A flash heating technique breaks down plastic waste and converts it to pure hydrogen and graphene with significantly less emissions and at a low cost.


A flash heating technique breaks down plastic waste and converts it to pure hydrogen and graphene with significantly less emissions and at a low cost.

A renewable, carbon-based absorbent is challenging MOFs in carbon capture technology, offering sustainable solutions for emissions reduction.
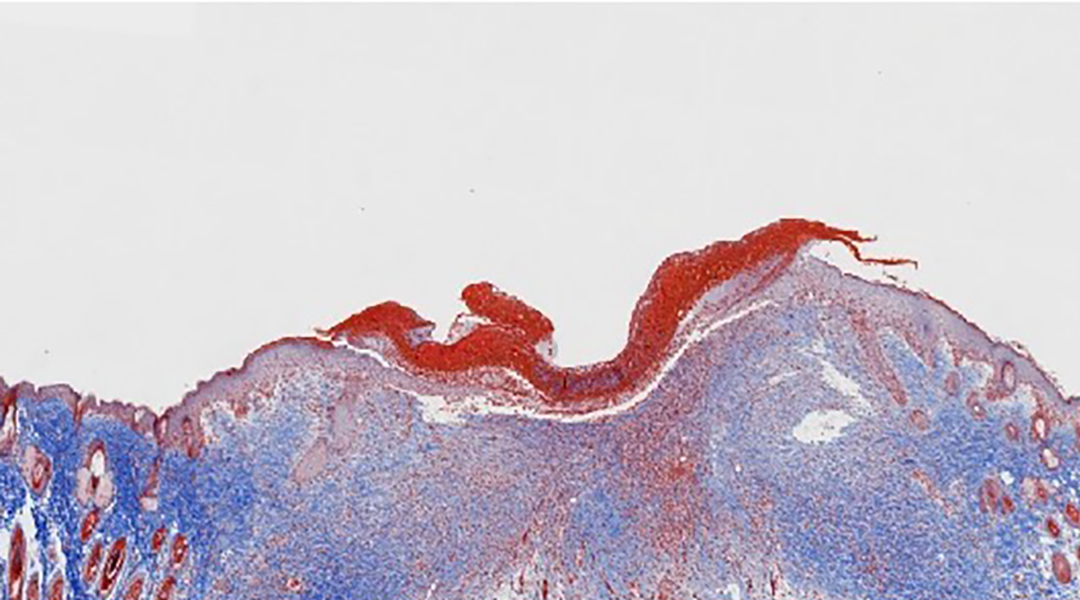
An engineered skin with a new secret ingredient helps avoid harmful inflammation while speeding up the wound healing process.
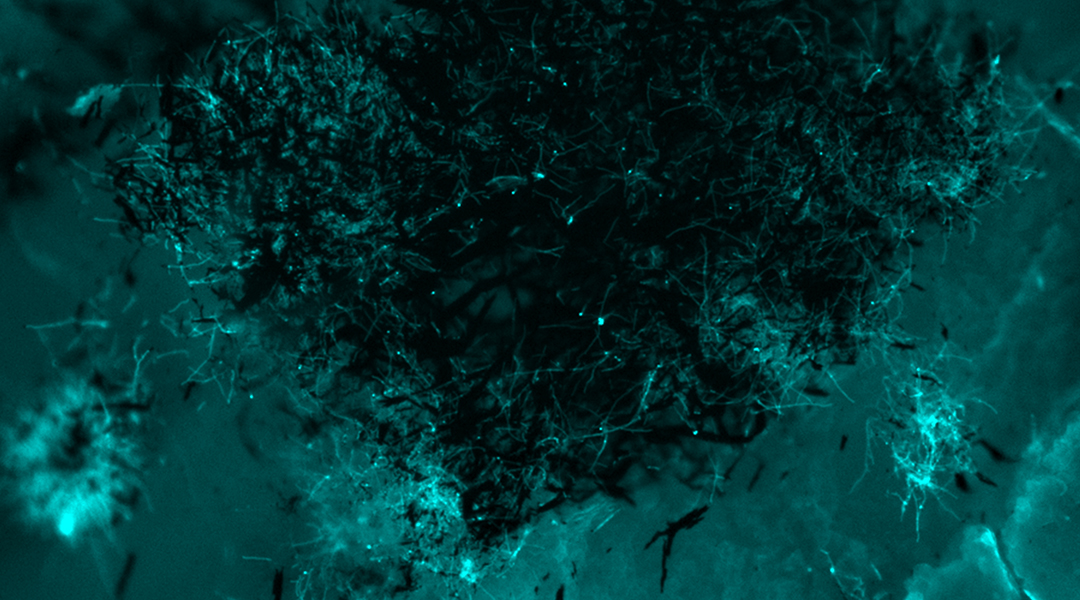
To curb the rising threat of fungal infections, researchers crafted iron oxide nanoparticles as speedy, effective, and inexpensive antifungal agents.

A tough gel electrolyte protects lithium metal anodes for safer and more efficient rechargeable batteries.

A device that generates electricity using moisture in the air could be the future of sustainable power generation.
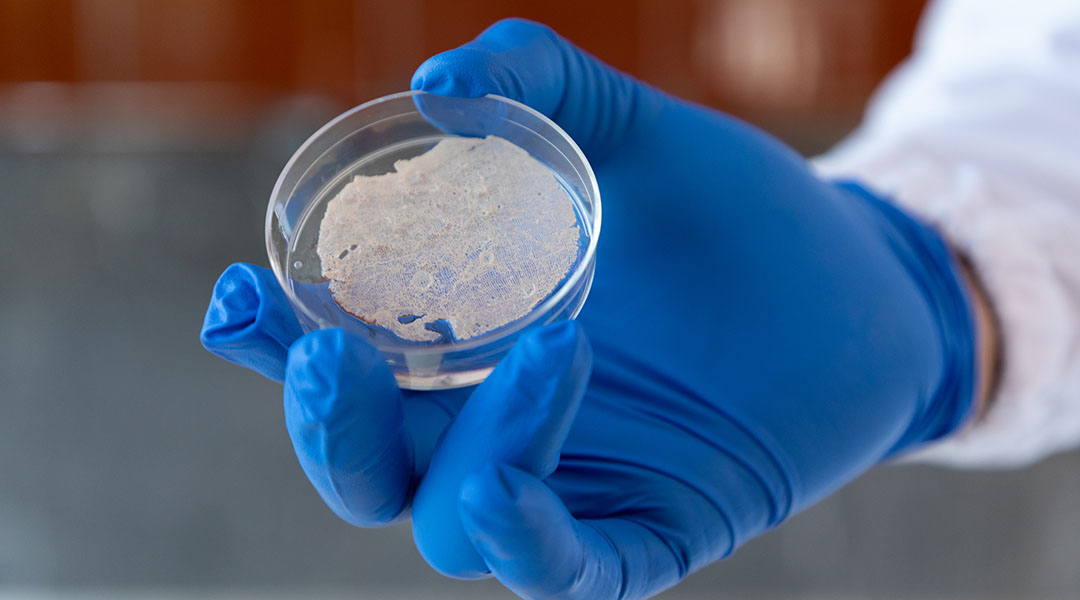

Using plant proteins derived from crop waste and spent grains adds new dimension to sustainable lab-grown meats.
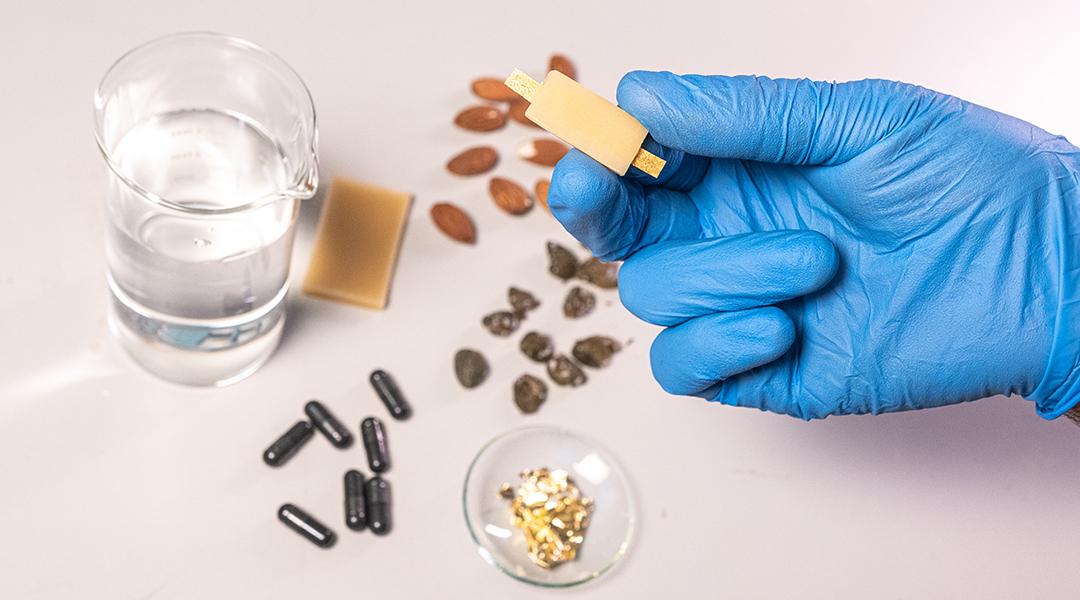

An edible and rechargeable battery to power devices used for GI tract monitoring, therapeutics, and analyzing food quality.
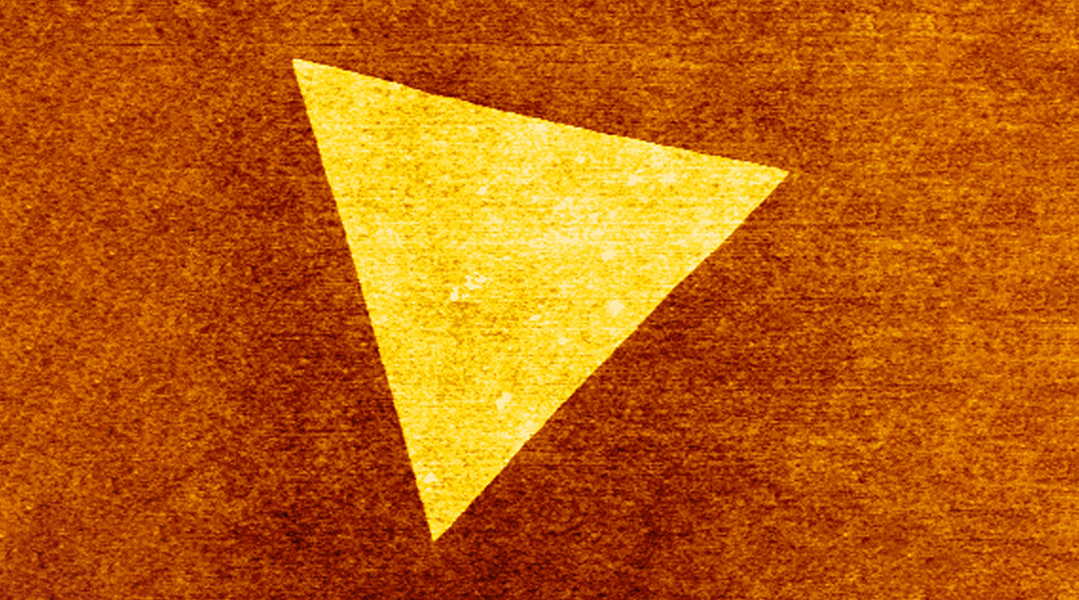

Using the adhesive properties of ice, researchers have developed a transfer method to move large sheets of 2D materials without breaking them.
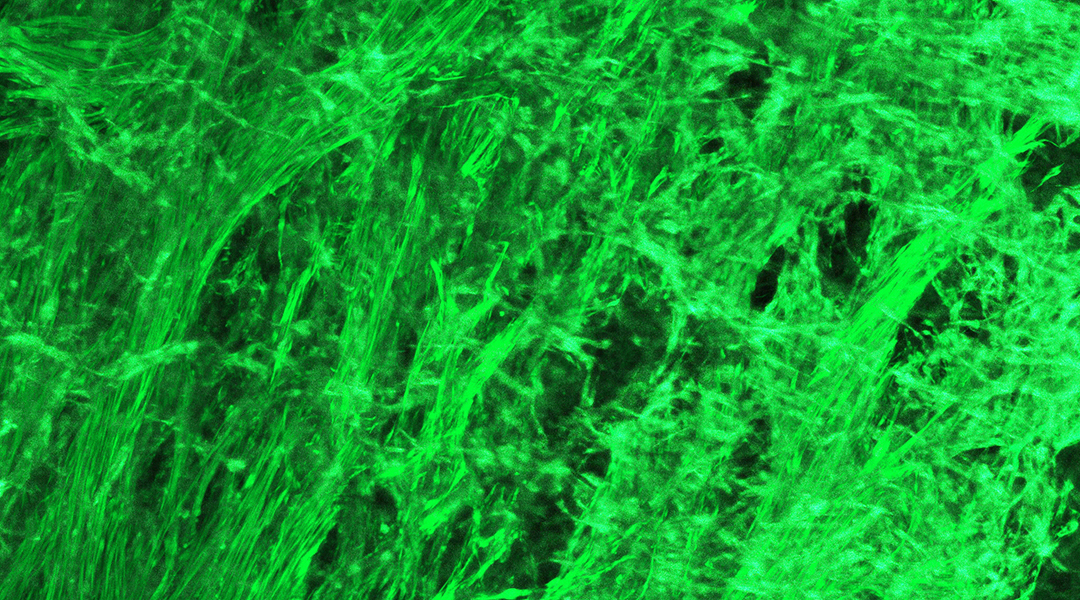
Engineered tissue mimics the contractions of the small intestine to break down artificial materials simulating partially digested food.