Excellent photocatalytic activity is realized after using an ion implanter to dope titanium oxide with carbon and nitrogen.


Excellent photocatalytic activity is realized after using an ion implanter to dope titanium oxide with carbon and nitrogen.
Protonic ceramic fuel cells operate in an intermediate temperature range (300–600 °C), avoiding the problems faced by other fuel cell types. Enhanced peak power densities have now been generated using a microstructured anode and a very thin electrolyte.

Developing strategies to enable solar-light driven splitting of water.

Sunlight is the ultimate renewable energy resource. This Excellence in Energy review describes the latest materials being explored for PEC water splitting systems, which turn sunlight into gaseous hydrogen and oxygen.
![A Protective Coating for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Electrodes [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/aenm201703647_ASN_image.jpg)
A coating is designed that significantly improves the performance of metal electrodes in high‐temperature, thin-film-based solid oxide fuel cells.
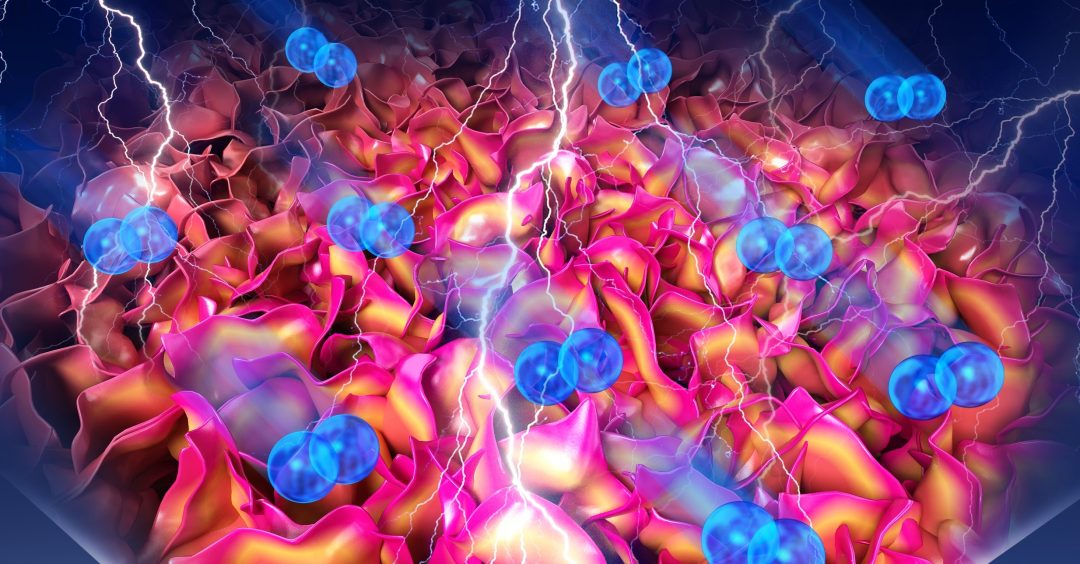
A new porous nanotube structure is created from pure metallic molybdenum disulfide, which is useful for fundamental electrochemical studies as well as showing good performance as a lithium-ion battery anode.
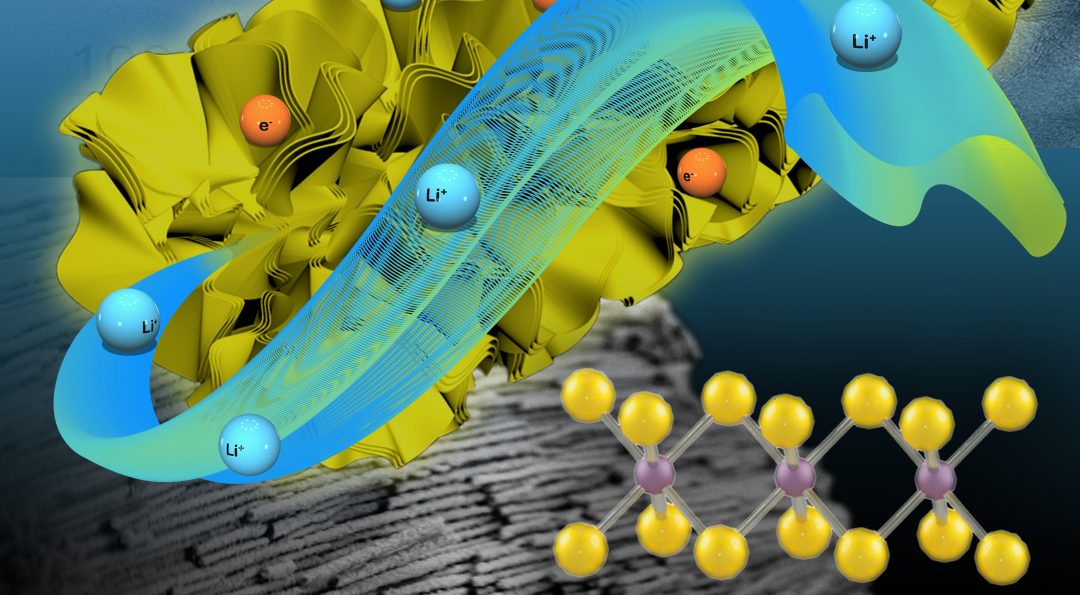
Arumugam Manthiram of the University of Texas at Austin was a Web of Science Highly Cited Researcher for 2017. Hear what he has to say about the problem of polysulfide shuttling in sulfur-based battery systems.
![3D Microflower Cathode Promotes Oxygen Diffusion in Lithium–Oxygen Batteries [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/aenm201800089_ASN_image.png)
Dr. Mingsen Zheng, Prof. Quanfeng Dong, and co-workers from Xiamen University design a plant-inspired, high-performance cobalt sulfide–porous carbon foil (PCF) electrode for lithium–air (Li–O2) batteries.
![Moisture-Resistant Perovskite Solar Cells Based on Low-Cost Dye [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/aenm201703007_ASN_image.jpg)
Dopant-free, moisture-resistant hole-transport materials (HTMs) for perovskite solar cells based on derivatives of the dye anthanthrone (ANT) are developed by Sagar M. Jain from Swansea University Bay Campus, Prashant Sonar from Queensland University of Technology, and co-workers.

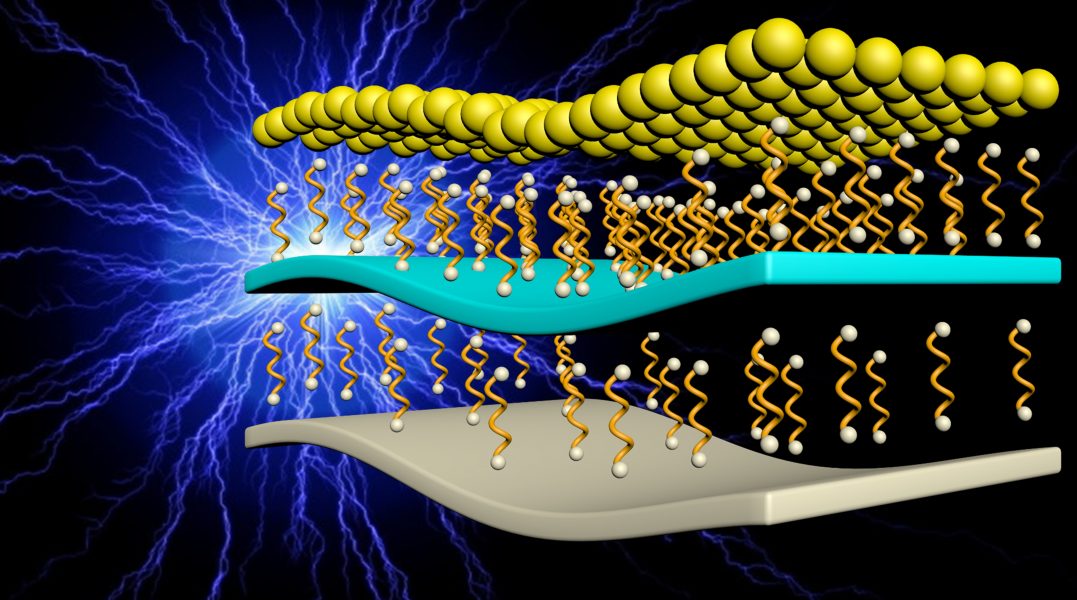
The addition of a liquid metal anode enables the design of a deformable battery with some unusual characteristics.