University of Würzburg physicists have modified silicon carbide crystals and found that they may have application in quantum computing.
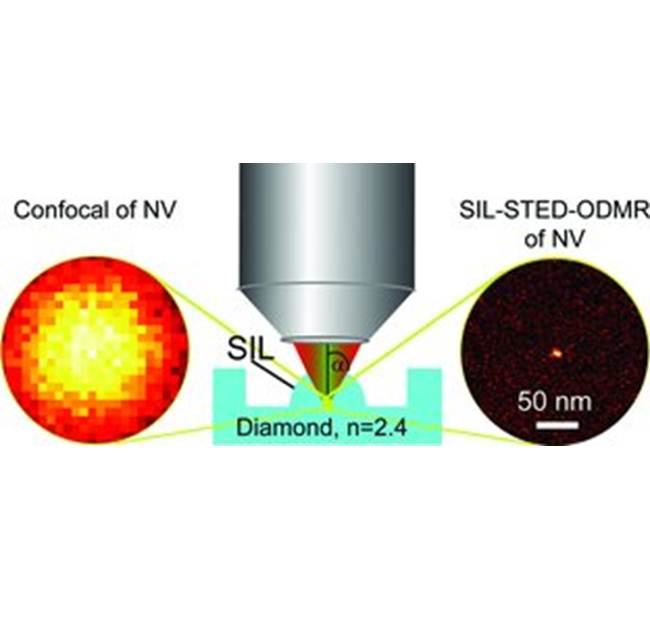
Maximum Resolution through Solid Immersion
Stefan Hell and co-workers have achieved maximum spatial resolution in far-field optical imaging by applying solid immersion lenses to stimulated emission depletion microscopy.
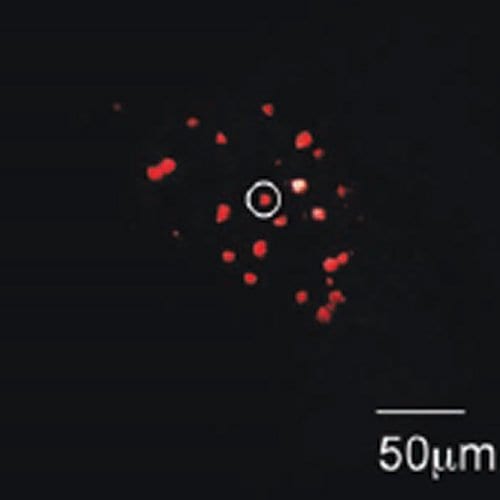
Russian Diamonds: Nanodiamonds with Valuable Flaws
Russian scientists have made nanodiamonds with a higher concentration of nitrogen vacancy centers, with a better efficiency than was previously possible.
Researchers explain the intricate interactions that shape DNA organization
Scientists uncover how the complex interactions between nucleosomes influence DNA’s organization in chromosomes.

Anti-aging for lasers: Gallium nitride lasers get a longevity boost
Scientists have uncovered the cause of rapid degradation in powerful gallium nitride lasers and develop a solution to extend their lifespan.

The next big thing in tech could come from these tiny light absorbers
When the light absorbers are made very small, almost all the device performance metrics improve—but doing this is easier said than done.

An organ-on-chip simulates the effects of cosmic radiation on astronauts
Future astronauts may be protected from galactic cosmic rays thanks to a novel organ-on-chip system containing interconnected human tissue.

Matter of science: Dialectics and the laws of nature
In this third and final article in a series on philosophy and science, we look at how modern science shows the validity of dialectical processes and how this can help guide science.
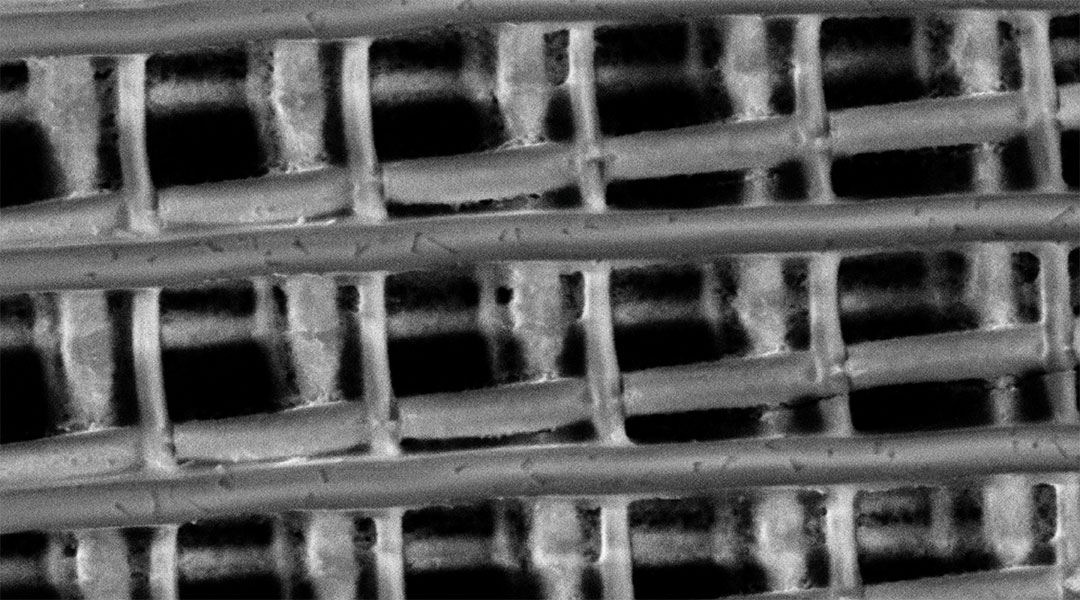
Scientists create the largest nonlinear photonic crystal to date
Their unprecedented control over light will lead to breakthroughs in telecommunications, medical imaging, and quantum computing.
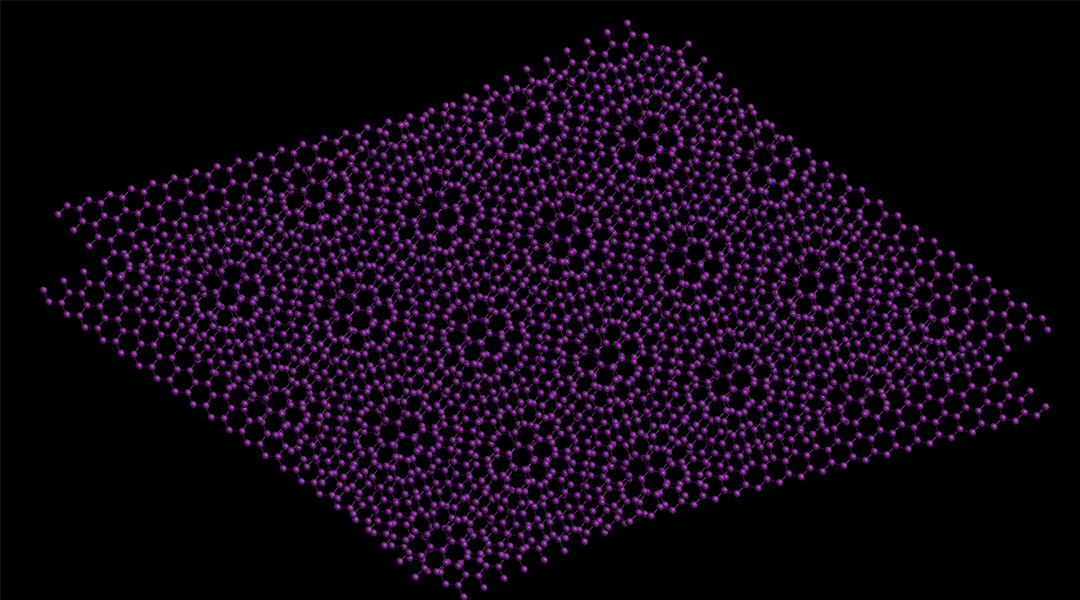
Could twisted bismuth pave the way to a practical superconductor?
“Magic angles” in twisted bismuth bilayers could induce superconductivity at more reasonable temperatures.










