Thanks to ultra-thin sensors and artificial muscles, future flexible microelectronics will be able to take on complex shapes to better interface with delicate biological tissues without causing damage.
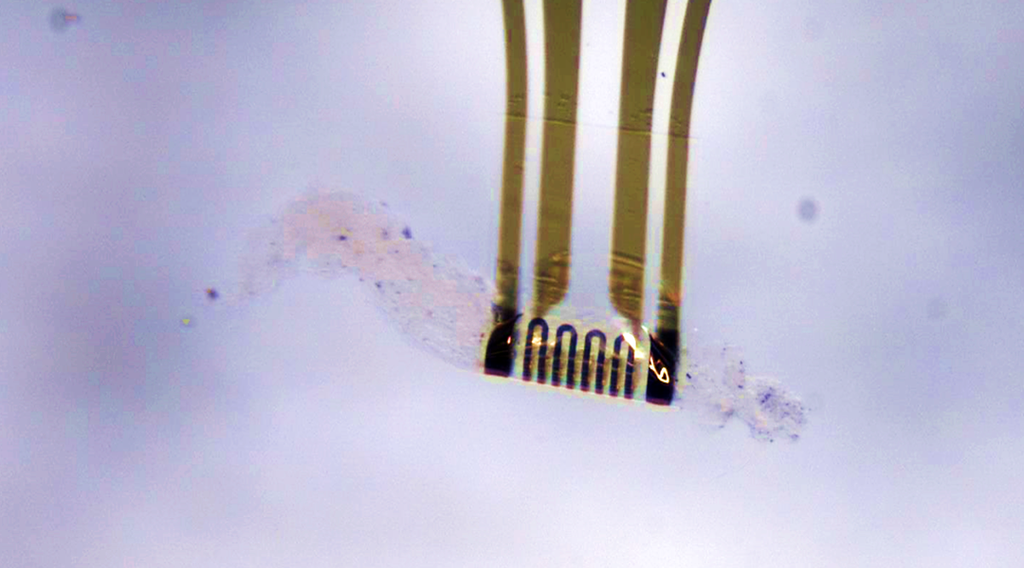

Thanks to ultra-thin sensors and artificial muscles, future flexible microelectronics will be able to take on complex shapes to better interface with delicate biological tissues without causing damage.
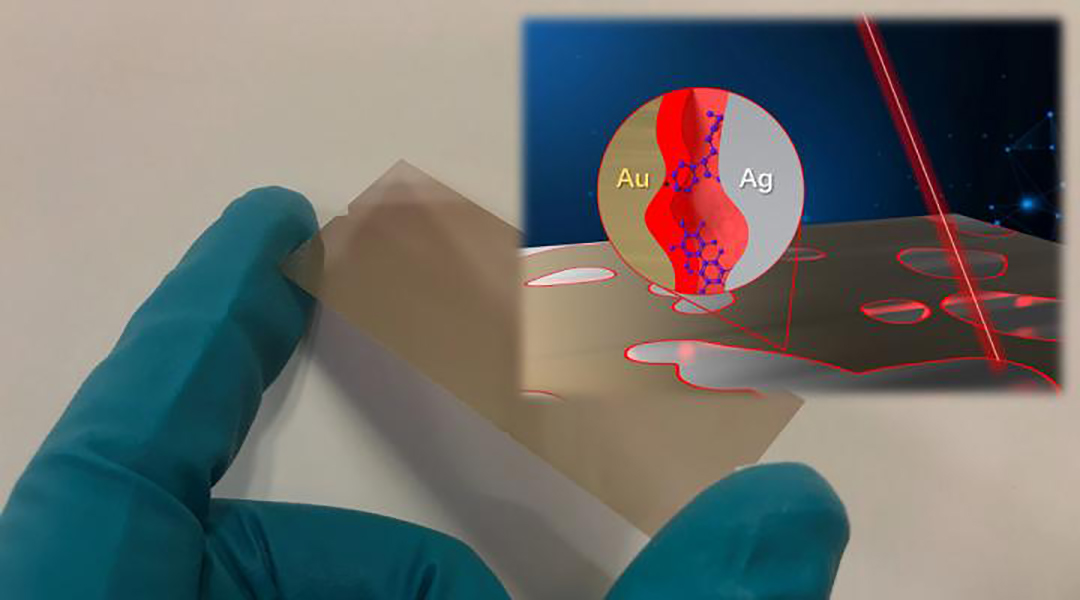
Study shows improvements to chemical sensing chip that aims to quickly and accurately identify drugs and other trace chemicals.
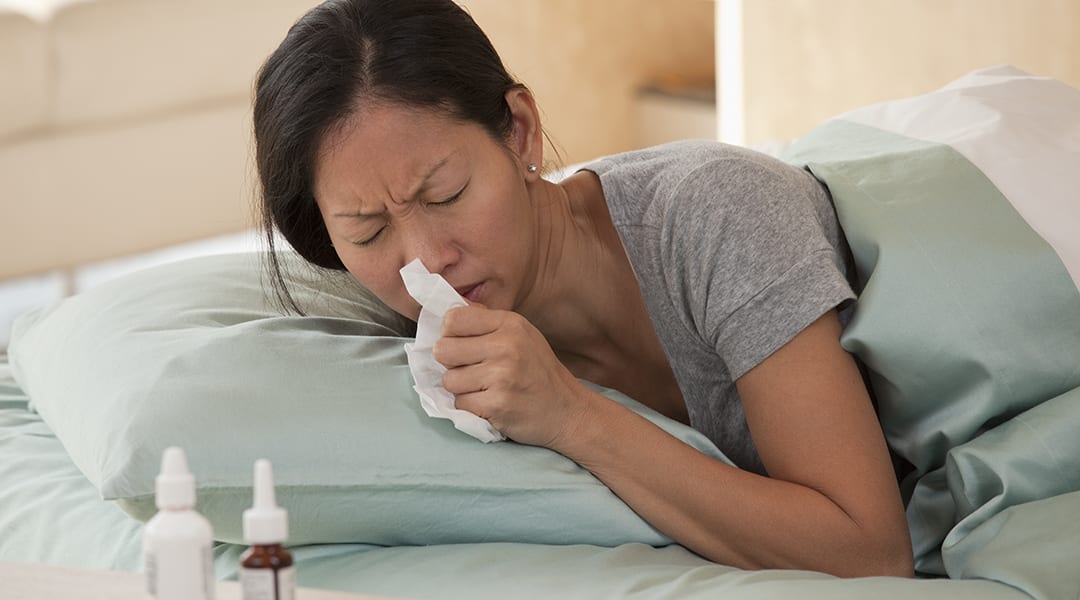

Scientists uncover how a sensor protein activates our immune system against the common cold. The findings may lead to more effective treatments of flu-like symptoms.
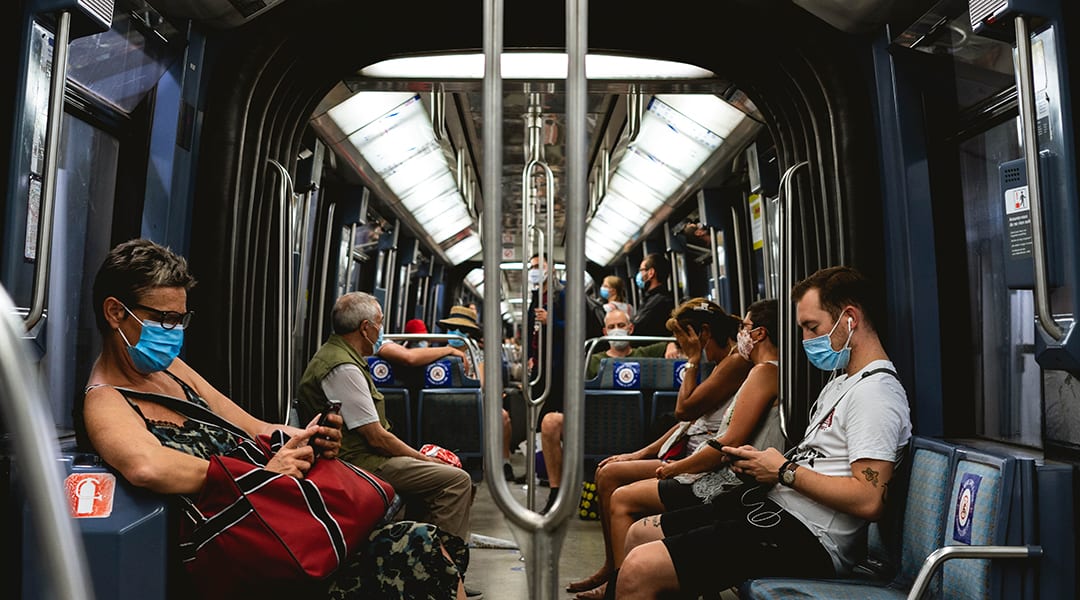

Developments in pathogen-detecting materials could provide an easy means of detecting viruses within public places.
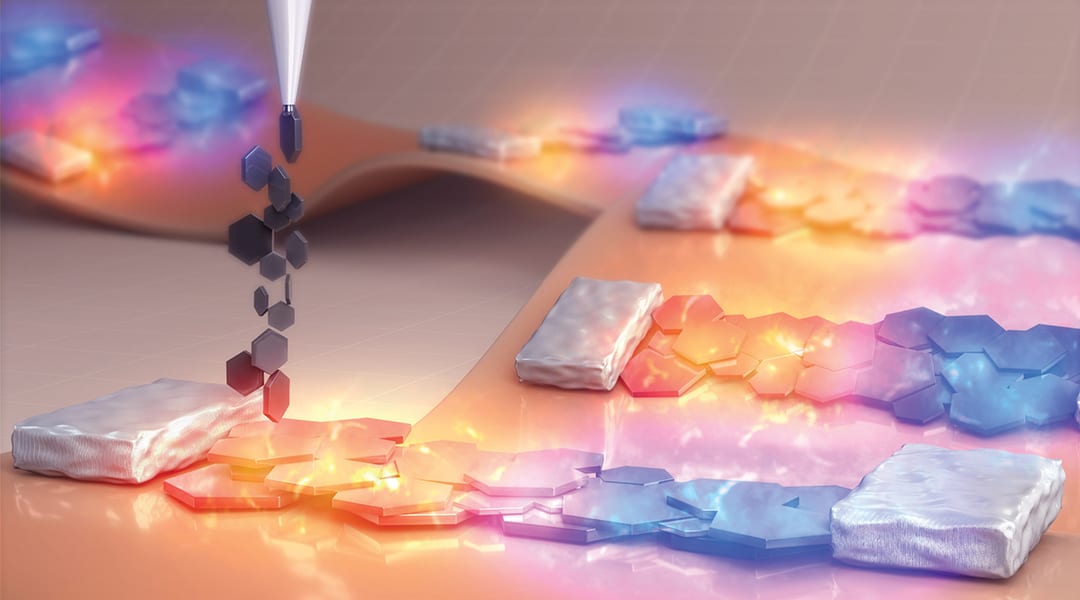
A simple approach to create high performance thermoelectric materials, which would allow one to turn their body heat into electricity.
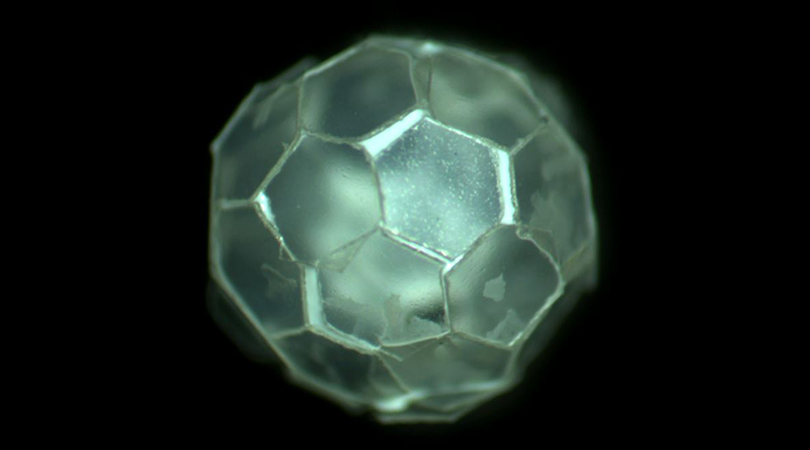

Creating versatile liquid marbles, stabilized with polymeric plates for more durability and broader applications.
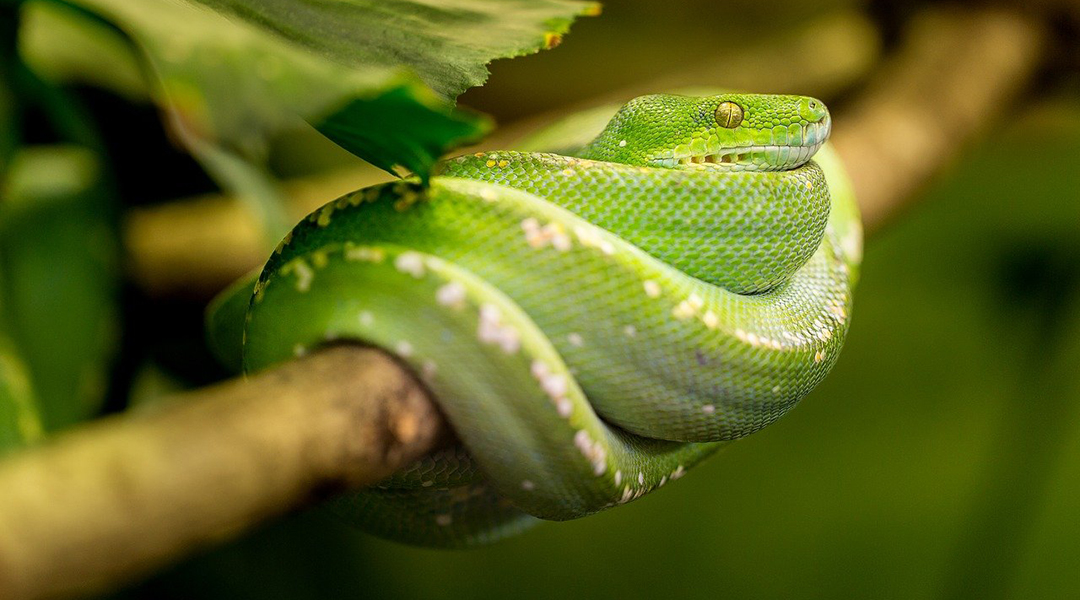

Researchers in Australia take inspiration from nature to create a soft-robotic gripper that moves away from the conventional hand-like design.
Complex 3D nanoscale architectures based on DNA self-assembly can conduct electricity without resistance and may provide a platform for fabricating quantum computing and sensing devices.
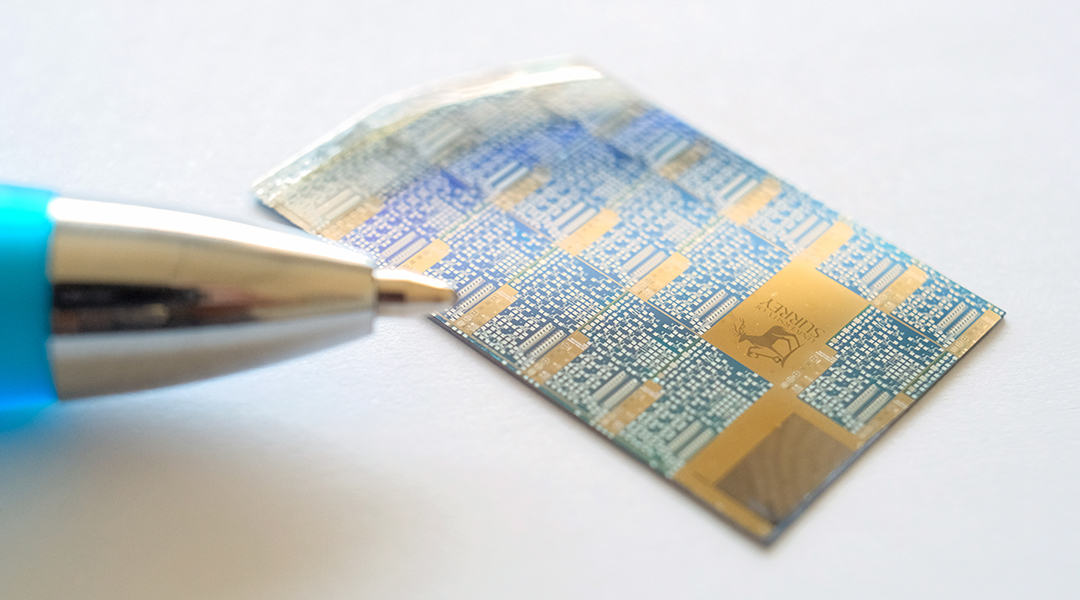
Multimodal thin-film transistors, or MMTs, could be pivotal in designing the next-generation of wearables and eco-disposable sensors.
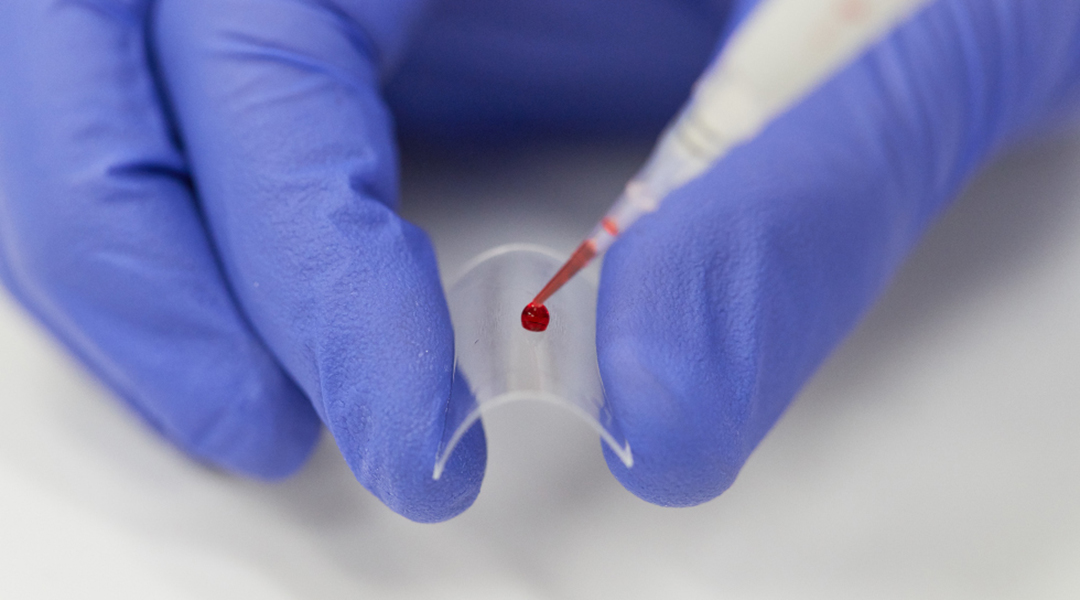
An inventive new approach lowers the limit of detection for a common assay, allowing researchers to identify elusive biomarkers in complex fluids, like the blood.