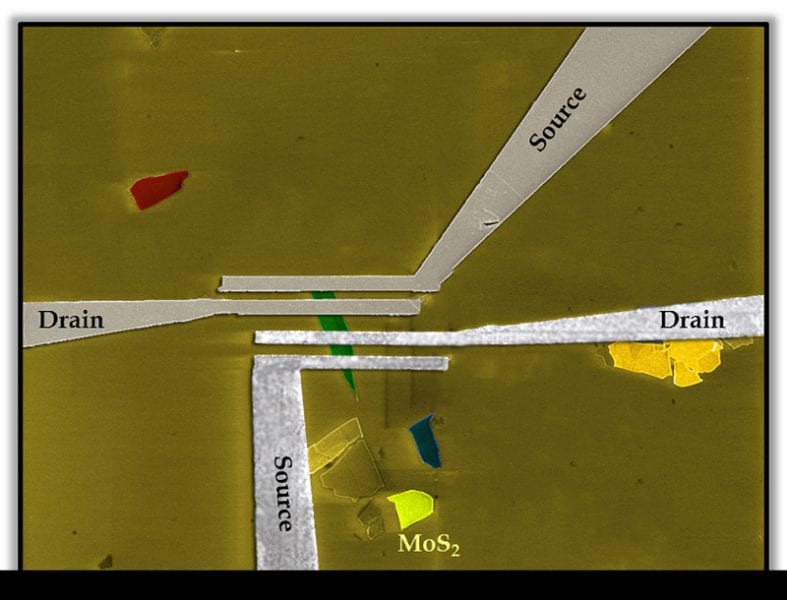
Technology is based on metal di-chalogenides, which are emerging as potential candidates to replace current CMOS materials.