Artificial cells with specialized internal chemistries could revolutionize how we approach precision medicine.


Artificial cells with specialized internal chemistries could revolutionize how we approach precision medicine.
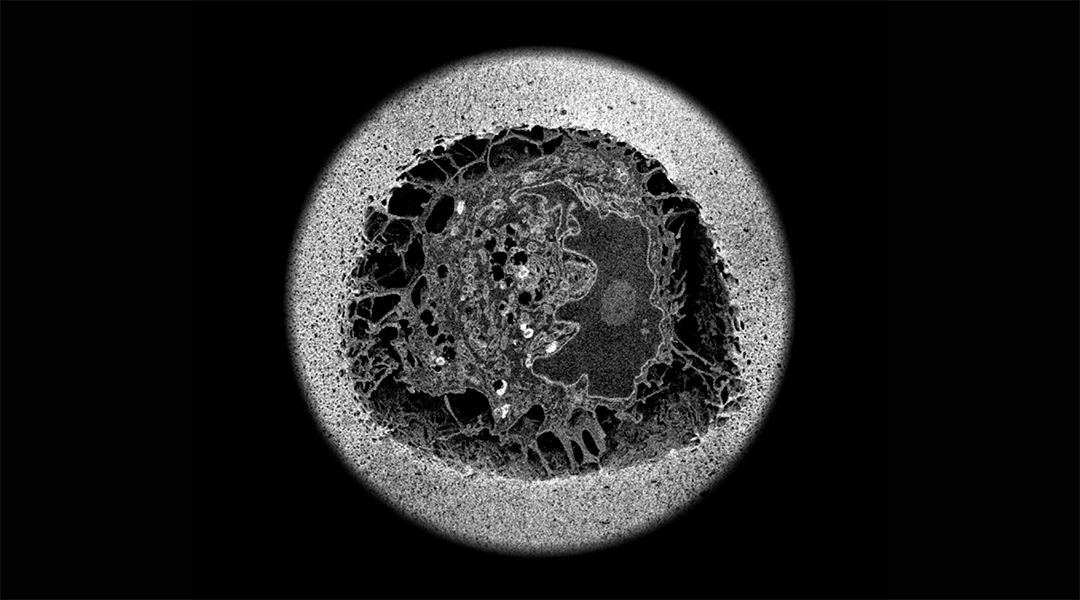
A natural chemical tether helps researchers attach cells to inert biomaterials for better cell models and therapies.
By using the advantage of hybrid nanomaterials, researchers may have unlocked a new pharmacological route for treating degenerative diseases.
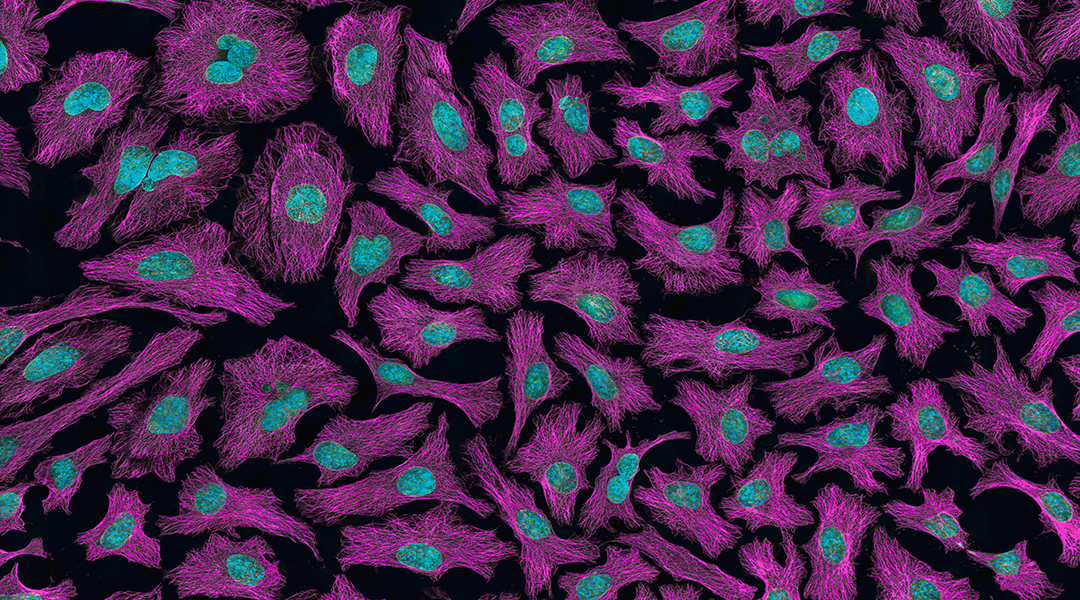
DNA robots built to transverse fluidic cell membranes and control cell function for future regenerative and cell-based therapies.
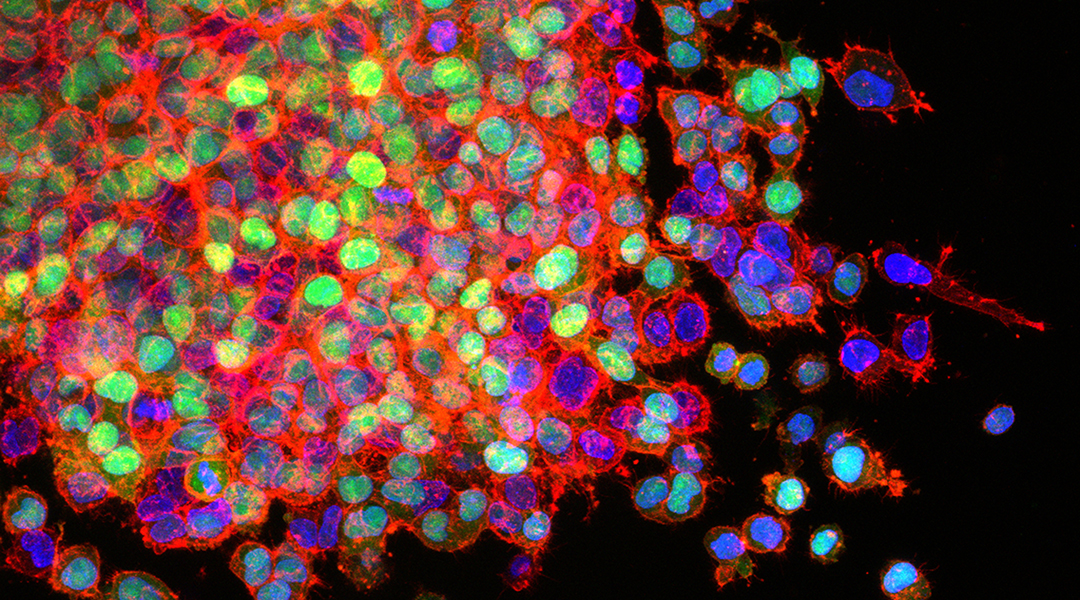
The surgical anesthesia drug, propofol, used in tumor removal, could help promote the spread of cancer by triggering changes in tumor cell properties.
A new type of hydrogel could radically transform a novel stem cell treatment for Parkinson’s disease.
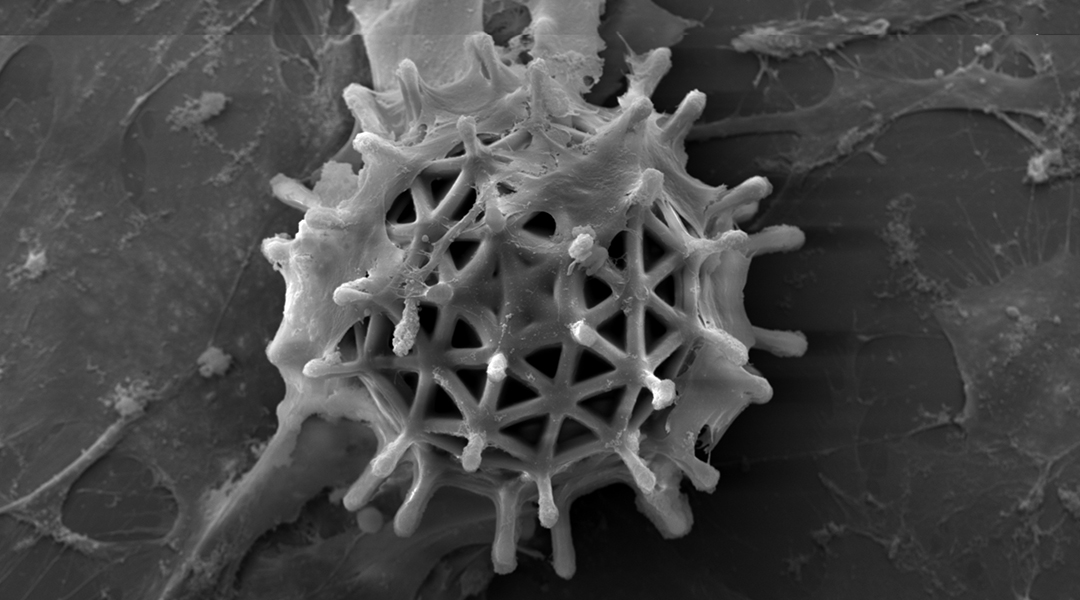
Researchers find the sweet spot between strength and biocompatibility in these tiny cell-carrying microrobots.
Bioorthogonal hydroamination of activated linear alkynes now suitable in living cells.
The device could improve personalized medicine by detecting whether a specific drug is likely to work for a patient before it is administered.
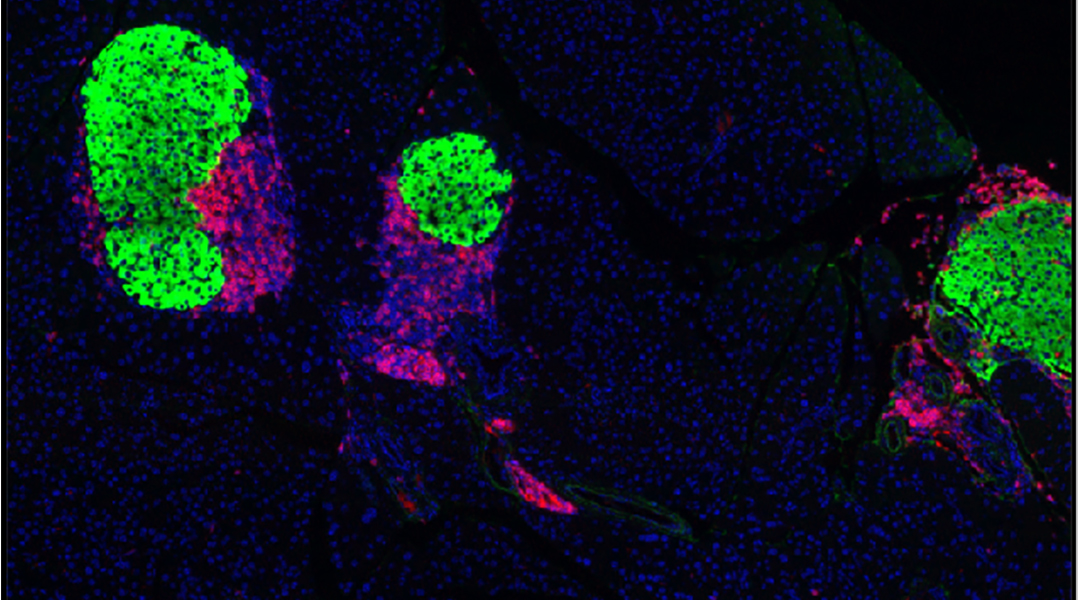
Bioengineered pancreatic beta cells adorned with immune checkpoint proteins prevent the progression of type 1 diabetes.