The Editors of Small Methods are pleased to publish this special biomedical virtual issue. This collection highlights outstanding research in Small Methods from the very first issue to now, in the areas of biosensing, biomedical engineering, nanomaterials, biotechnology, peptide and polymer Science, and bioimaging.
Biosensing
Surface‐Enhanced Raman Nanoprobes with Embedded Standards for Quantitative Cholesterol Detection
Xin Jiang, Ziyang Tan, Li Lin, Jing He, Chang He, Benjamin D. Thackray, Yuqing Zhang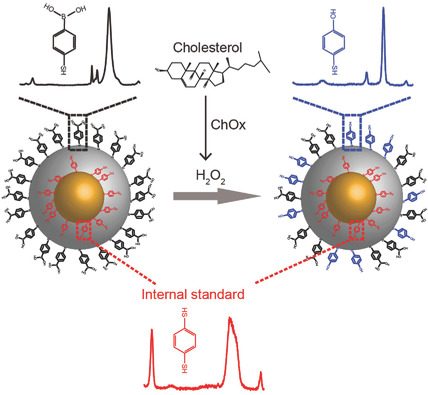 , Jian Ye
, Jian Ye
Cholesterol is an essential molecule in human body and many diseases can be detected in their early stages by monitoring intracellular cholesterol levels. Herein, metallic surface‐enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) core–shell nanoparticles with an embedded standard are designed for nondestructive detection of H2O2 and cholesterol. Using these SERS nanoprobes quantitative detection of H2O2 and cholesterol in solution and inside live cells at a single‐cell level is demonstrated.
Jun Gao, Nan Zhang, Dengxin Ji, Haomin Song, Youhai Liu, Lyu Zhou, Zhi Sun, Josep M., Jornet, Alexis C. Thompson, R. Lorraine Collins, Yun Song, Suhua Jiang, Qiaoqiang Gan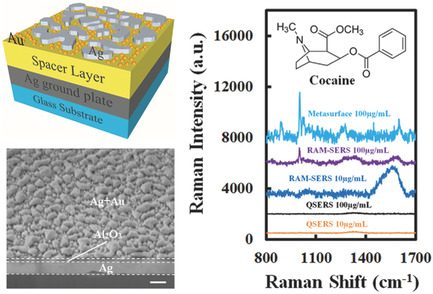
To overcome the difficulty of quantitative analysis in the practical application of SERS sensing, a superabsorbing metasurface with hybrid Ag-Au nanostructures was proposed. This structure efficiently localizes the excitation laser energy at the edges of the nanoparticles, resulting in enhanced sensing resolution and a more uniformed distribution. This leads to a superior performance for potential quantitative sensing of drugs and chemicals.
Recent Trends in Nanomaterials‐Based Colorimetric Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria and Viruses
Yoojin Choi, Ji Hyeon Hwang, Sang Yup Lee 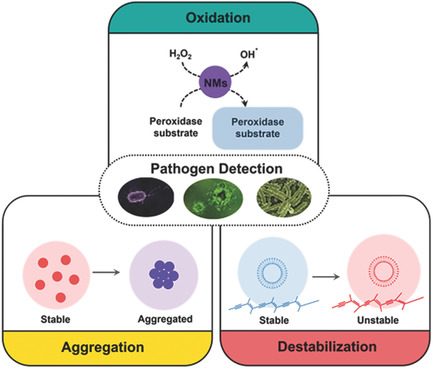
Nanomaterials have been adopted as a versatile signal transduction and amplification tool for rapid and sensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. This paper reviews recent trends and advances in detecting and diagnosing pathogenic bacteria and viruses using colorimetric biosensors employing various nanomaterials. In addition, it is discussed how nanomaterials and bioreceptors can be better integrated together to develop rapid and sensitive colorimetric detection system in the future.
Construction of Plasmonic Nano-Biosensor-Based Devices for Point-of-Care Testing
Yangyang Wang, Jianhua Zhou, Jinghong Li 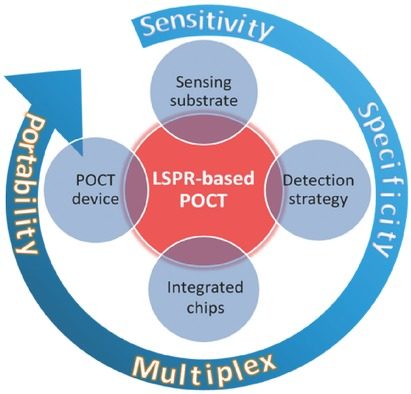
A synopsis of Localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) nano‐biosensors and LSPR‐based point‐of‐care testing (POCT) devices is provided by delineating the fundamental principles of LSPR sensing, various metal nanostructures, the modification layers on LSPR nanostructures, and the integration of LSPR biosensors into devices. The challenges and perspectives of developing LSPR‐based POCT techniques are highlighted.
Recent Advances and Perspectives in Microfluidics-Based Single-Cell Biosensing Techniques
Jiacheng He, Ayoola T. Brimmo, Mohammad A. Qasaimeh, Pengyu Chen, Weiqiang Chen 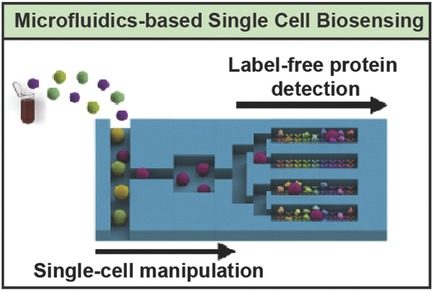
Recent advances in microfluidics‐based single‐cell manipulation and emerging approaches for label‐free single‐cell biosensing are reviewed. The advantages and limitations of these technologies are summarized and challenges to establish the integrated microfluidic biosensing systems for real‐time single‐cell secretomics are discussed.
Designed Microdevices for In Vitro Diagnostics
Xuming Sun, Jing jing Wan, Kun Qian 
In vitro diagnostics (IVD) refers to in vitro tests of biological specimens and contributes to two‐thirds of clinical diagnosis. Herein, the principle, design, and application of microdevices regarding these two routes in recent progress for IVD are shown. The roles of materials in devices toward diverse applications are elucidated.
Monitoring Neutropenia for Cancer Patients at the Point of Care
Hakan Inan, James L. Kingsley, Mehmet O. Ozen, Huseyin Cumhur Tekin, Christian R. Hoerner, Yoriko Imae, Thomas J. Metzner, Jordan S. Preiss, Naside Gozde Durmus, Mehmet Ozsoz, Heather Wakelee, Alice C. Fan, Erkan Tüzel, Utkan Demirci 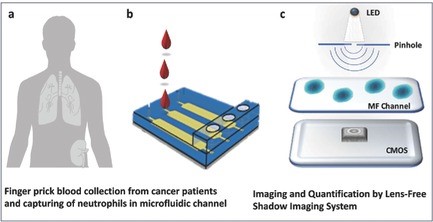
Neutrophils have a critical role in regulating the immune system. The immune system is compromised during chemotherapy, increasing infection risks and imposing a need for regular monitoring of neutrophil counts. A reliable method is presented that selectively captures and quantifies white blood cells (WBCs) and neutrophils from a finger prick volume of whole blood by integrating microfluidics with high-resolution imaging algorithms.
Md Nazmul Islam, Mostafa Kamal Masud, Md Hakimul Haque, Md Shahriar Al Hossain, Yusuke Yamauchi, Nam‐Trung Nguyen, Muhammad J. A. Shiddiky 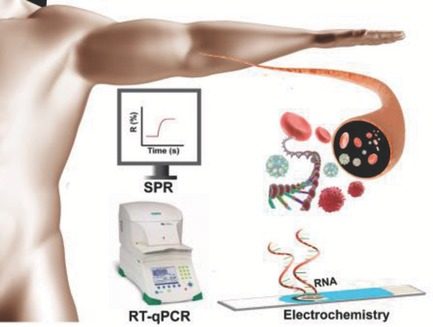
The recent developments of RNA biosensors are concisely reviewed with a special emphasis on electrochemical-detection approaches. All the types of clinically relevant RNAs and their diagnostic and prognostic potential in cancer are outlined. Major challenges associated with current techniques are identified. The current requirements that still need to be met for effective screening of RNA biomarkers in both research and clinical settings.
Biomedical Engineering
Wenzhe Li, Bin Shao, Changliang Liu, Huayi Wang, Wangshu Zheng, Weiyao Kong, Xiaoran Liu, Guobin Xu, Chen Wang, Huiping Li, Ling Zhu, Yanlian Yang 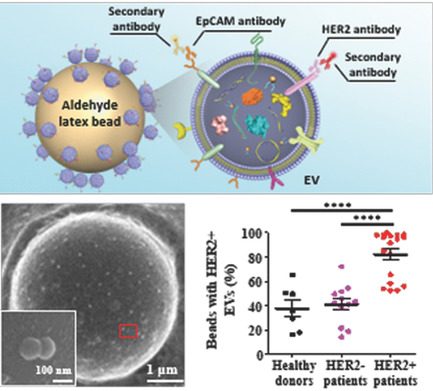
Blood‐based detection and molecular phenotyping are highly desired for the early diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of cancer. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) carry molecular information from the cells of origin and are biomarkers of cancer. In this paper, an assessment of the detection and molecular phenotyping of serum EVs based on microbead‐assisted flow cytometry is established. The clinical utility of this method is validated in the diagnosis and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) phenotyping of breast cancer.
Near Infrared Boron Dipyrromethene Nanoparticles for Optotheranostics
Ling Huang, Gang Han 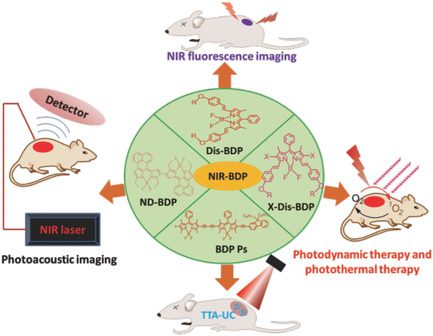
Boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY) is a class of fluorescent dyes. Near infrared (NIR)‐emitting BODIPY dyes containing nanoparticles have recently been developed for a wide array of cutting‐edge cancer optotheranostic applications. This study discusses their use as photoswitchable fluorescence probes toward in vitro single‐molecule imaging, photoacoustic imaging, photodynamic therapy (PDT), triplet–triplet annihilation upconversion (TTA‐UC) and their biological uses.
Photothermal Adjunctive Cytoreductive Surgery for Treating Peritoneal Metastasis of Gastric Cancer
Shunhao Wang, Chongwei Chi, Haidong Cheng, Xueting Pan, Shanshan Li, Fengrong Zhang, Sharen Gaowa, Jinzuo Ye, Yamin Mao, Kunshan He, Jie Tian, Huiyu Liu 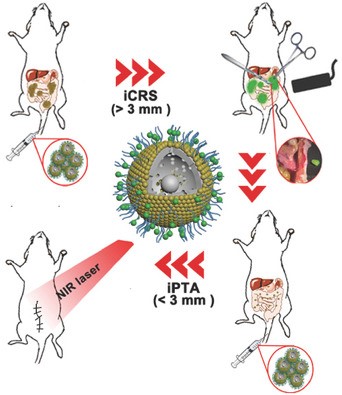
To improve the survival rates in selected patients with peritoneal metastasis (PM) accepting cytoreductive surgery (CRS) and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy, novel gold nanoshells conjugated with indocyanine green (I‐GSNs) for image‐guided photothermal adjunctive CRS (iPTA‐CRS) are synthesized. The strategy is significantly more effective for removing subcutaneously transplanted tumors, inhibiting PM nodules of the gastric tumor, and enhancing the survival rate.
Supramolecular Vesicles for Stimulus‐Responsive Drug Delivery
Pengyao Xing, Yanli Zhao 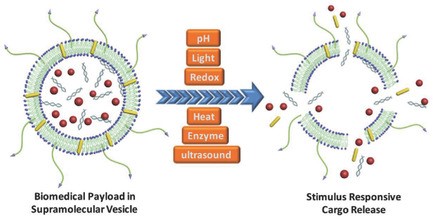
Developing smart controlled‐release systems for cancer therapy is highly desired in biomedicine. This paper reviews recent significant development of vesicles constructed by supramolecular self‐assembly for stimulus‐responsive drug delivery and therapeutics. Strategies regarding the design, synthesis, characterization, and biomedical applications of supramolecular vesicle carriers are highlighted.
Signed‐For Delivery in the Mitochondrial Matrix: Confirming Uptake into Mitochondria
Kurt Hoogewijs, Andrew M. James, Michael P. Murphy, Robert N. Lightowlers
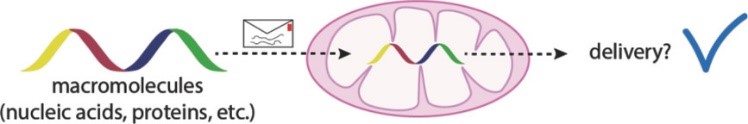
Mitochondria are known for their ability to provide energy, and impairment of ATP production can lead to a variety of diseases. Technical progress in this field has been severely hampered by the inability to correctly determine whether uptake into the mitochondrial matrix of nucleic acids and related oligomers has occurred. In this review, the methods that have been used to determine translocation of macromolecules into mitochondria in the past are described, and some recent developments in the field are discussed.
Advances in Stimuli‐Responsive Polypeptide Nanogels
Zhongyu Jiang, Jinjin Chen, Liguo Cui, Xiuli Zhuang, Jianxun Ding, Xuesi Chen
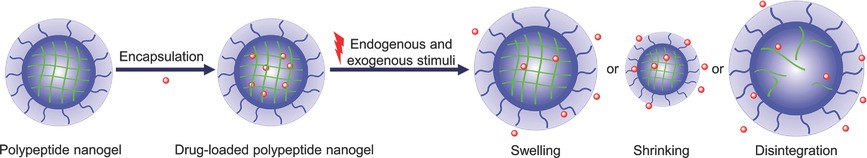
Polymer nanogels are nanosized particles of hydrogels formed by physically or chemically crosslinking polymers. Polypeptide nanogels exhibit many advantages like stable 3D structures, high drug‐loading efficiency, excellent biocompatibility, stimuli responsiveness, and so forth. In this review, a comprehensive introduction to the preparation and applications of diverse stimuli‐responsive polypeptide nanogels is given. Moreover, the opportunities and challenges of polypeptide nanogels for the development of biomedicine are briefly predicted.
Micro‐ and Macrobioprinting: Current Trends in Tissue Modeling and Organ Fabrication
Marco Santoro, Javier Navarro, John P. Fisher 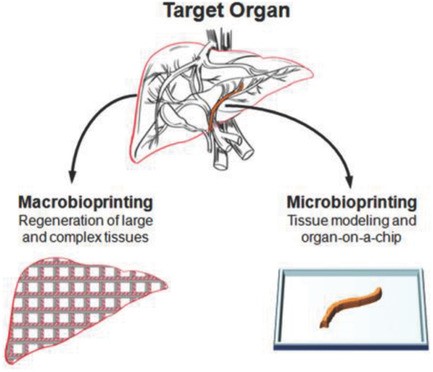
Bioprinting holds great promise in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine research. It has two different routes: fabricate large tissue surrogates for transplantation purposes in vivo (macrobioprinting), and model the tissue microenvironment in vitro (microbioprinting). The latest advances in both macro‐ and microbioprinting are reviewed, emphasizing their impact on specific areas of tissue engineering.
Red Blood Cells for Drug Delivery
Junjie Yan, Jicheng Yu, Chao Wang, Zhen Gu 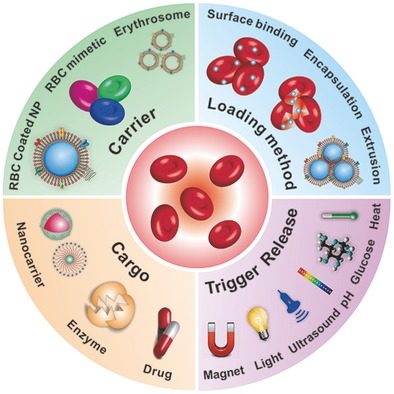
Red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, have been promising endogenous candidates for drug delivery for more than four decades. Here, the loading methods and loading therapeutics by RBC carriers are surveyed, and recent advances in the design of stimuli‐triggered RBC carriers highlighted.
Nanomaterials
Biophysical Assessment of Pulmonary Surfactant Predicts the Lung Toxicity of Nanomaterials
Yi Yang, Yakun Wu, Quanzhong Ren, Lijie Grace Zhang, Sijin Liu, Yi Y. Zuo 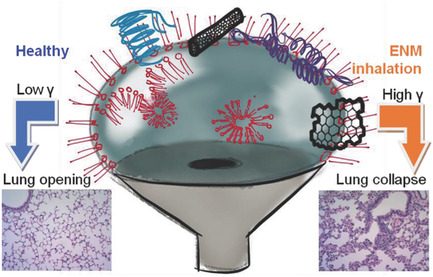
Develop precautionary tools to evaluate acute lung toxicity of engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) is in urgent need. In this paper, constrained drop surfactometry (CDS) is developed to quantitatively evaluate pulmonary surfactant (PS) inhibition caused by ENMs. Compared to commonly used animal models, CDS holds great promise for the development of an animal‐free, easy‐to‐use, and low‐cost precautionary assay for the prediction of acute lung toxicity of inhaled ENMs.
Shuang Zhu, Linji Gong, Jiani Xie, Zhanjun Gu, Yuliang Zhao 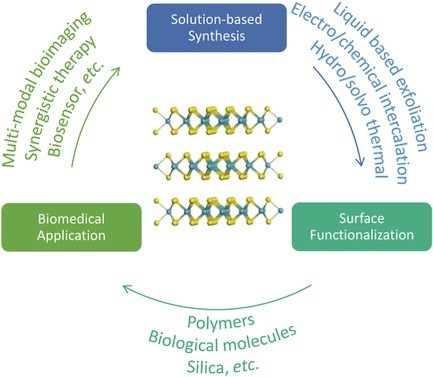
With the rapid development of nanotechnology, the emerging transition‐metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) have become one of the most promising inorganic nanomaterials for medical applications due to their distinctive structures and properties. This paper reviewed recent advances in the design, synthesis, and surface modification of TMDC‐based nanomaterials specific for biomedical applications.
Microfluidic Synthesis of Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications
Li‐Li Li, Xiaodong Li, Hao Wang 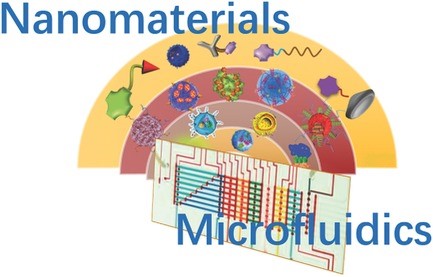
The recent progress in the design principles of microfluidic systems for nanomaterials synthesis is summarized. In addition, microfluidics, on the microscale, expand the synthesis space, precisely controlled nanostructures, and high-throughput fabrication of multifunctional nanoparticles.
Immunostimulation and Immunosuppression: Nanotechnology on the Brink
Flavia Fontana, Patrícia Figueiredo, Tomás Bauleth‐Ramos, Alexandra Correia, Hélder A. Santos 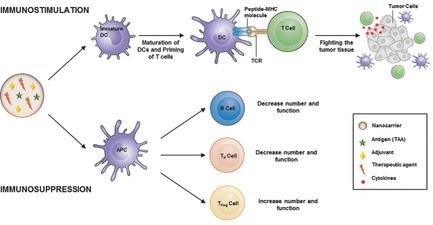
Immunotherapy is revolutionizing current therapies in cancer and in autoimmune diseases, showing impressive results in clinical trials. This review analyzed the properties influencing the immunomodulation effect of nanomaterials, and summarized recent applications of nanomaterials for the delivery of antigens, adjuvants, chemotherapeutics, and immunomodulatory drugs.
Biotechnology
High‐Throughput Optical Mapping of Replicating DNA
Francesco De Carli, Nikita Menezes, Wahiba Berrabah, Valérie Barbe, Auguste Genovesio, Olivier Hyrien
Genome‐wide methods to map DNA replication use large cell populations, which smoothes out variability between chromosomal copies. In this paper, the Bionano Genomics Irys system, an optical DNA mapping device, is repurposed for high‐throughput optical mapping of replicating DNA 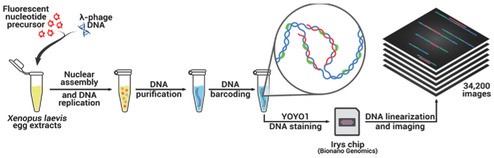 (HOMARD). HOMARD combines direct fluorescent labeling of replication tracks and nicking endonuclease sites with DNA linearization in nanochannel arrays and dedicated image processing. It opens the way to genome‐wide analysis of DNA replication at the single‐molecule level.
(HOMARD). HOMARD combines direct fluorescent labeling of replication tracks and nicking endonuclease sites with DNA linearization in nanochannel arrays and dedicated image processing. It opens the way to genome‐wide analysis of DNA replication at the single‐molecule level.
Data‐Matrix Technology for Multiparameter Monitoring of Cell Cultures
Marianna Barbalinardo, Denis Gentili, Francesca Lazzarotto, Francesco Valle, Marco Brucale, Manuela Melucci, Laura Favaretto, Massimo Zambianchi, Ana I. Borrachero‐Conejo, Emanuela Saracino, Valentina Benfenati, Davide Natalini, Paolo Greco, Maria Giovanna Di Carlo, Giulia Foschi, Massimiliano Cavallini 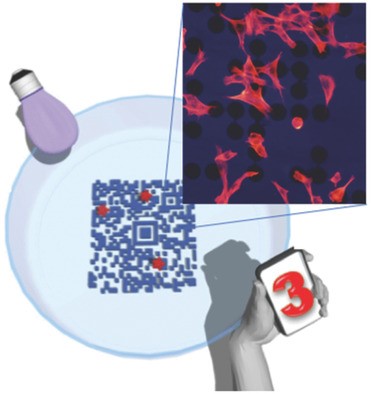
A data‐matrix (DM)‐technology approach in cell biology is implemented as an efficient method for the multiparameter monitoring of cell cultures. The proposed method takes advantage of the know‐how developed for fault tolerance in digital information technology by measuring the amount of errors induced by intervening cells upon checking a DM code placed behind them. It gives continuous access to several quantitative parameters of the observed culture, such as cell coverage, mean size, viability, and transfection efficiency.
Paolo Actis 
Major methodological advances in engineering and molecular biology have enabled the ‘omics analysis of individual cells. However, a single cell needs to be lysed or fixed before any in‐depth analysis can be performed. This paper reviews methods that extract the contents of living cells without affecting their viability. These methods are empowering the biological community to repeatedly interrogate a single cell over time.
DNAzymes: Selected for Applications
Devon Morrison, Meghan Rothenbroker, Yingfu Li 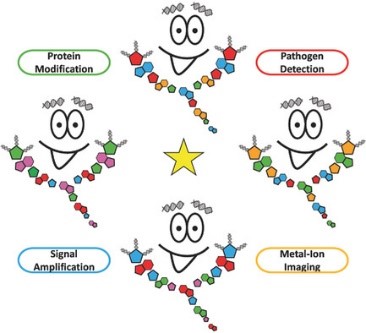
DNAzymes are single‐stranded DNA molecules with catalytic activity. In this review, examples of new DNAzymes including RNA‐cleaving DNAzymes engineered to mimic some intriguing functions of naturally occurring protein‐based enzymes are discussed. Ligand‐responsive DNAzymes, and analyte‐activated DNAzyme in biosensing applications are highlighted.
Biochips—New Platforms for Cell‐Based Immunological Assays
Ning Shao, Lidong Qin 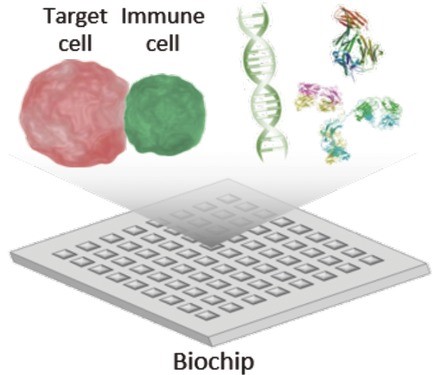
Development of biochips that seek to realize various types of immune cell analysis on microscale platforms and enhance both basic and applied immunological research is significant. In this paper, state‐of‐the‐art designs and examples for biochip‐based analysis and manipulation of immune cells are reviewed, and the potential of this emerging technology to enhance the understanding of immunology and improve disease diagnosis and treatment is discussed.
Aung Than, Ke Liang, Shaohai Xu, Lei Sun, Hongwei Duan, Fengna Xi, Chenjie Xu, Peng Chen 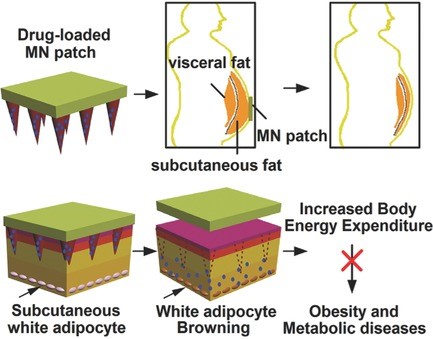
Excess white adipose tissue (WAT), or obesity, is the leading cause of many diseases. A new strategy is reported using disposable transdermal patches equipped with detachable polymeric microneedle (MN) arrays for painless and bloodless drug delivery to subcutaneous WAT. Such an MN approach can achieve a much lower effective dose as compared to systemic administration and enables long‐term home‐based treatment.
Enriching Nanomaterials Omics Data: An Integration Technique to Generate Biological Descriptors
Georgia Tsiliki, Penny Nymark, Pekka Kohonen, Roland Grafström, Haralambos Sarimveis 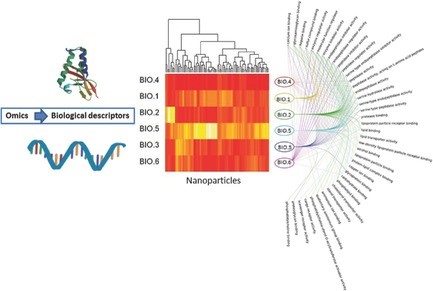
An integration methodology is presented where high‐throughput omics data are enriched with biological‐pathway information to produce a novel set of biological (BIO) descriptors by decomposing omics data to meaningful clusters in terms of both their mechanistic interpretation and correlation affinity. The methodology is applied to an extensive proteomics data set and demonstrates that BIO descriptors are beneficial for modeling prediction, outperforming the prediction accuracy of the original omics data, and offering a readily available biological interpretation of the findings.
Purified Cas9 Fusion Proteins for Advanced Genome Manipulation
Jovan Mircetic, Iris Steinebrunner, Li Ding, Ji‐Feng Fei, Aliona Bogdanova, David Drechsel, Frank Buchholz 
A variety of purified Cas9 fusion proteins are generated, and their utility is tested in a number of assays. The results show that purified Cas9 fusion proteins are versatile and efficient reagents that facilitate advanced genome manipulation.
Peptide and Polymer Science
Haipei Liu, Duy Tien Ta, Michael A. Nash 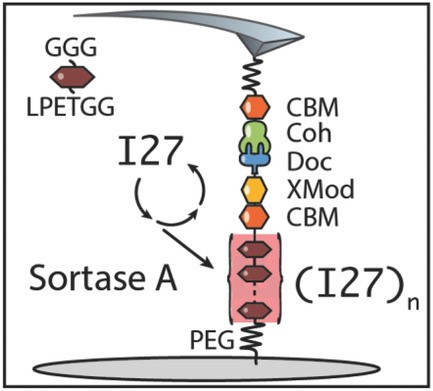
A new approach to polyprotein synthesis is presented relying on posttranslational enzyme‐mediated oligomerization of domains. Mutant variants of immunoglobulin 27 (I27) and a bacterial cellulose binding module (CBM) fused to an Ig‐like X‐module (XMod), and a mechanostable receptor called Dockerin (Doc) are produced with complementary peptide tags. This approach is advantageous for assembly of polyproteins from domains that lack proper folding or are insoluble in a polyprotein format is studied.
A Trifunctional Linker for Purified 3D Assembled Peptide Structure Arrays 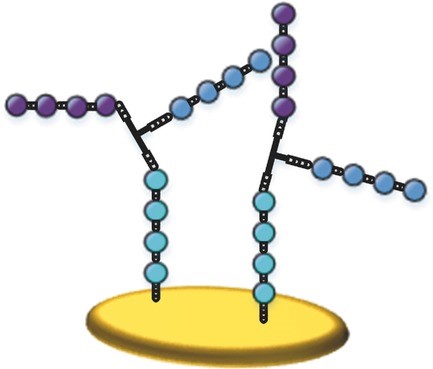
Daniela S. Mattes, Simone Rentschler, Tobias C. Foertsch, Stephan W. Münch, Felix F. Loeffler, Alexander Nesterov‐Mueller, Stefan Bräse, Frank Breitling
Peptide arrays, which bear different peptides arranged in separate spots, permit high‐throughput screening to investigate linear and cyclic binding sites. In this paper, a trifunctional linker is developed. Due to the spatial proximity, the peptides interact and can form an assembled peptide structure. As a proof of concept, assembled peptide structures are demonstrated on beads and on a polymer surface and the approach can be validated via matrix‐assisted laser desorption/ionization spectrometry.
Preparation of Particulate Polymeric Therapeutics for Medical Applications
Jia Zhuang, Ronnie H. Fang, Liangfang Zhang 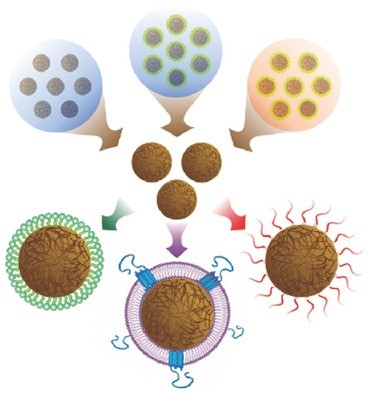
Particulate therapeutics fabricated from polymeric materials have become increasingly popular over the past several decades. Polymeric systems are easy to synthesize and have tunable parameters, giving them significant potential in clinic. In this review, the current preparation methods and representative applications are discussed. Lipid coatings and other surface‐modification techniques for introduction of additional functionalities are also mentioned. Insights on the development of these polymeric platforms are provided.
Bioimaging
Cutting‐Edge Nanomaterials for Advanced Multimodal Bioimaging Applications
Ming‐Kiu Tsang, Yuen‐Ting Wong, Jianhua Hao 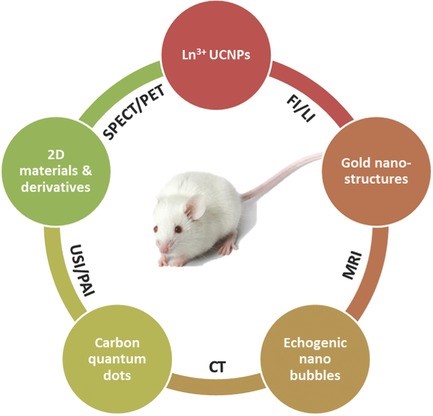
An overview and considerations for multimodal bioimaging regarding the nanomaterials are presented. The recently emerged nanomaterials and traditional nanomaterials for multimodal bioimaging are highlighted. Finally, some suggestions for toxicity studies of nanomaterials and new strategies are presented for realizing the advance of multimodal bioimaging.
Ultrasound-Mediated Diagnosis and Therapy based on Ultrasound Contrast Agents
Young Il Yoon, Wei Tang, Xiaoyuan Chen 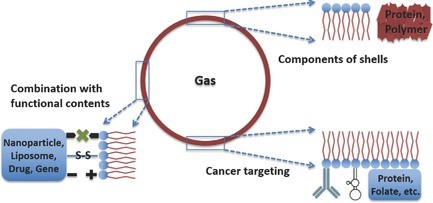
With the development of ultrasound‐imaging devices, the recent advent of ultrasound contrast agents (UCAs) has expanded the sphere of ultrasound’s influence to therapy. UCAs, which are generally gas‐filled and microsized bubbles, have been grafted onto multifunctional particles or molecules to selectively detect various diseases and effectively treat them. The focus here is an introduction to and the preparation of therapeutic and multimodal UCAs. High‐intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is described in depth. To close, the future and challenges of diagnosis and therapy with ultrasound are reviewed.
Jeong‐Eun Park, Minho Kim, Jae‐Ho Hwang, Jwa‐Min Nam 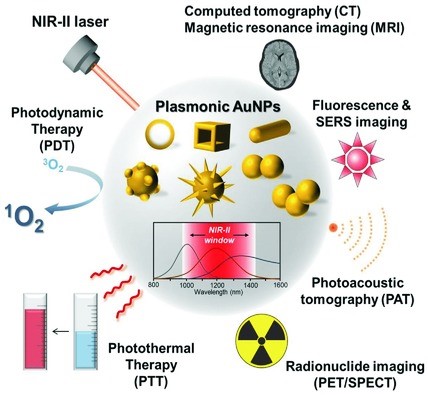
An overview of recently reported NIR-II-window-responsive plasmonic gold nanostructures is presented, and the opportunities, challenges, and future directions for these nanostructures in biomedical research fields are discussed.














