A fabric-based haptic sleeve controls drone flight through arm movement and helps train users by applying corrective forces to body joints.
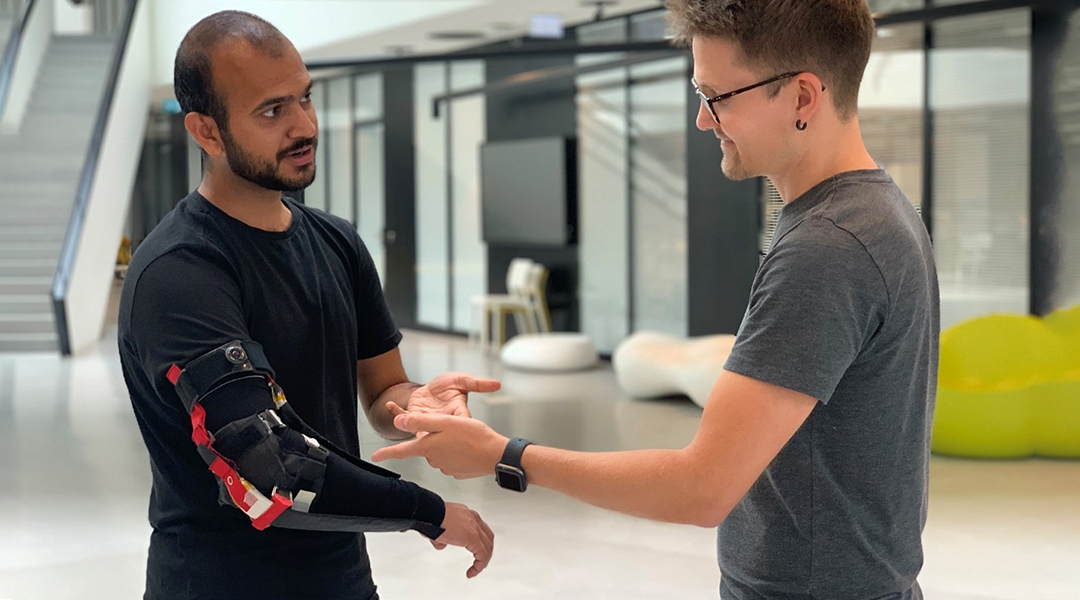


A fabric-based haptic sleeve controls drone flight through arm movement and helps train users by applying corrective forces to body joints.
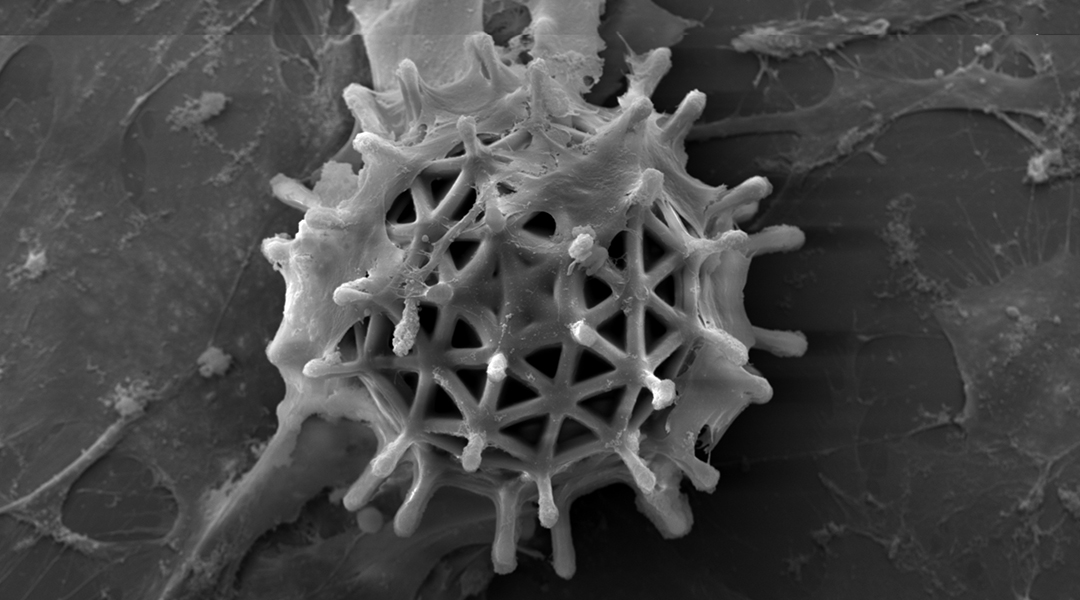
Researchers find the sweet spot between strength and biocompatibility in these tiny cell-carrying microrobots.

A new true random number generator offers better encryption by taking advantage of a flaw in memristor memory devices.
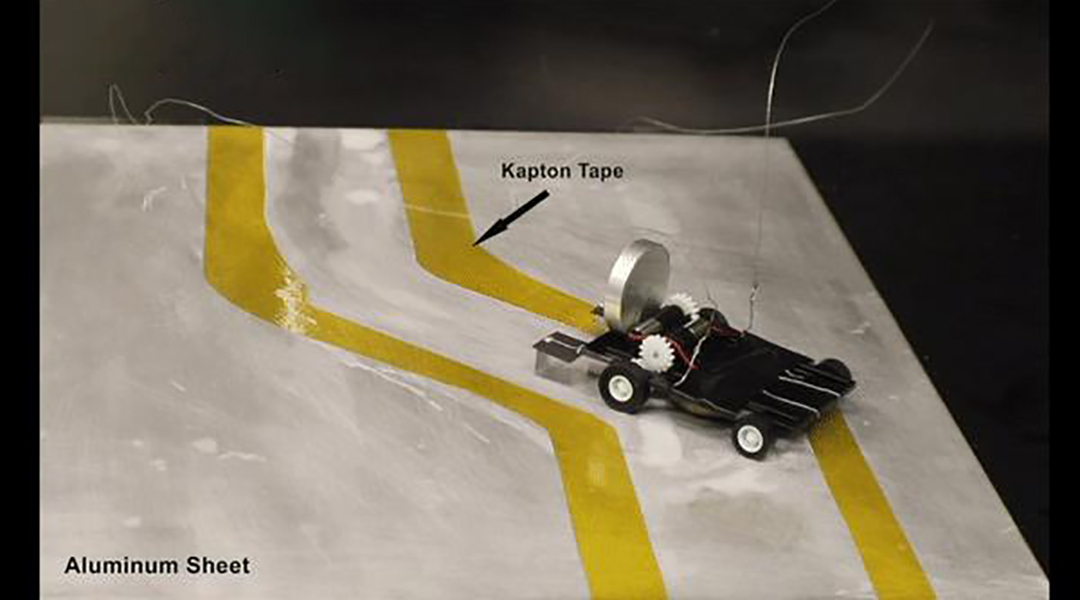
The “metal-eating” robot can follow a metal path without using a computer or needing a battery.
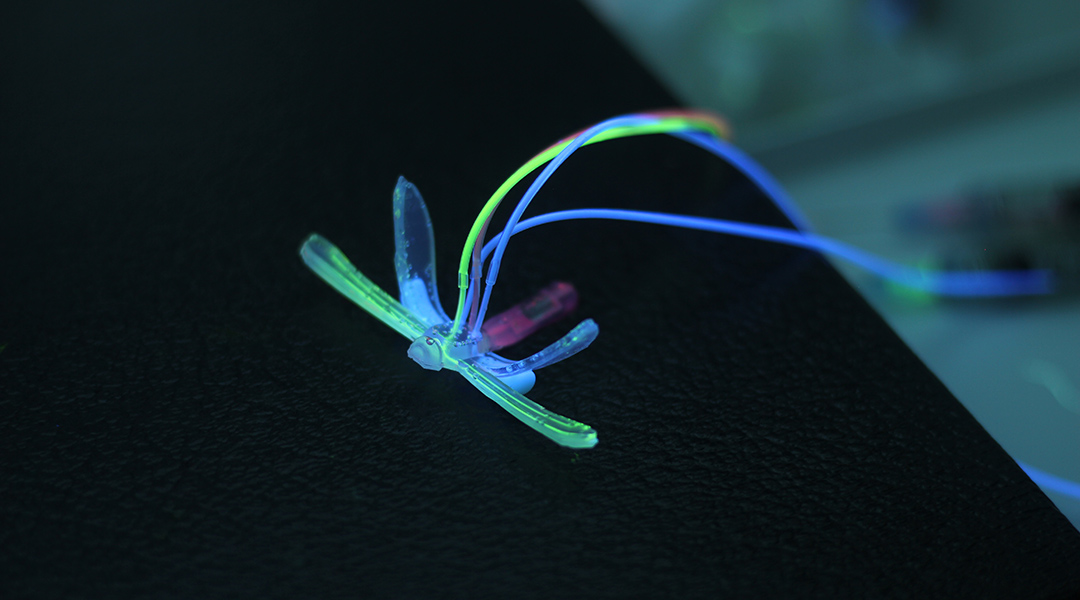
Electronics-free DraBot uses air pressure, microarchitectures, and self-healing hydrogels to watch for changes in pH, temperature, and the presence of contaminants.
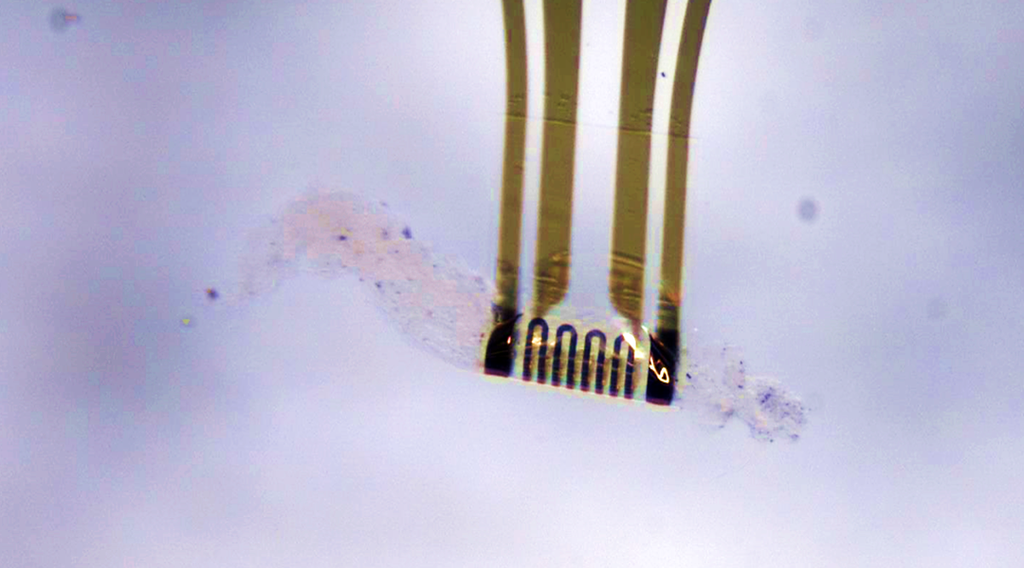
Thanks to ultra-thin sensors and artificial muscles, future flexible microelectronics will be able to take on complex shapes to better interface with delicate biological tissues without causing damage.

Building inclusive education systems will be key to ensuring no one is left behind and that advances in AI and robotics benefit everyone in society.
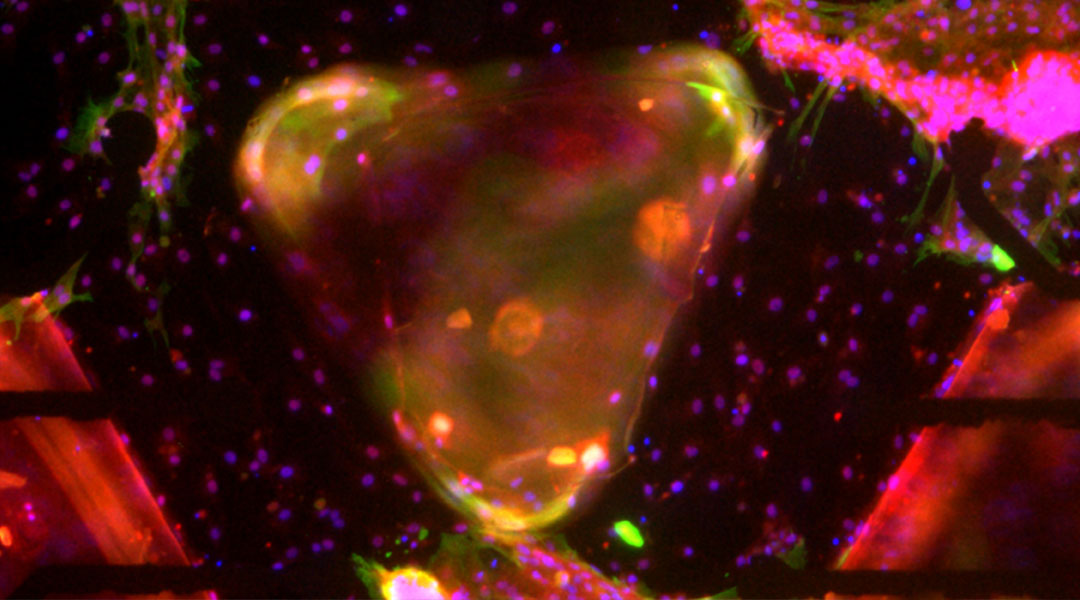
Researchers build the first biocomputers from heart cells and demonstrate their ability to perform complex computational tasks.
AI and robotics meet fluidics to accelerate materials development, allowing researchers to create quantum dots in under an hour.
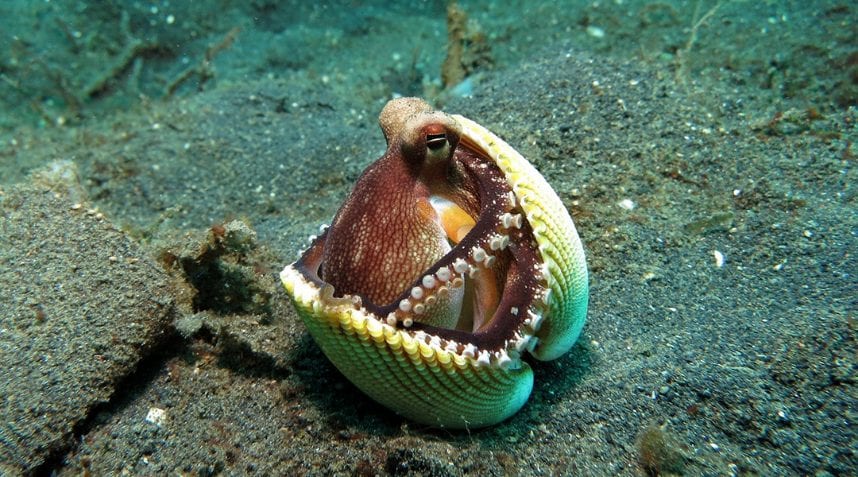

A gelatin-based hydrogel allows researchers to create a flexible, remote controlled robot capable of squeezing through tight spaces.