Researchers develop a biomimetic hydrogel with photodynamic antimicrobial effect.


Researchers develop a biomimetic hydrogel with photodynamic antimicrobial effect.

Advanced Science News celebrates the life and work of radio and plant biology pioneer, J. C. Bose.
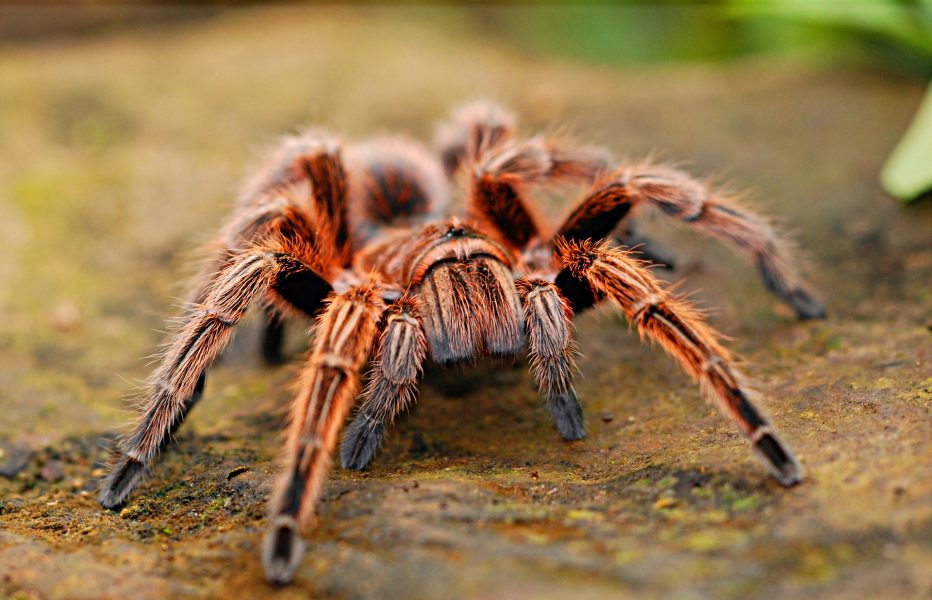

The potential of spider venom for environmentally friendly insecticides
Proteins with similar domain structures and activities have been found throughout eukaryotes, demonstrating that this protein family arose from an ancient ancestor.

Spatial and temporal control of drug production is achieved by optogenetical triggering a hydrogel-encapsulated bacterial system.
An atypical, low‐power, atmospheric pressure plasma source for application in plasma medicine.
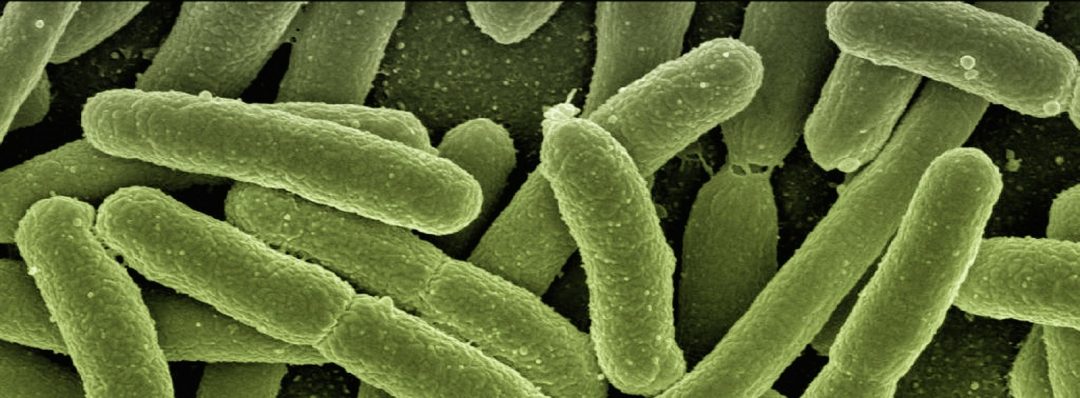
Intestinal bacteria can create an electric current, according to a new study from Lund University in Sweden.
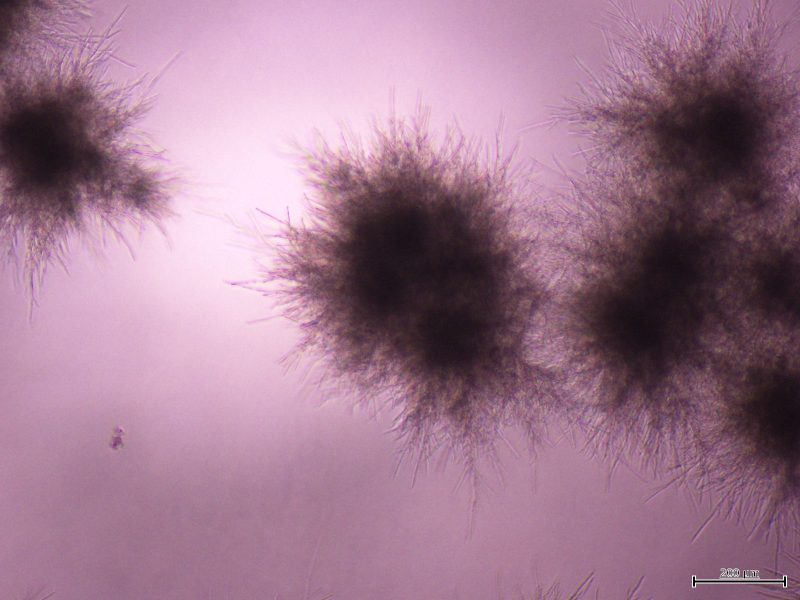
Mammalian barrier surfaces are densely populated by symbiont fungi in much the same way the former are colonized by symbiont bacteria. The fungal microbiota, otherwise known as the mycobiota, is increasingly recognized as a critical player in the maintenance of health and homeostasis of the host.

Scientists developed a packaging wrap comprised of cellulose from wood pulp and chitin from crabs and shrimp shells.
The broad applications of LOV domains in optogenetics are reviewed.