Precision micromanufacturing of electrospun microfibers can create 3D scaffold structures which support the growth of tessellated microtissues.


Precision micromanufacturing of electrospun microfibers can create 3D scaffold structures which support the growth of tessellated microtissues.
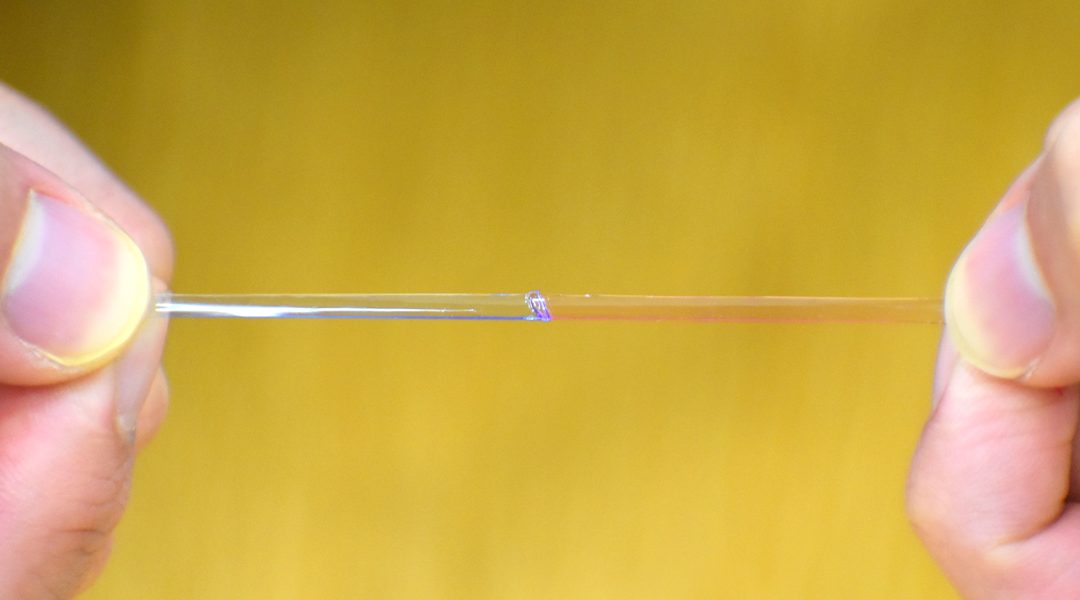
Robust electronic skin by utilizing supramolecular chemistry to produce a tough, self-healing elastic material.
![High-Performance n-Type Thin-Film Transistors [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/adma201707164_ASN_image.png)
Dr. Yang Wang, Prof. Tsuyoshi Michinobu, and colleagues from Tokyo Institute of Technology report a novel synthesis for high-molecular-weight n-type semiconducting copolymers with high electron mobilities in unipolar n-channel organic transistors.

The first seeds towards non-invasive edible electronics are sown.
![Highly-Ordered Hydrogels as Mimics for Natural Ligaments [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/adma201704937_ASN_image.png)
Researchers from Hokkaido University in Sapporo, Japan, report a method to fabricate hydrogels with hierarchical fibrous structures that mimic tendons and ligaments.
![Two-Phase Coexistence in Organometal Halide Perovskites Induces a Superlattice [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/adma.201705230_ASN_image.png)
The structure of organometal halide perovskites is elucidated, revealing a coexistence of crystal phases at room temperature that induces a self-organized superlattice.
![Chiral Cellulose Films for Polarization-Based Encryption [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/adma201705948_ASN_image.png)
Chiral photonic cellulose films are prepared, and their ability to reflect circularly polarized light (CPL) is explored. The films are promising for novel photonics applications, including polarization-based encryption.
![Enzyme-Like Hydrogel for Biosensing Applications [Video]](https://www.advancedsciencenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/adma201706887_ASN_image.png)
Professor Feng Zhang from Guangzhou Medical University, Professor Hao Pei from East China Normal University, and co-workers report a flexible electrochemical sensor based on a 3D-printable hydrogel. The device could be used as a glucose sensor, demonstrating its potential in biosensing applications.
A novel technology to display information on transparent screens offers new opportunities in next-generation electronics, such as augmented reality devices, smart surgical glasses, and smart windows.
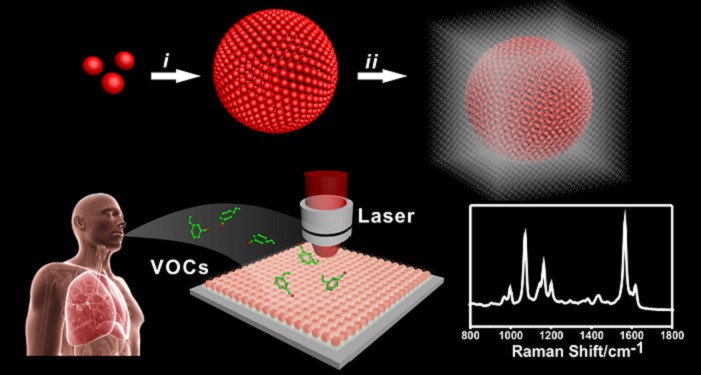
A biosensor based on SERS to detect lung cancer volatile organic compound (VOC) from exhaled breath.