A microRNA-responsive drug release system will strengthen the selectiveness of the photodynamic therapy system.
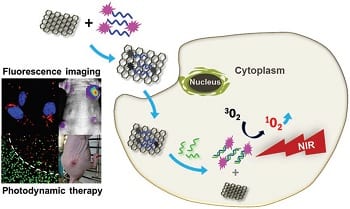

A microRNA-responsive drug release system will strengthen the selectiveness of the photodynamic therapy system.
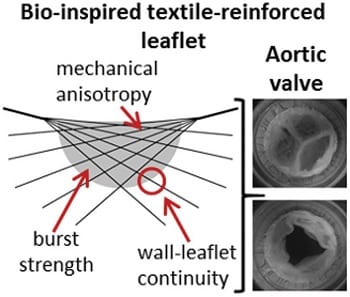
The BioTexValve demonstrates the potential of bio-inspired textile-reinforcement for the fabrication of functional tissue-engineered heart valves for the aortic position.
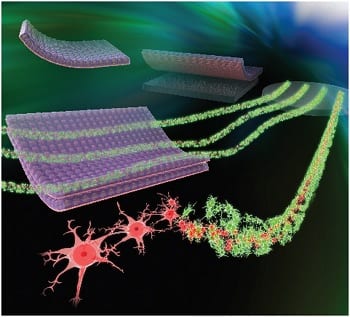
This new tissue engineering approach may be useful to establish a technology for regenerative medicine and drug discovery using the patient’s own neurons.
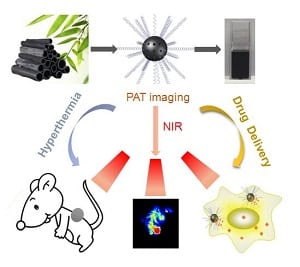
A promising multifunctional nanocarrier for opto-acoustic imaging-guided chemotherapy or phtotothermal therapy is presented.
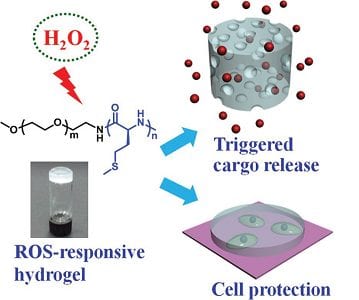
Researchers designed and synthesized a novel ROS-responsive thermogelling hydrogel based on methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(L-methionine) diblock copolymers.
A patient-derived stem cell source offers great potential for individual-tailored cell therapies and regenerative medicine.
Researchers have proposed a new idea to deliver anti-cancer drugs to tumor sites by combining immunotherapy and nanoparticles.
This nanocarrier shows excellent oxygen-carrying properties and ATP-responsive drug release, which makes it a potent agent for cancer therapy.
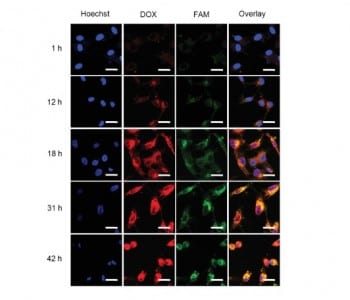
A tumor prodrug, which is able to monitor drug release and therapeutic success in real time, is developed.
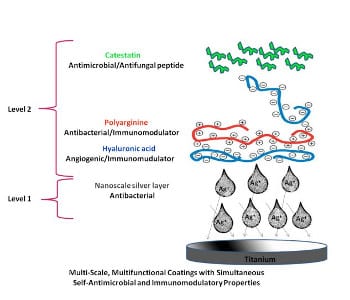
Rejection or diminished functionability of implants are frequent problems. A new type of coating could limit associated infections and inflammations.