Alco Bio Fuel digitally transform their way of operations. Now, software helps to monitor and fine-tune performance of the generator.


Alco Bio Fuel digitally transform their way of operations. Now, software helps to monitor and fine-tune performance of the generator.

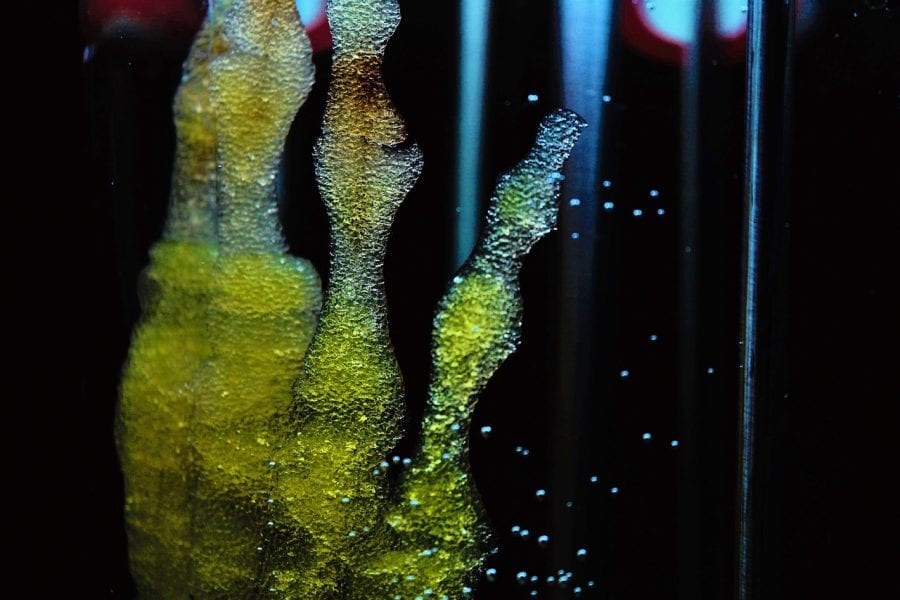
A team of researchers develop a unique molding process for generating all-liquid structures via interfacial jamming of cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) surfactants. The structures have long-term stability and can adapt or respond to external stimuli, allowing for potential applications in encapsulation, sensors, and liquid electronic devices.

Researchers design a bio-inspired batoid robot from non-toxic hydrogels operated with Au microelectrodes.
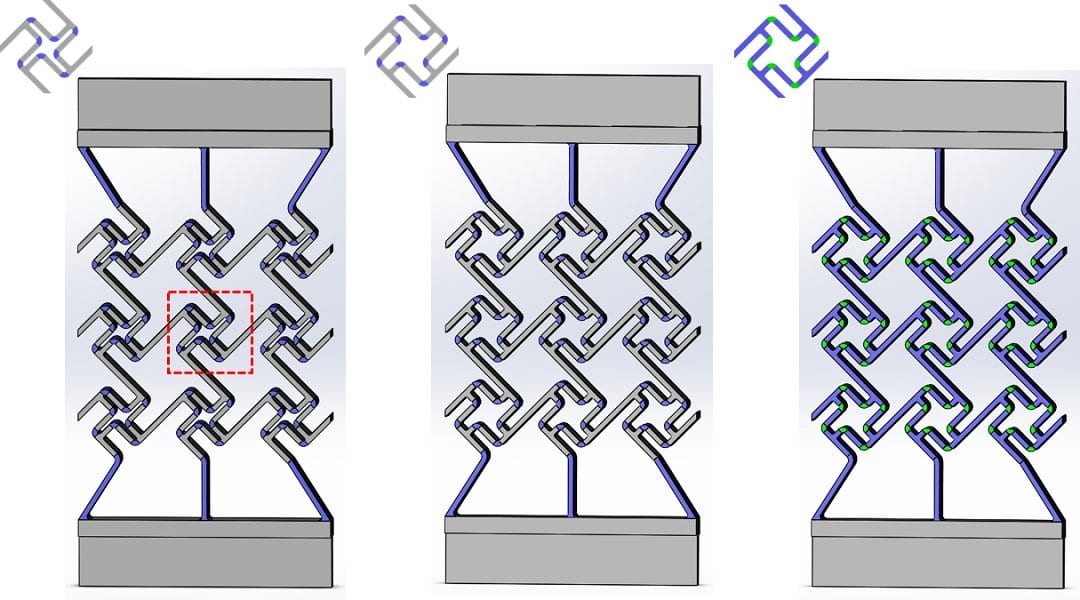
New designs were fabricated via multimaterial 3D printing and potential applications of sequential particle release mechanisms were systematically explored.
Xavier Crispin and co-workers from Linköping University, Sweden, report a thermoelectric polymer aerogel with dual-sensing capability. This single-material device can deliver independent pressure and temperature assessments.

Latest Advanced Healthcare Materials covers.
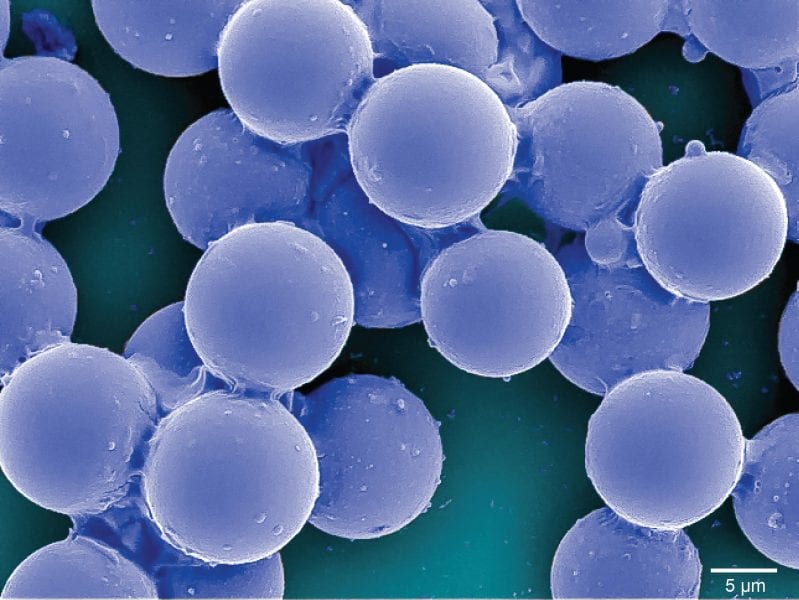
A simple and convenient method to fabricate thermoresponsive gel particles with tunable size across multiple size scales opens new directions in biomaterials, optics, and pharmaceutics.

Advanced Healthcare Materials papers you have downloaded and read the most in the past two months.
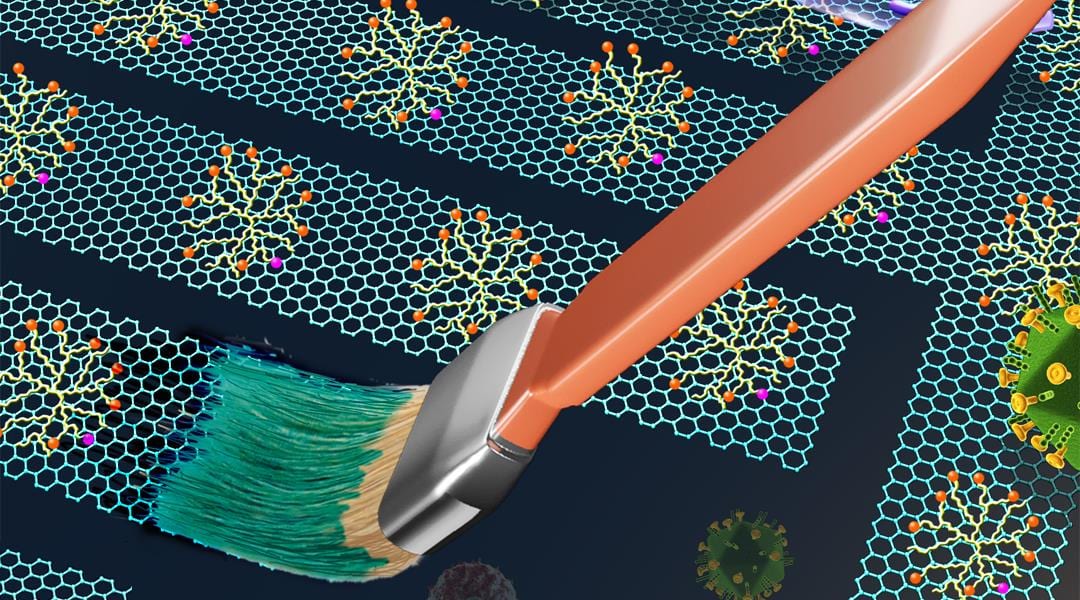
Flexible graphene nano-inks with an excellent bioactivity pave the way for next generation biomedical applications.

A group of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) generate living materials and devices by 3D printing genetically programmed bacterial cells. The living bioink can be used to print novel materials including logic gates and a living tattoo for chemical detection on human skin.