An advanced 4D bioprinting approach uses shape-morphing, biopolymer hydrogels to form the basis for blood vessels and other tubular structures in artificial tissues and organs.
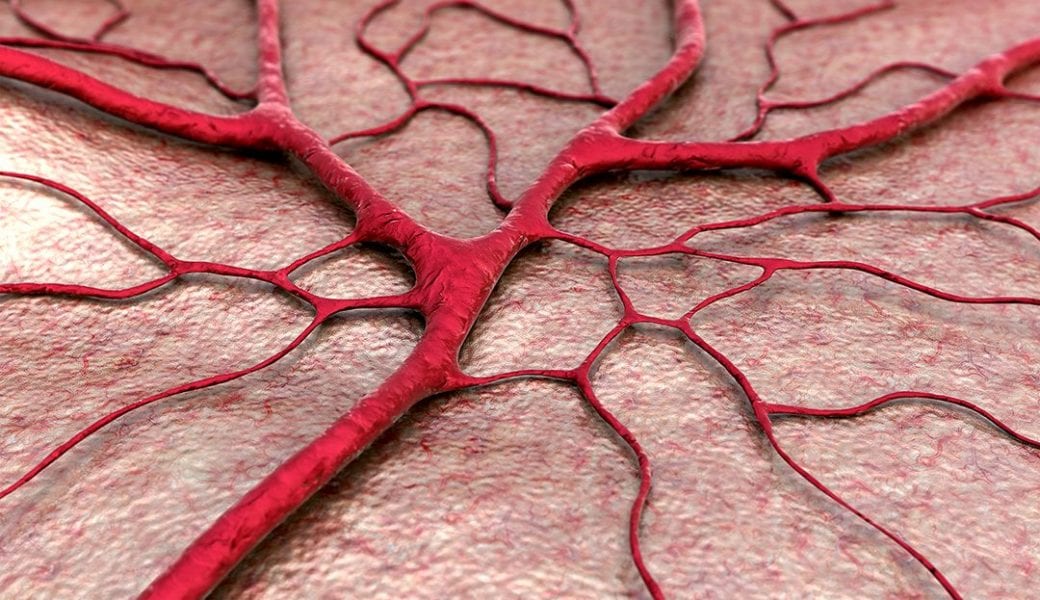

An advanced 4D bioprinting approach uses shape-morphing, biopolymer hydrogels to form the basis for blood vessels and other tubular structures in artificial tissues and organs.
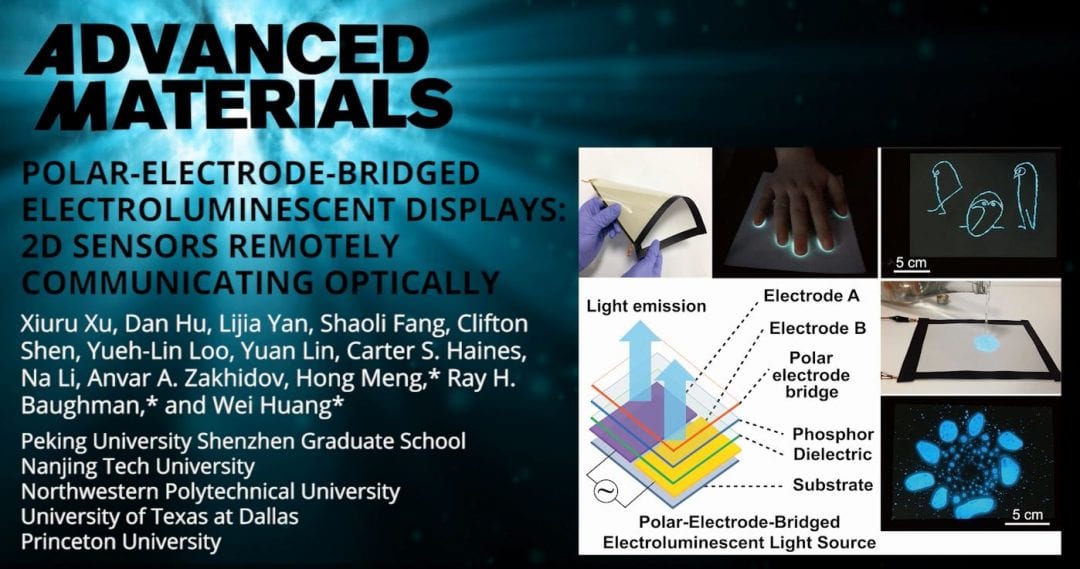
Researchers introduce a new device concept for electroluminescent displays, which does not require transparent electrodes and can be used as remotely readable, spatially-responsive sensors that emit light in response to the accumulation and distribution of materials on the device surface.
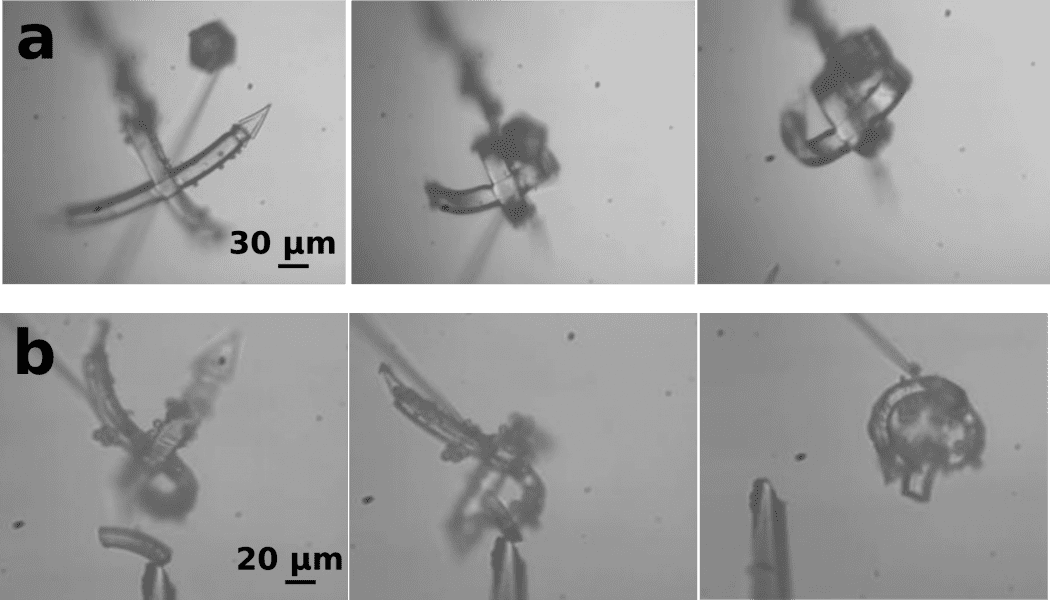

A microscopic light-fueled microhand designed to capture microscopic objects.
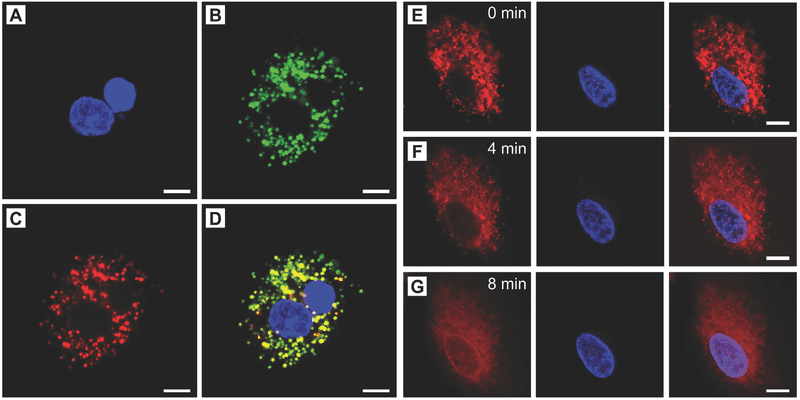
Natural fatty acid eutetic mixtures offer an inexpensive, chemically stable and biocompatible gating material alternative for NIR-triggered drug release nanoparticles for cancer therapy.
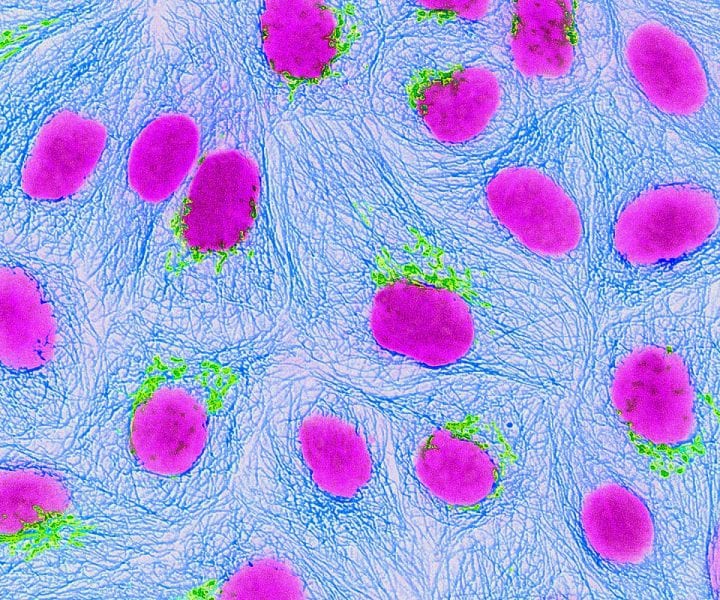
Magnetogenetics is a promising approach manipulating cellular functions in tissues and organisms with high spatial and temporal resolution.
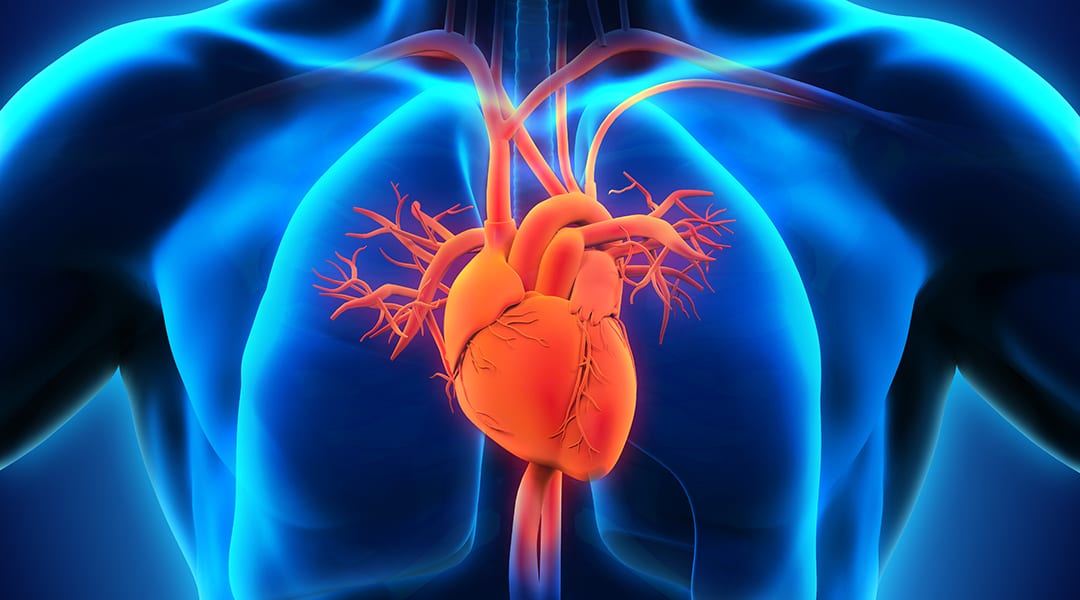
A flexible self-powered ultrasensitive pulse sensor (SUPS) based on a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) is presented.

University of Waterloo researchers develop a bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst based on graphene that can recharge zinc-air batteries more efficiently.

Highly efficient, red-emissive carbon quantum dots (R-CQDs) with a quantum yield of 53% are prepared and a CQD-phosphors-based warm white-light-emitting diode (WLED) is realized for the first time.
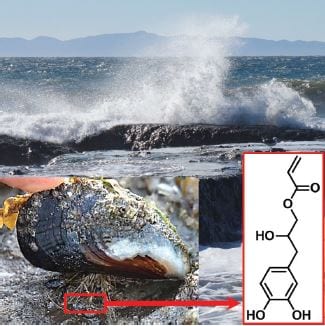
High hardness/rigidity compromises the extensibility and flexibility in state-of-the-art load-bearing polymer composites, including dental-resin composites. A look at an alternative.
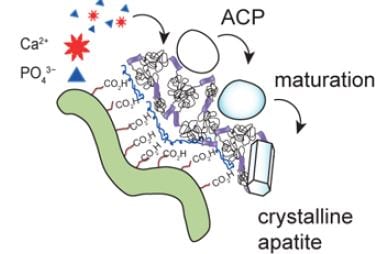
There is a growing body of evidence that a secondary structure of highly negatively charged proteins can play an important role in localizing calcium and phosphate ions to promote the formation of the HAp deposits.