A new fire-warning technology integrated into children’s clothing can be linked up to a mobile device for early detection and proactive safety measures.
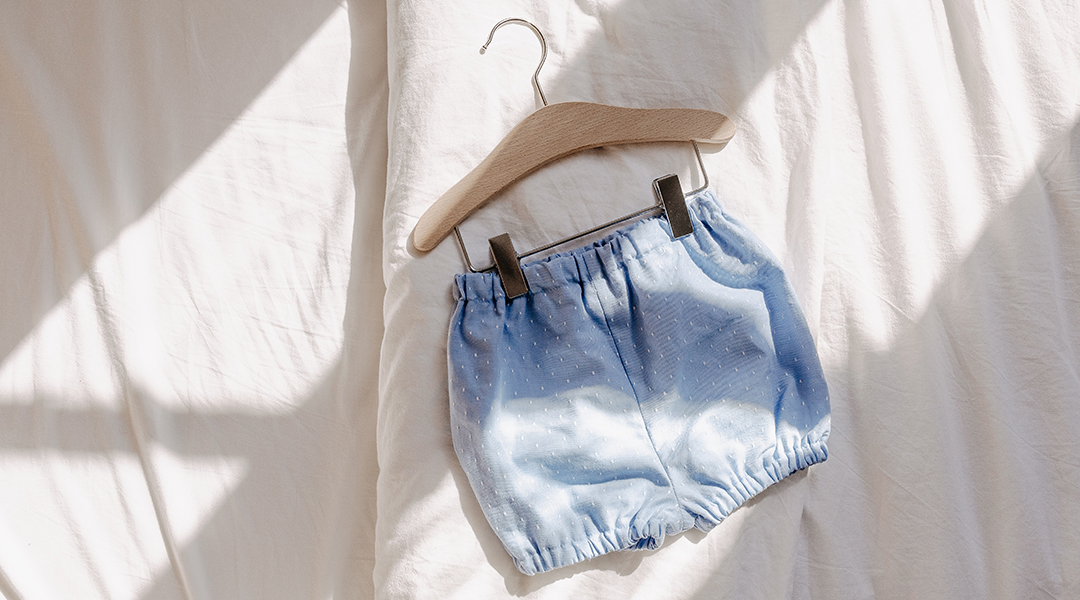


A new fire-warning technology integrated into children’s clothing can be linked up to a mobile device for early detection and proactive safety measures.

A device that generates electricity using moisture in the air could be the future of sustainable power generation.
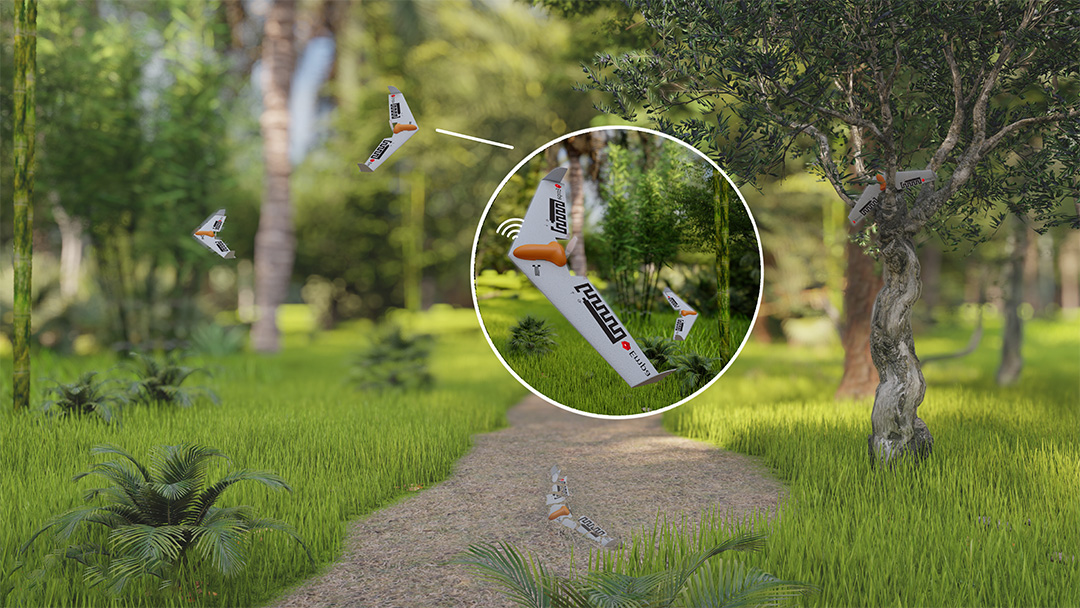

The forest floor should be able to make a meal out of this new drone made of almost completely from biodegradable parts.
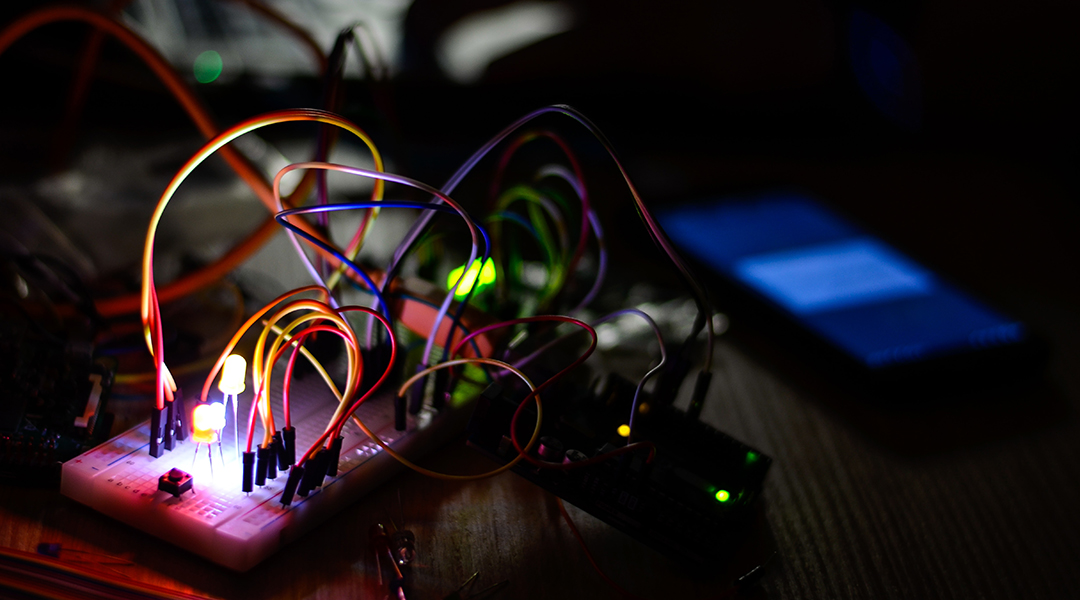
An optical device uses light-based signals for computation and communication and is a vital step toward advanced neuromorphic computers.
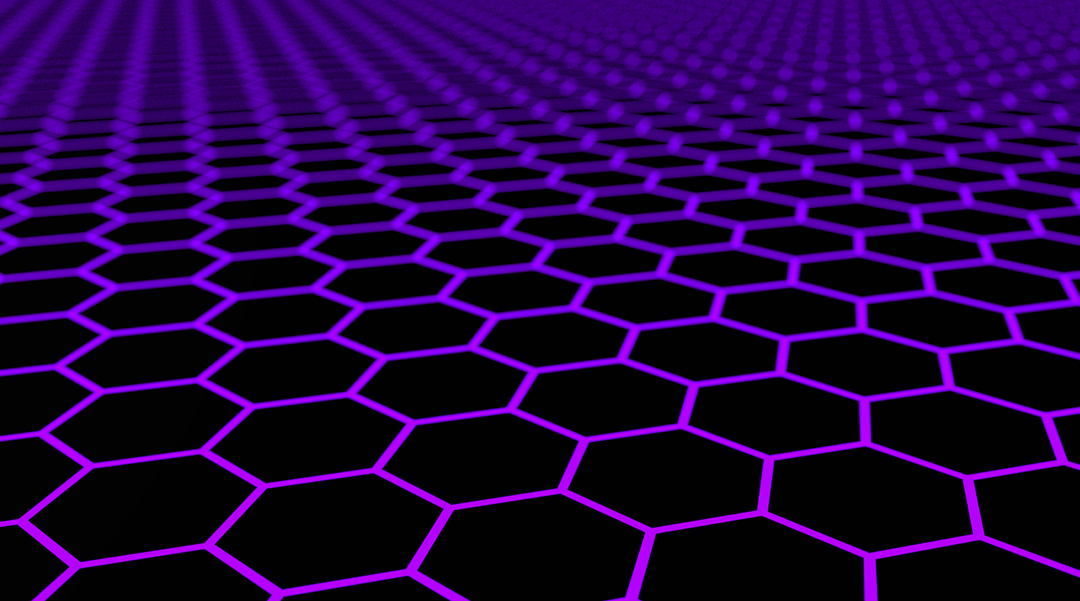
Scientists are exploring the behavior of electrons in helicoidal graphene strips, a unique form of graphene with a twisted shape.
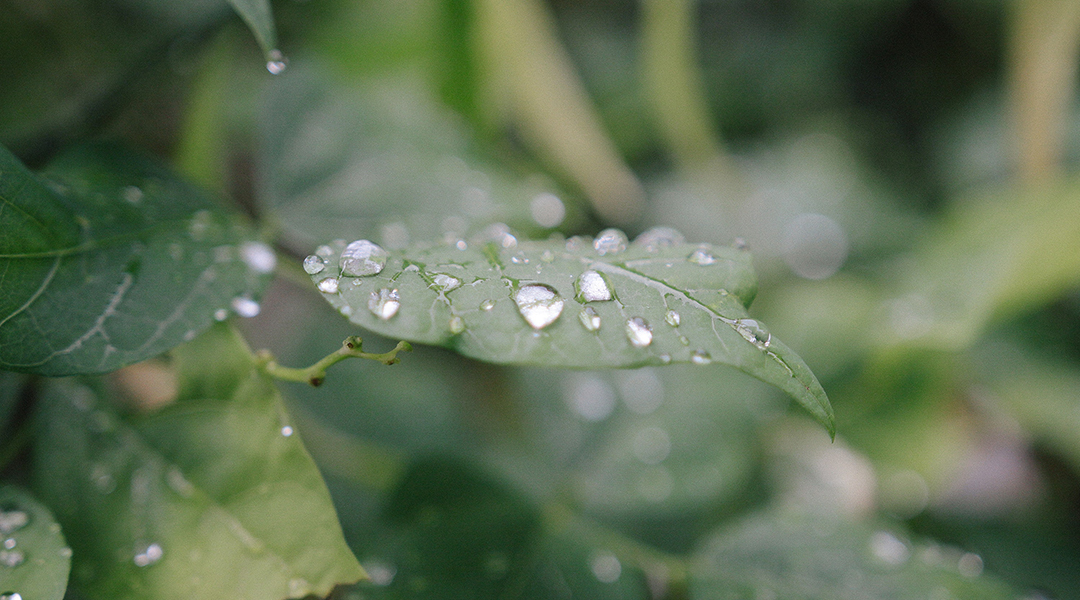

By accurately detecting moisture levels, this artificial leaf sensor could help increase crop yields while reducing the need for pesticides.
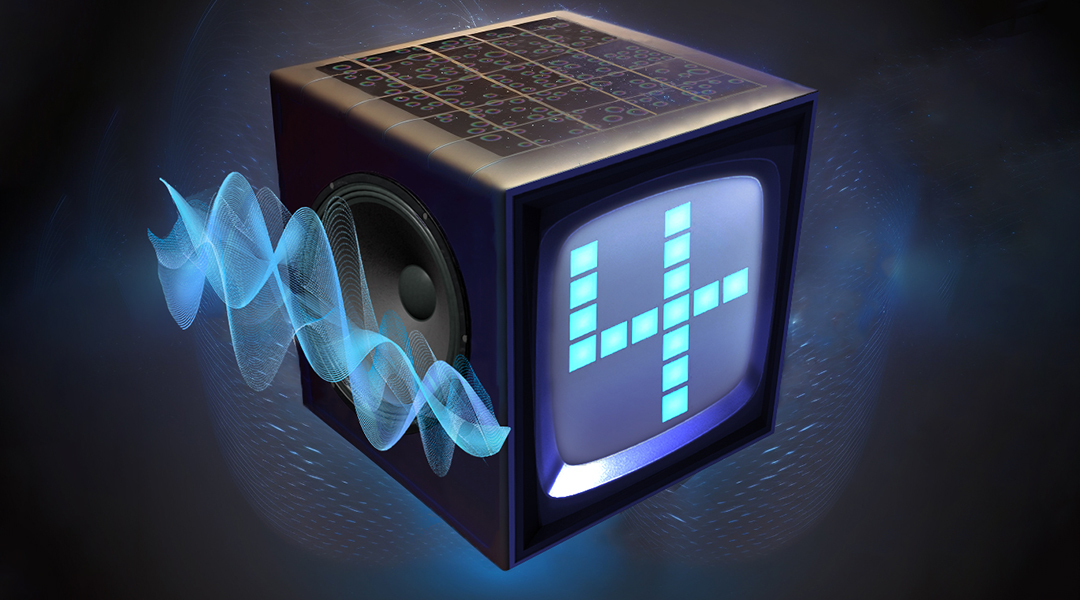

A thin film composed of small magnetic whirls called skyrmions performs voice pattern recognition with an accuracy approaching 99%.
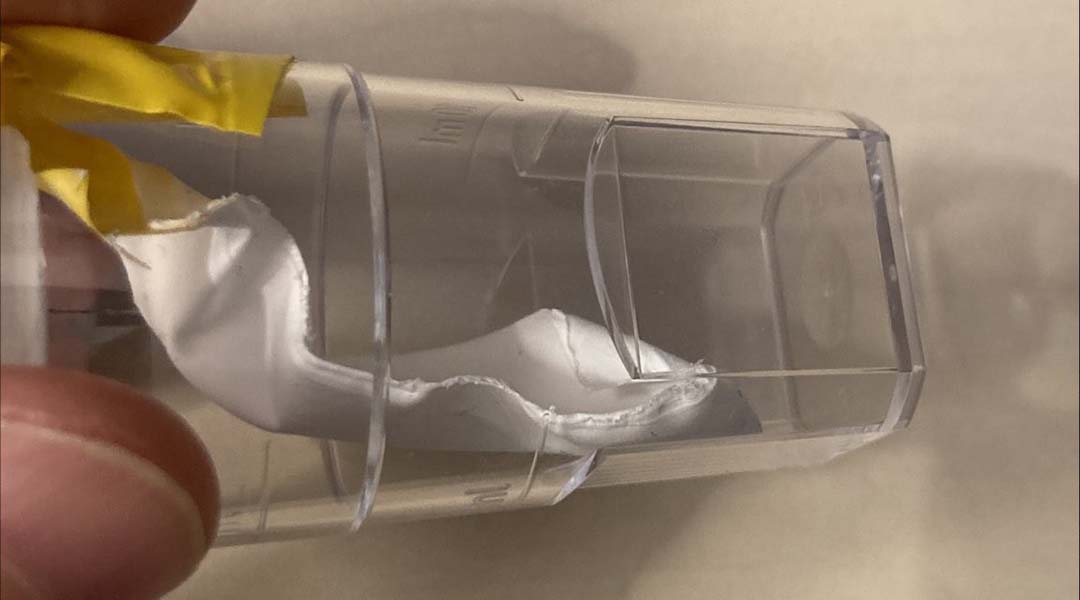

A new triboelectric laminate can convert movement to electricity 400 times more efficiently in wearable and implantable technologies.
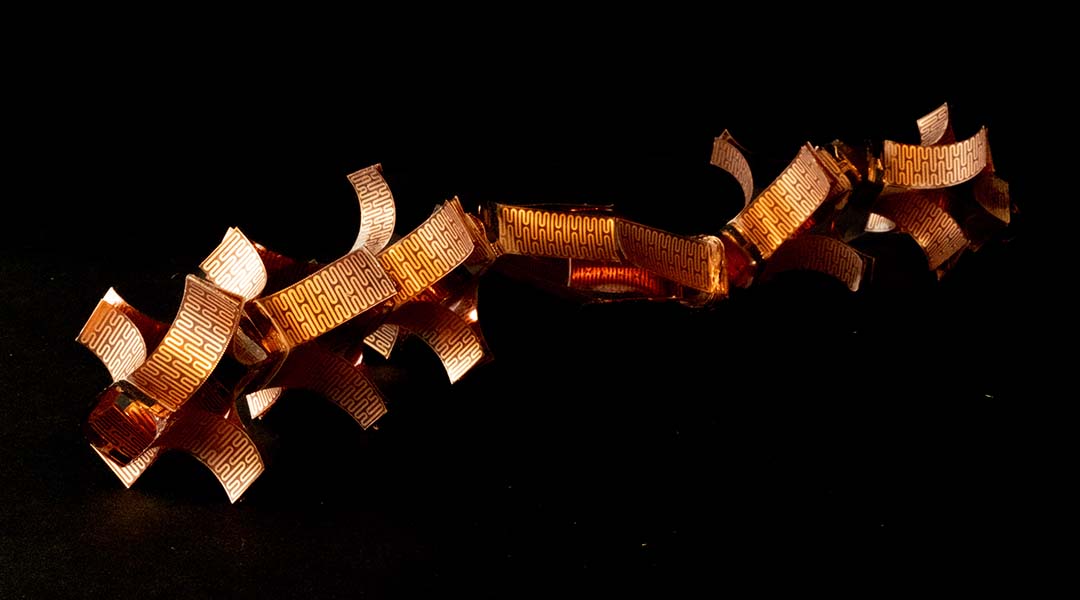
The replacement of rigid parts could help robots more closely mimic the humble worm to help them squeeze into tight spots.
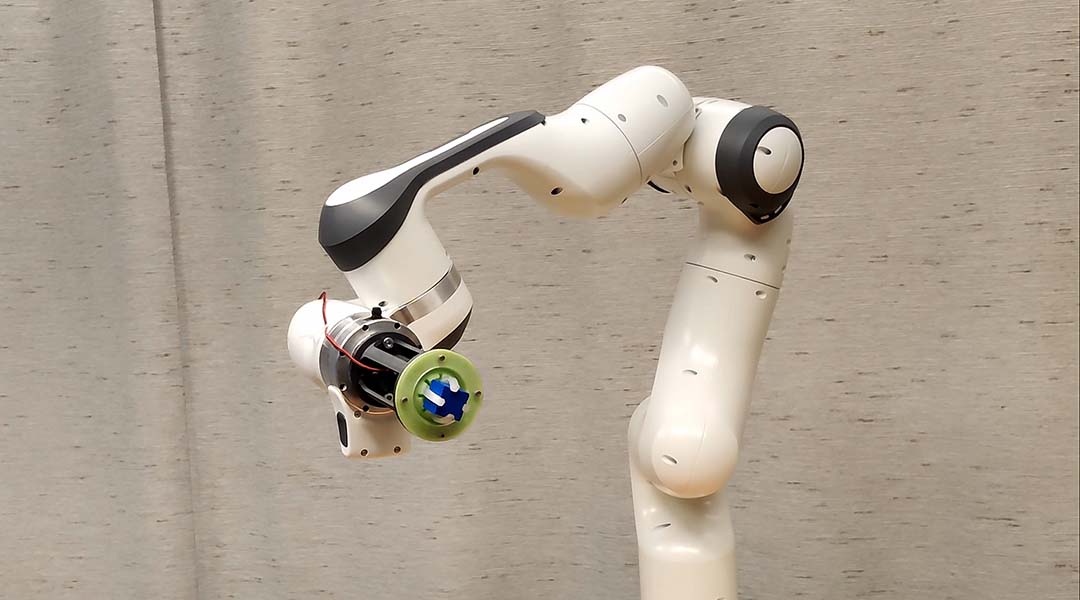

An innovative design allows for sensitive soft robots that can navigate difficult tasks and environments without bulky sensors.