Using Raman spectroscopy as a means of detection, researchers have built an extensive database of signatures to detect any cancer.


Using Raman spectroscopy as a means of detection, researchers have built an extensive database of signatures to detect any cancer.
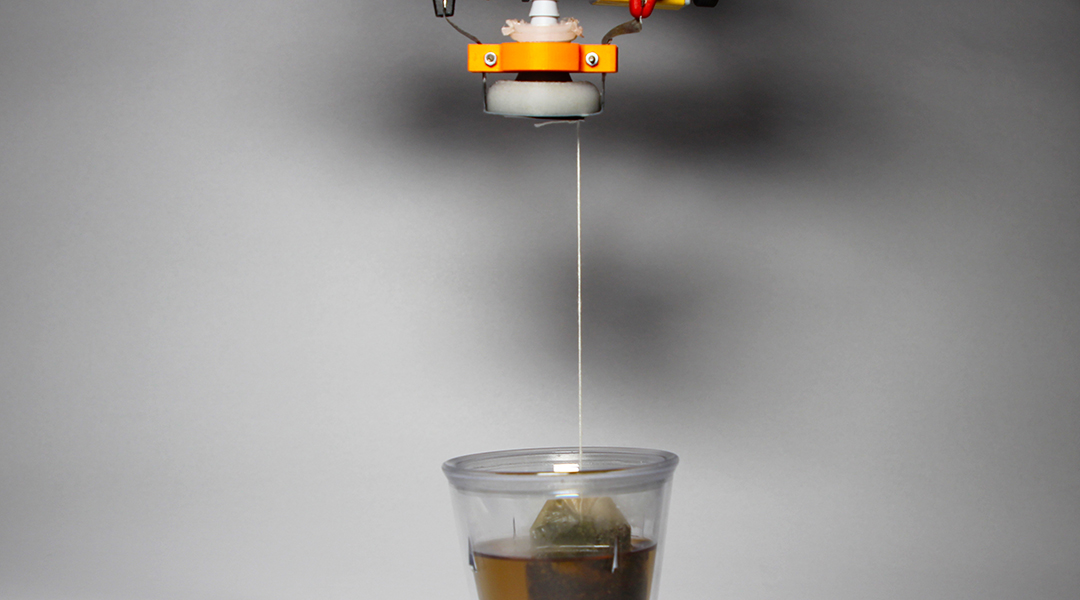

Resembling a balloon filled with coffee grounds, this gripper uses granular jamming and electrostatic interactions to manipulate objects.
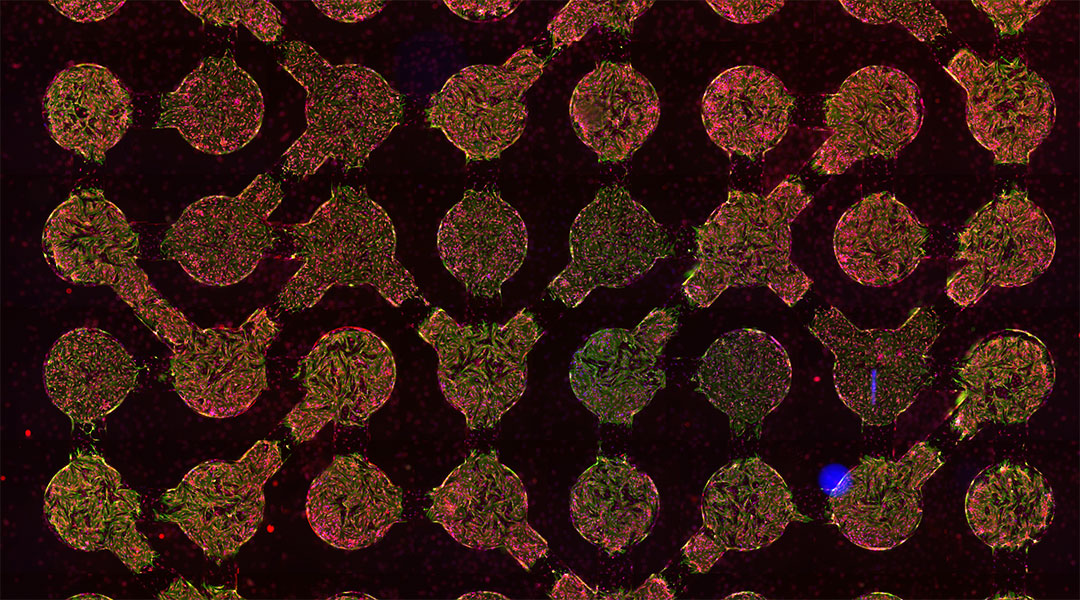
A biocomputer built from connected heart cells solves computational problems with high accuracy and at a low computational cost.
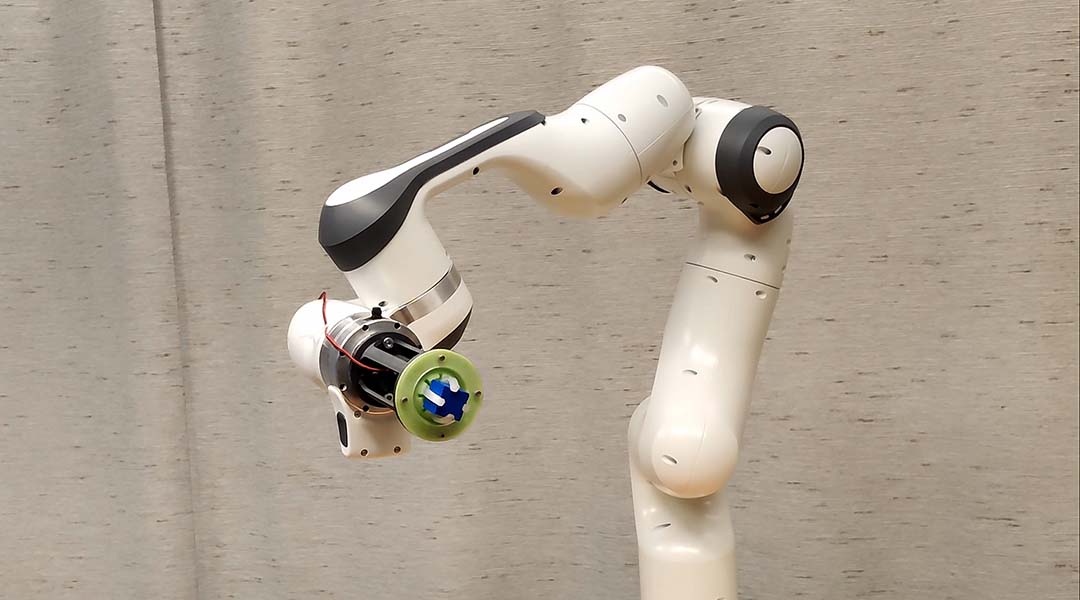

An innovative design allows for sensitive soft robots that can navigate difficult tasks and environments without bulky sensors.

Crediting ChatGPT as an author on scientific papers has sparked debate around the role it should play in the scientific literature.
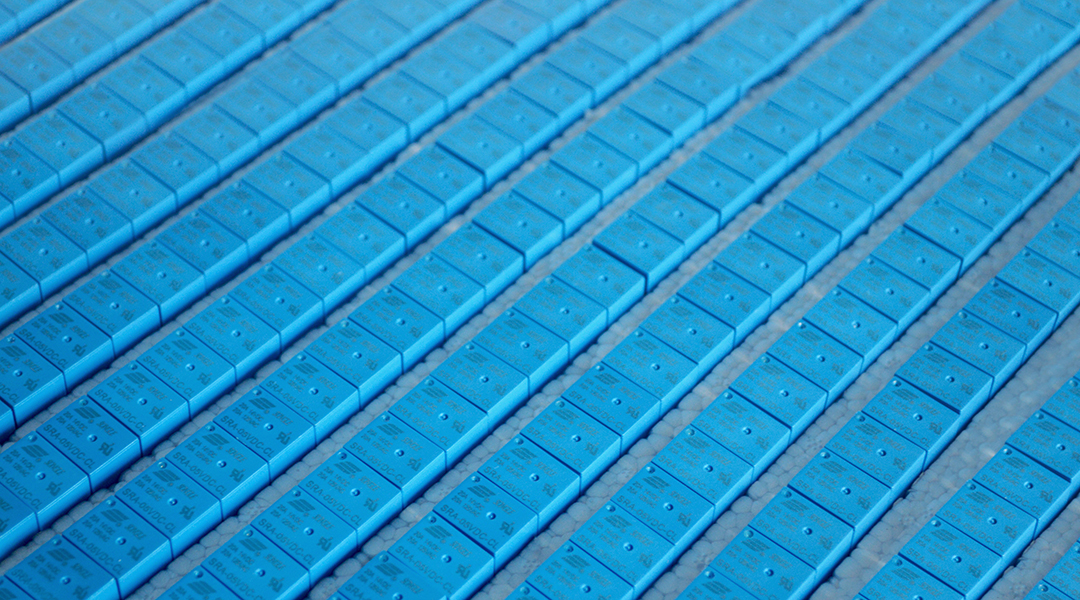

A device brings memory and processing together, helping minimizing errors and avoiding increasing energy demands due to huge amounts of data.
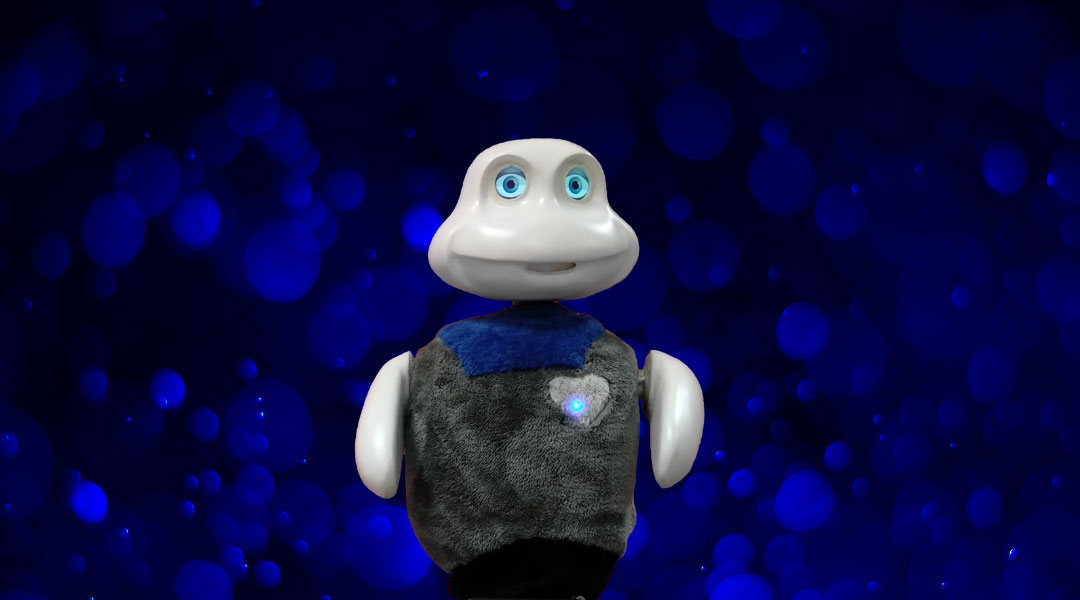

Modeling involuntary aspects of human behavior, such as blinking or even jet lag, might help build trust in robot-human interactions.
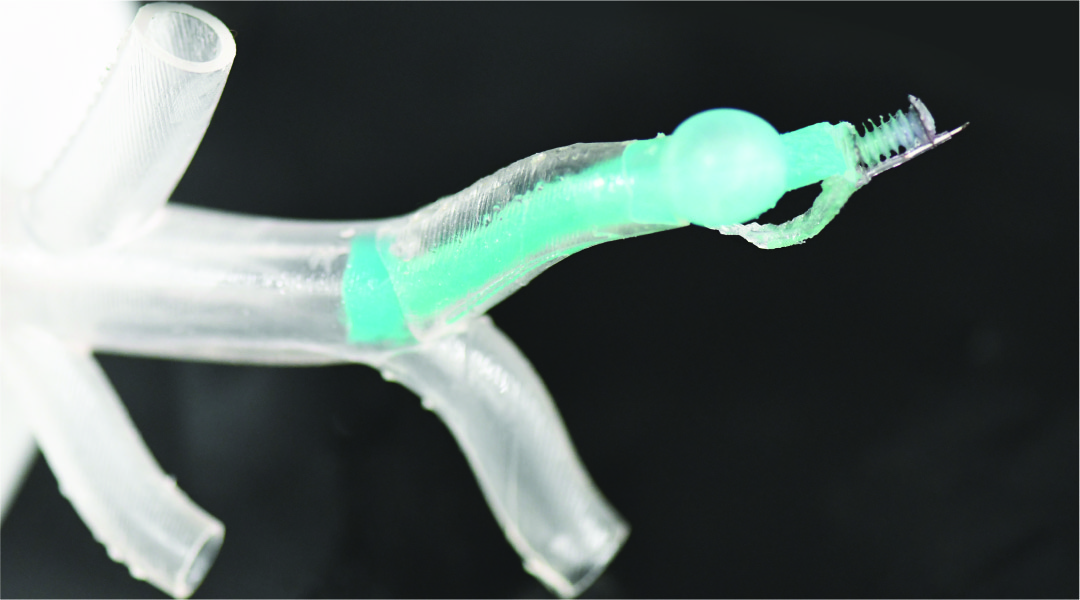
This tiny soft robot can be steered through the branches of the lungs without causing damage for safer diagnosis.
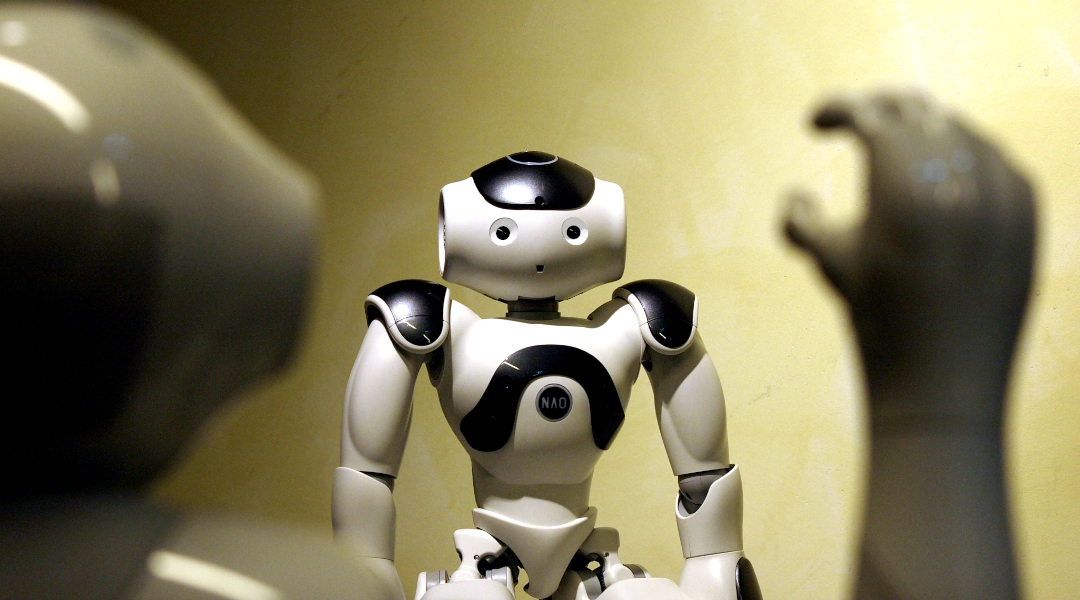

Event cameras mimic the human eye to allow robots to navigate their environment, and a new approach helps minimize computational costs.
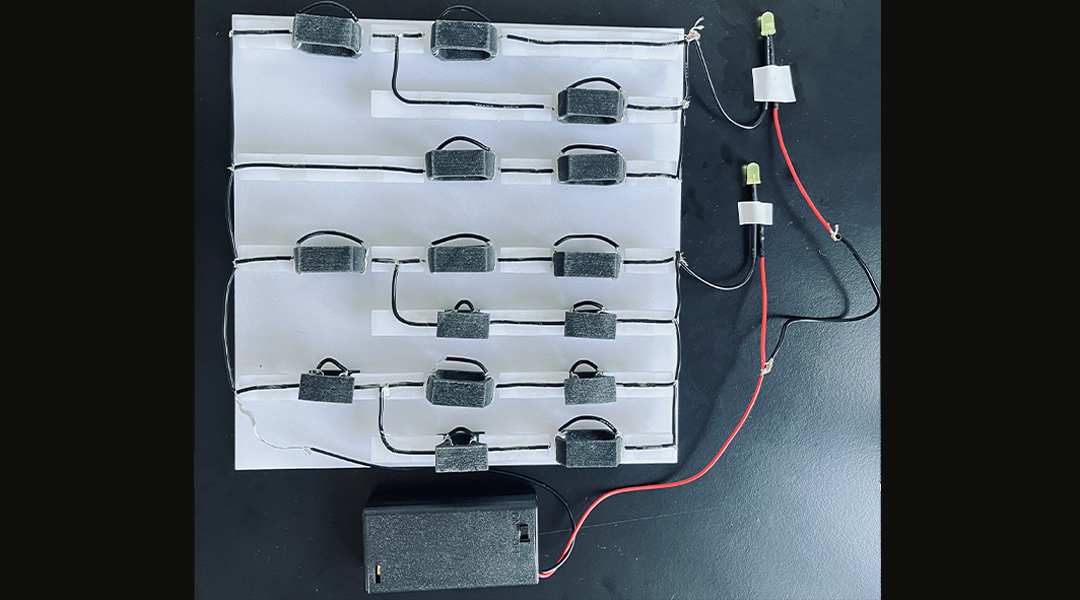
Putting a modern spin on old tech, scientists create a mechanical computer from metamaterials for situations where electronic computers break down.