A new biomimetic strategy provides a platform for the synthesis of ligand-targeted nanovesicles that can mediate selective drug delivery to specific tissues.

A new biomimetic strategy provides a platform for the synthesis of ligand-targeted nanovesicles that can mediate selective drug delivery to specific tissues.
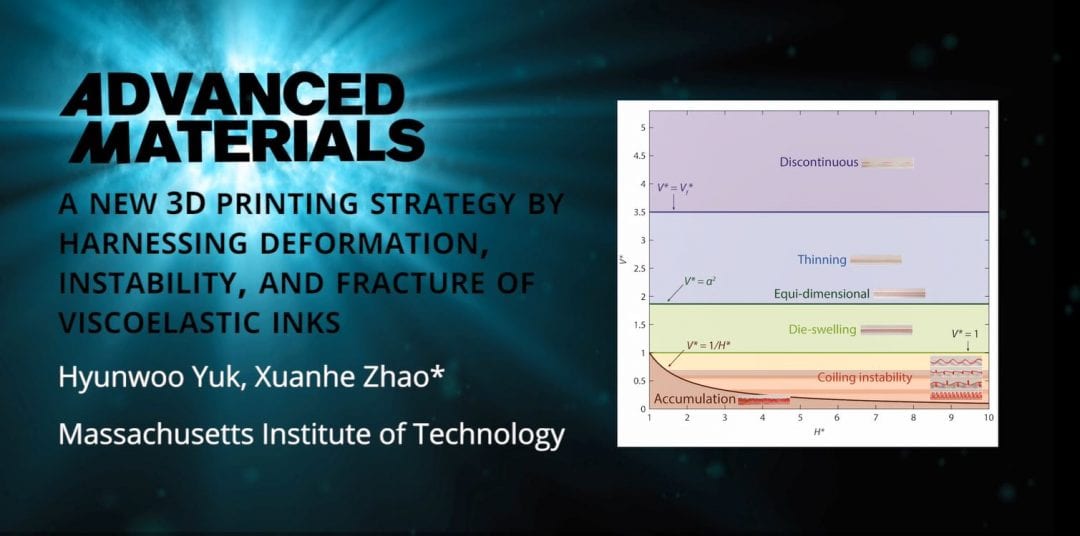
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) researchers introduce a new 3D printing strategy that overcomes the limitations of direct ink writing. Structures can be printed in six different modes, and can even be printed to have different kinetic properties.
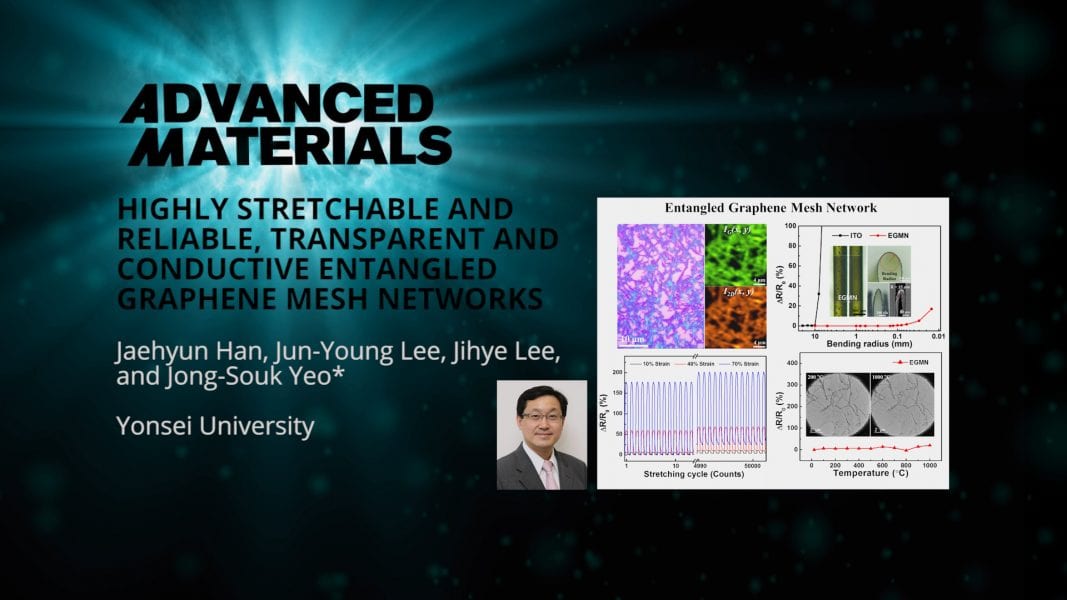
A highly stretchable, transparent, conductive entangled graphene mesh network (EGMN) is developed by a team researchers at Yonsei University, South Korea. The device is mechanically durable, and electrically and thermally stable, even in harsh environmental conditions.
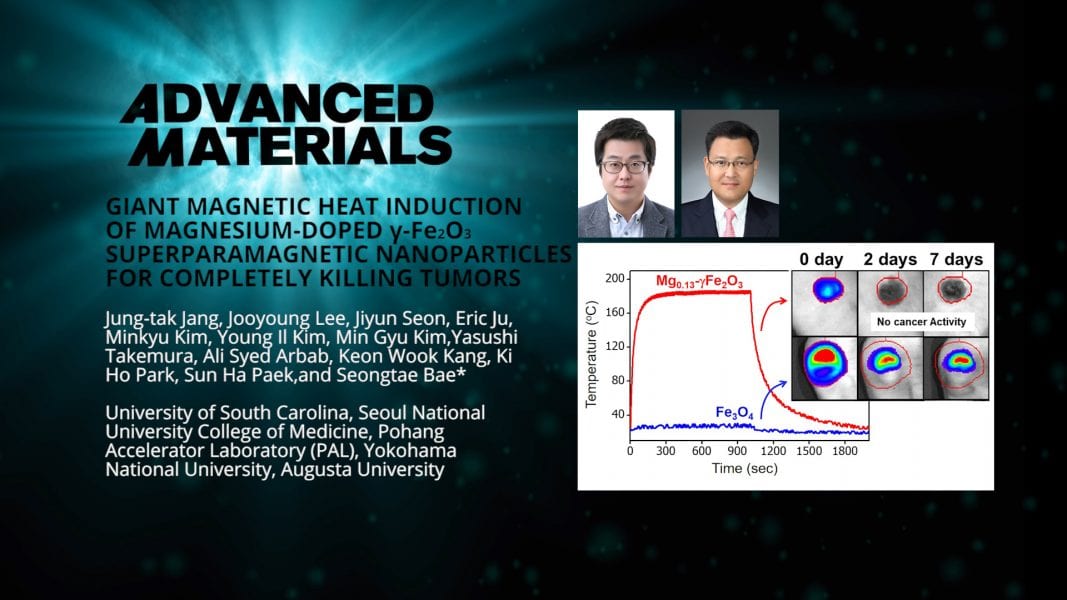
Researchers develop a new anticancer agent composed of magnesium shallow-doped iron oxide superparamagnetic nanoparticles (SPNPs). The magnetic fluid hyperthermia (MNFH) agent is highly biocompatible and is able to completely eradicate Hep3B-induced tumors.
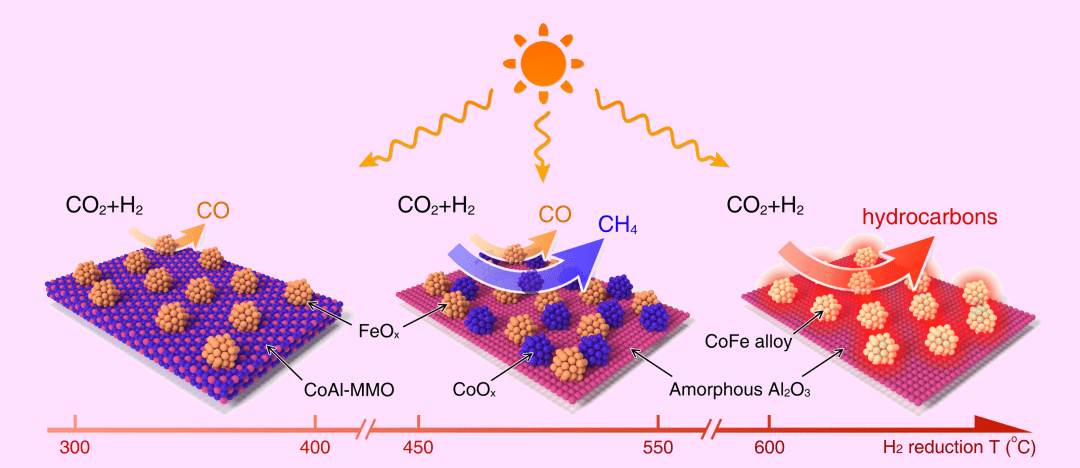
A vibrant new catalyst platform for harnessing abundant solar-energy to produce high-value hydrocarbons from a CO2 feedstock is demonstrated.

Researchers from MIT present a strategy to increase printing resolution beyond the nozzle size, while drawing diverse complex patterns with a linear nozzle path.
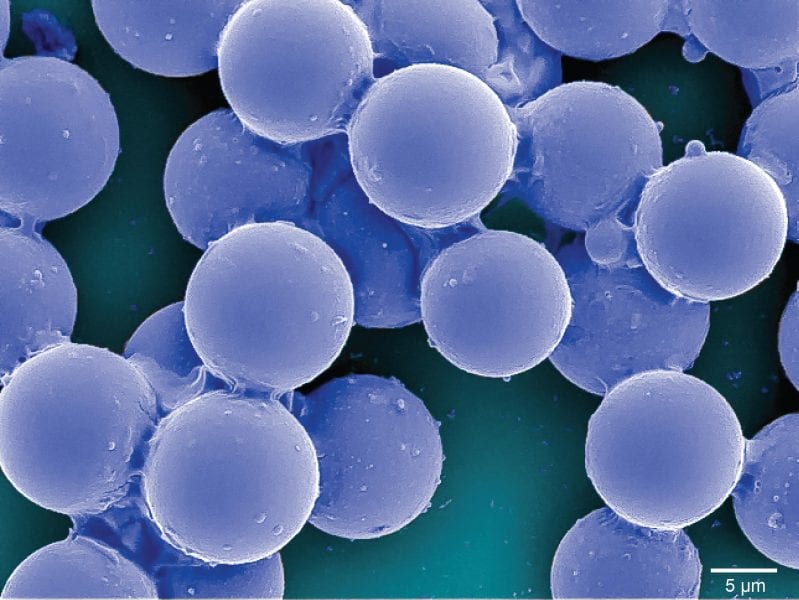
A simple and convenient method to fabricate thermoresponsive gel particles with tunable size across multiple size scales opens new directions in biomaterials, optics, and pharmaceutics.
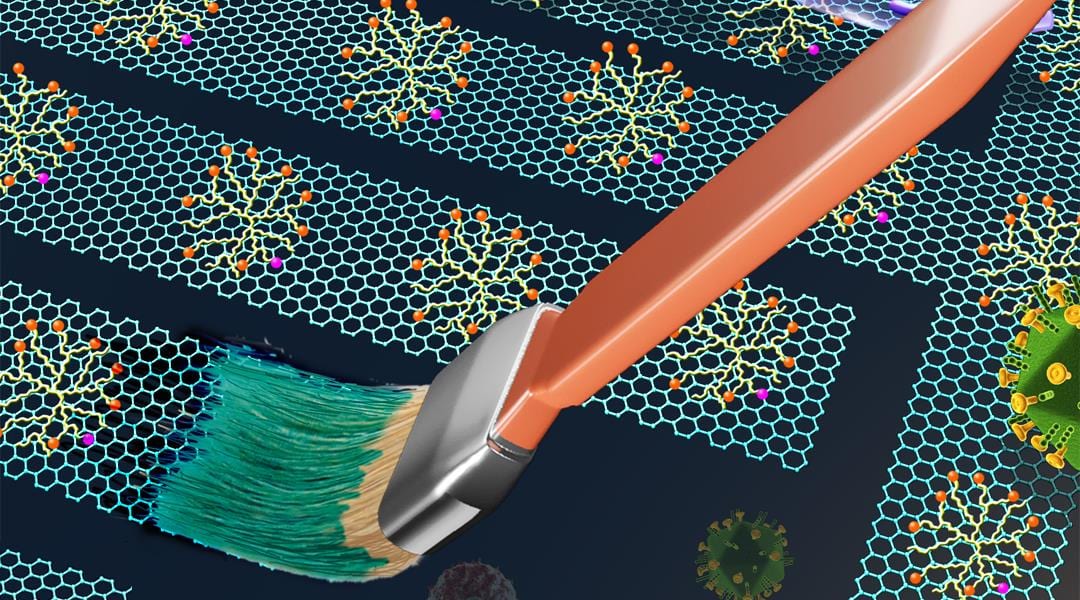
Flexible graphene nano-inks with an excellent bioactivity pave the way for next generation biomedical applications.

A team of researchers use in-situ transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to record the dynamic evolution of structural and electrical interfacial properties of zirconium dioxide films on aluminum oxide and indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) substrates. This investigation paves the way towards faster, more efficient high-speed electronic devices.

Chunmeng Shi and co-workers from the Third Military Medical University in Chongqing, China, introduce a small-molecule-based cancer theranostic agent for simultaneous cancer-cell mitochondrial targeting, NIR imaging, and chemo-/PDT/PTT/multimodal therapeutic activities.