A protocol for a unique high-throughput assay to identify novel small-molecule inhibitors of cell migration.
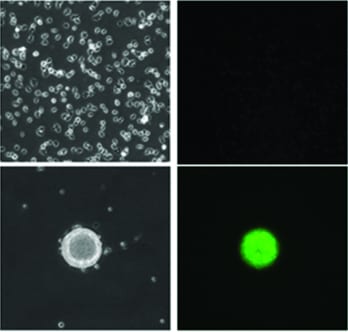

A protocol for a unique high-throughput assay to identify novel small-molecule inhibitors of cell migration.
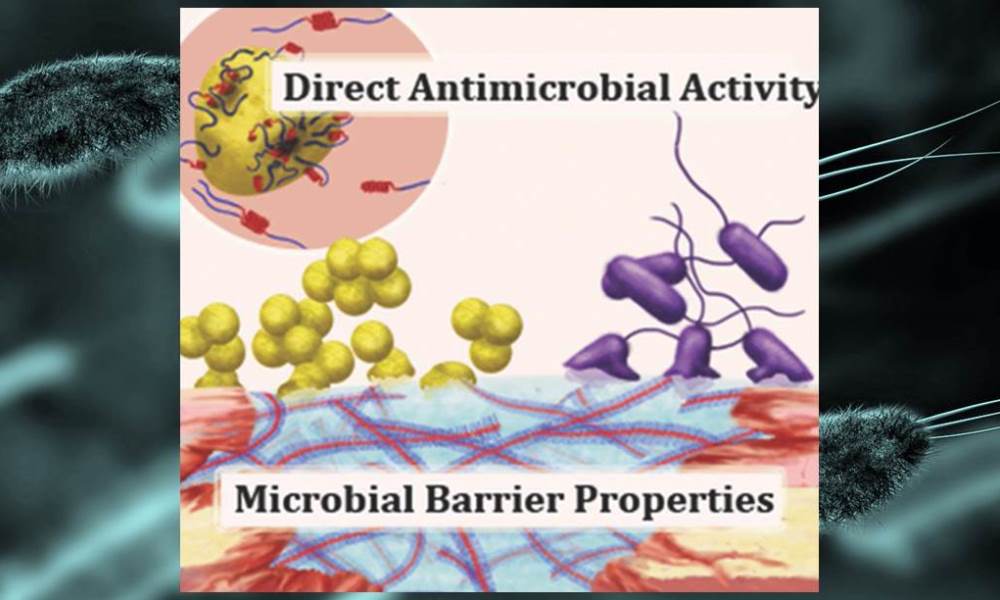
A new approach to prevent wound infections: Antimicrobial activities and microbial barrier properties can be designed in a single biopolymer.

Research highlights from this month’s Advanced Healthcare Materials issues.
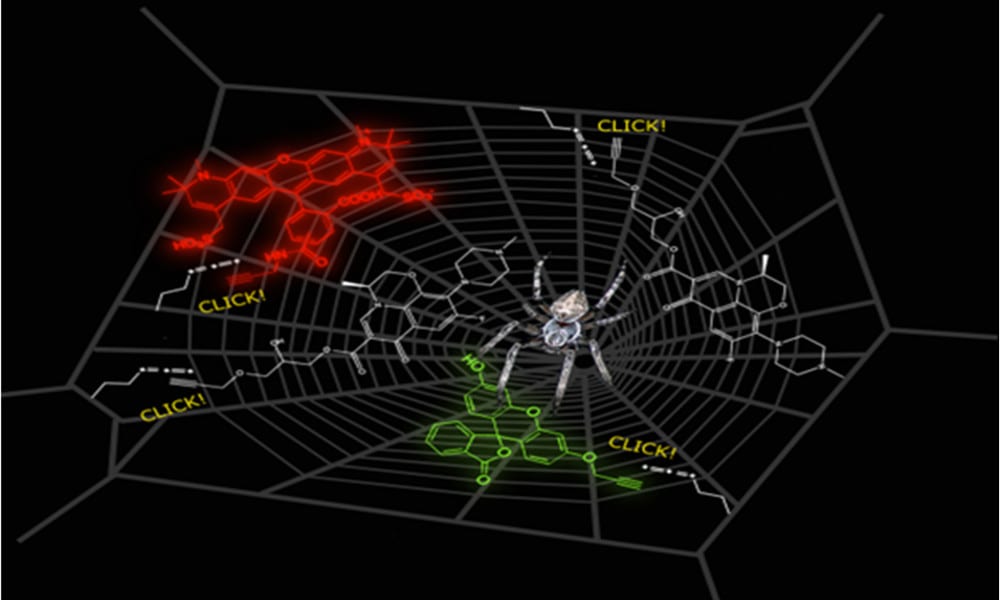
Researchers from the University of Nottingham report a novel method for making antibiotic spider silk.
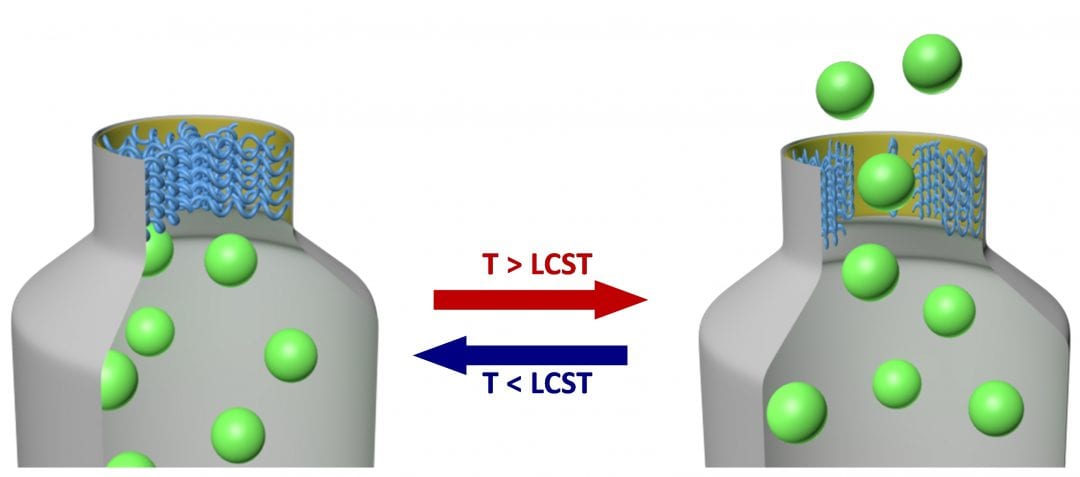
Researchers from Oslo report on the influence of temperature and polymer spacer length on the phase behavior of aqueous polymer solutions
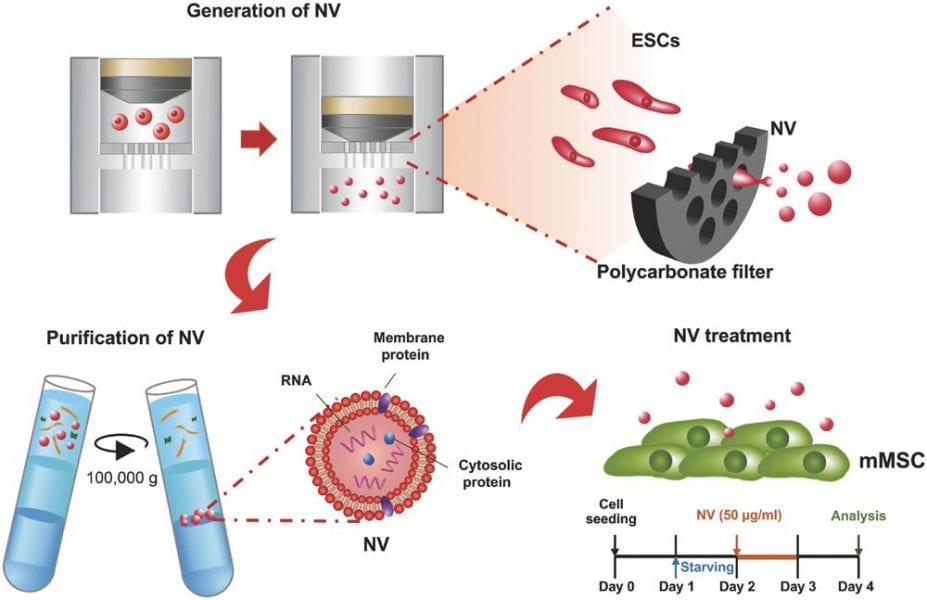
“Man-made” extracellular vesicle-mimetic nanovesicles developed with characteristics similar to those of extracellular vesicles.
Researchers report the first example of a hydrogel for wound healing with both rapid self-healing ability and high mechanical strength.
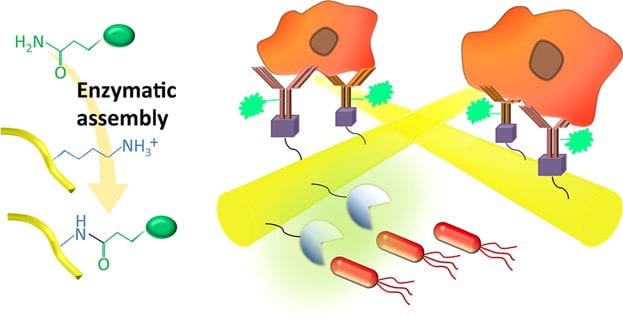
Biofunctionalized native spider silk fibers can be used in a wide spectrum of biomedical and biotechnological applications.
A prototype theranostic device based on thermally triggered release of a fluorescent antibiotic from polymer coated porous silicon films is developed.
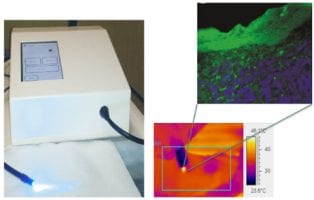
Irradiation with a blue-LED haemostatic device improved the healing process in superficial skin wounds without adverse side effects.