Skin-friendly epidermal electronic devices fabricated using flexible, stretchable, and degradable protein-based substrates could offer a viable solution to real-time health and fitness monitoring.
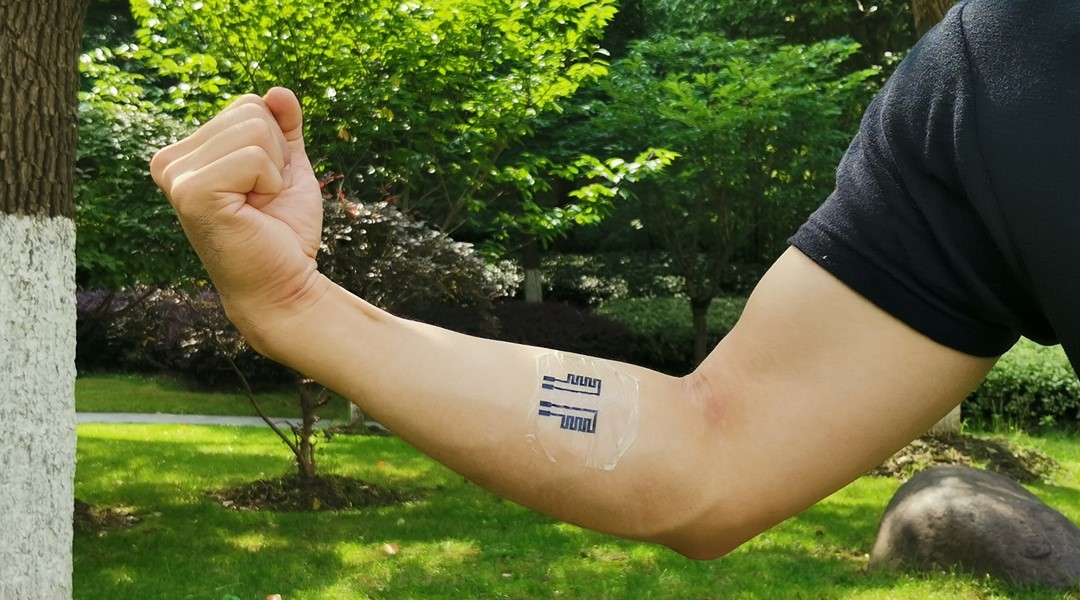

Skin-friendly epidermal electronic devices fabricated using flexible, stretchable, and degradable protein-based substrates could offer a viable solution to real-time health and fitness monitoring.
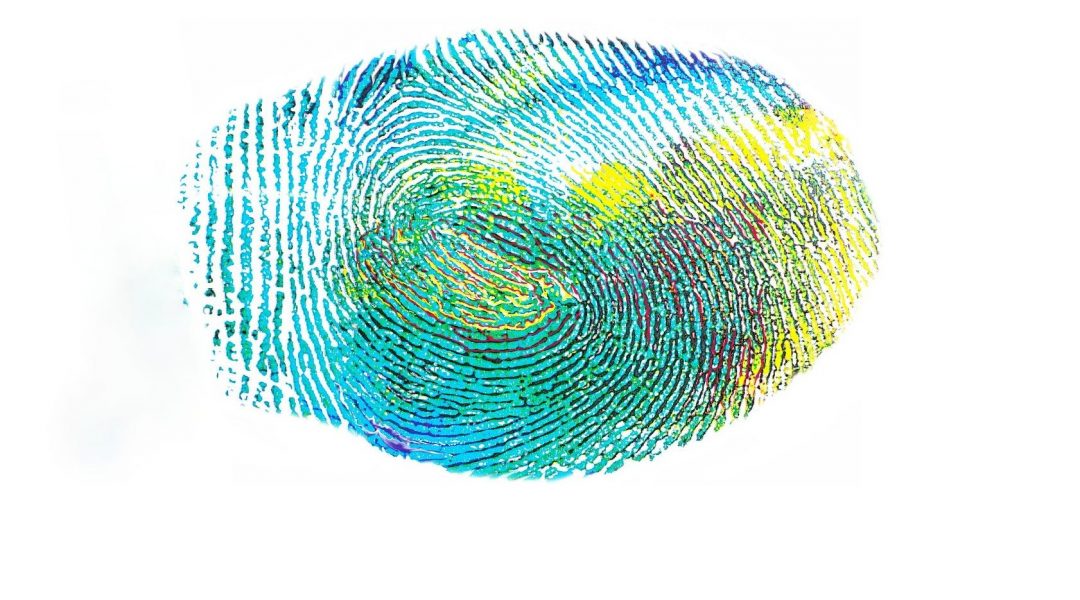

Researchers create a soft robotic electronic skin with fingerprint-like patterns with future applications in prosthesis, wearable sensors, and medical devices.

Rechargeable calcium batteries have the prospect of high-energy and low-cost.
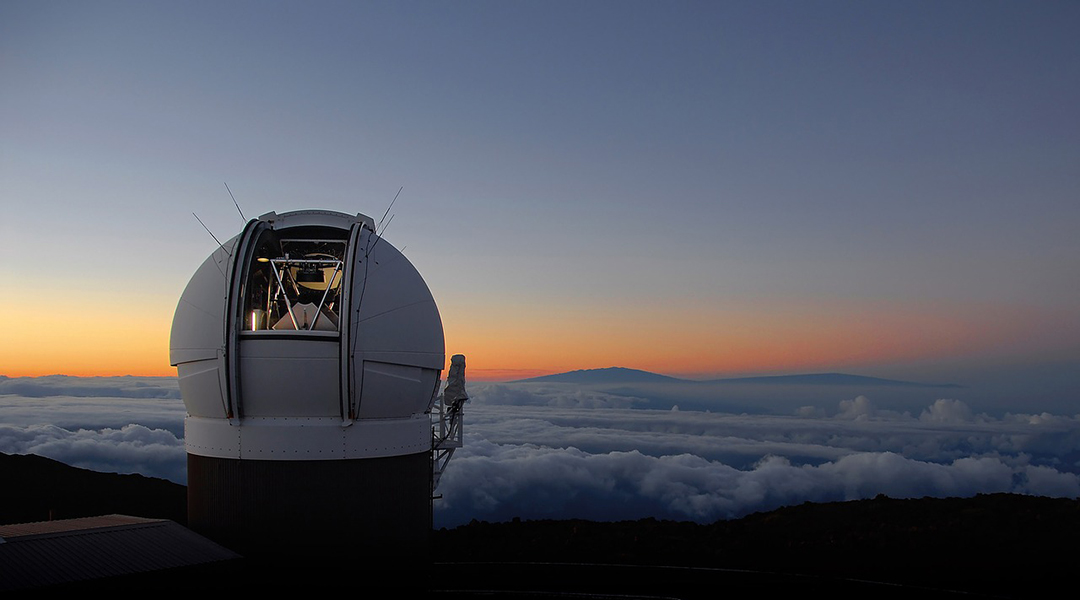

Astronomers report the results of a decade-long observational study of the gamma-ray loud binary, HESS J0632+057.
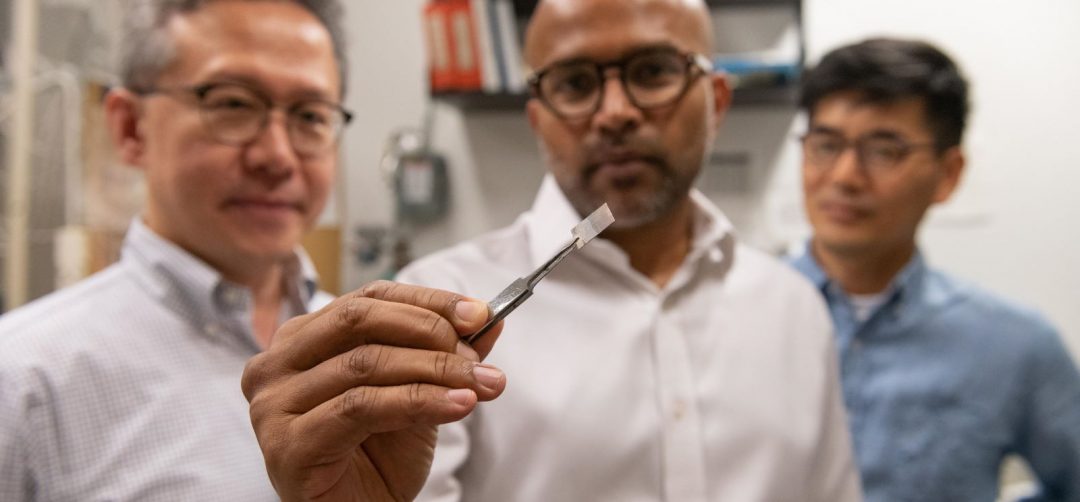
Atom-thick layers of platinum supported by graphene could provide cost-effective fuel cell catalysts with unprecedented catalytic activity and longevity.
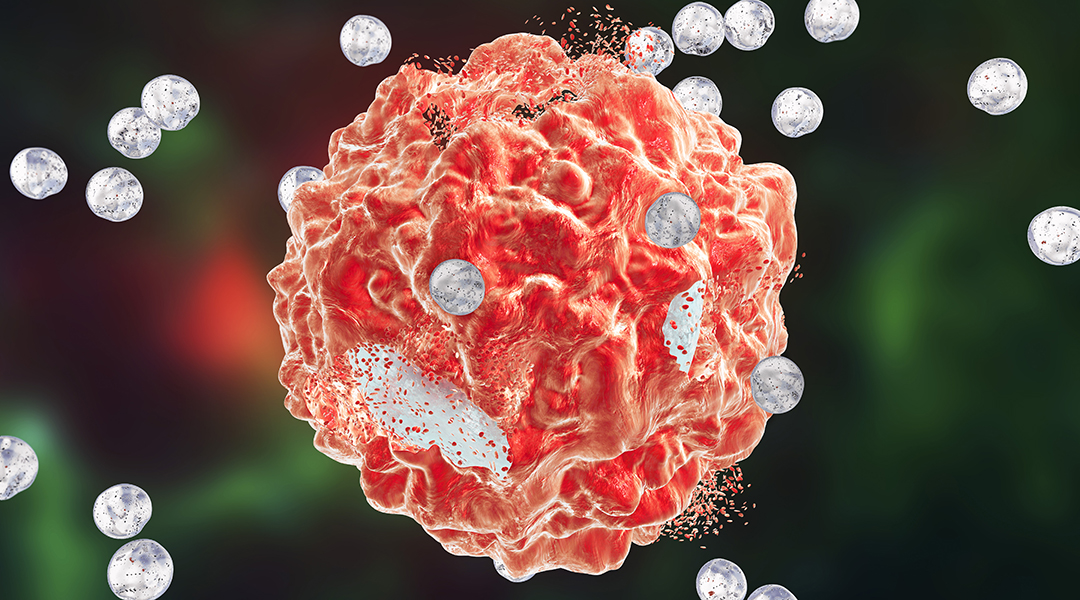
Nanotechnology has emerged as an innovative tool in medicine that could alter the landscape in relation to disease treatment and prevention.
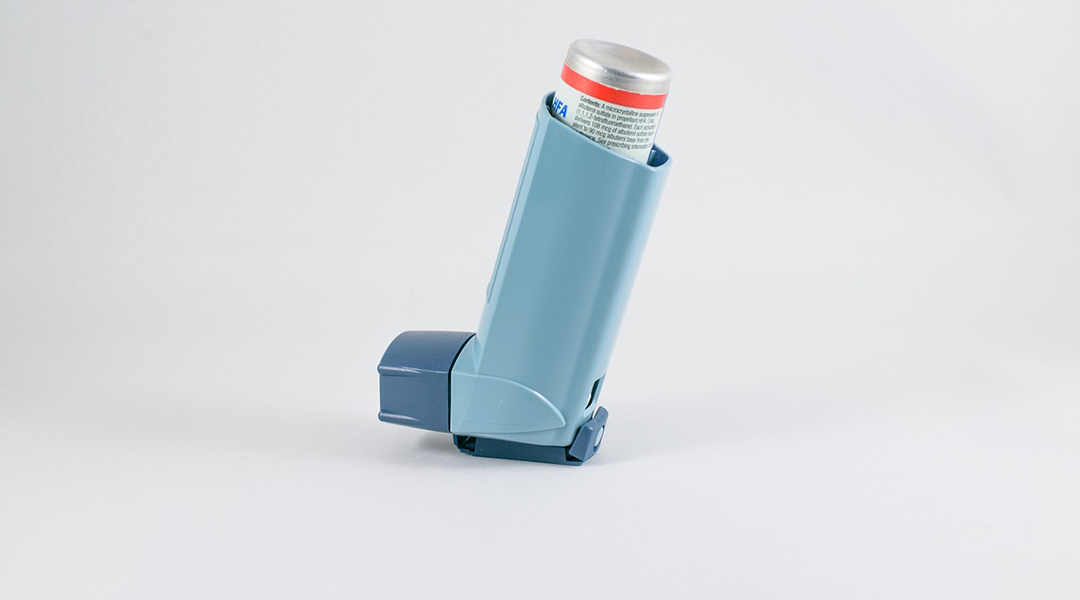

Many nanomaterials can be used to develop inhalable nanomedicines that can be administered with various aerosolization devices.

Appliction of an AC current results in a self-sustaining oscillating polymer surface.
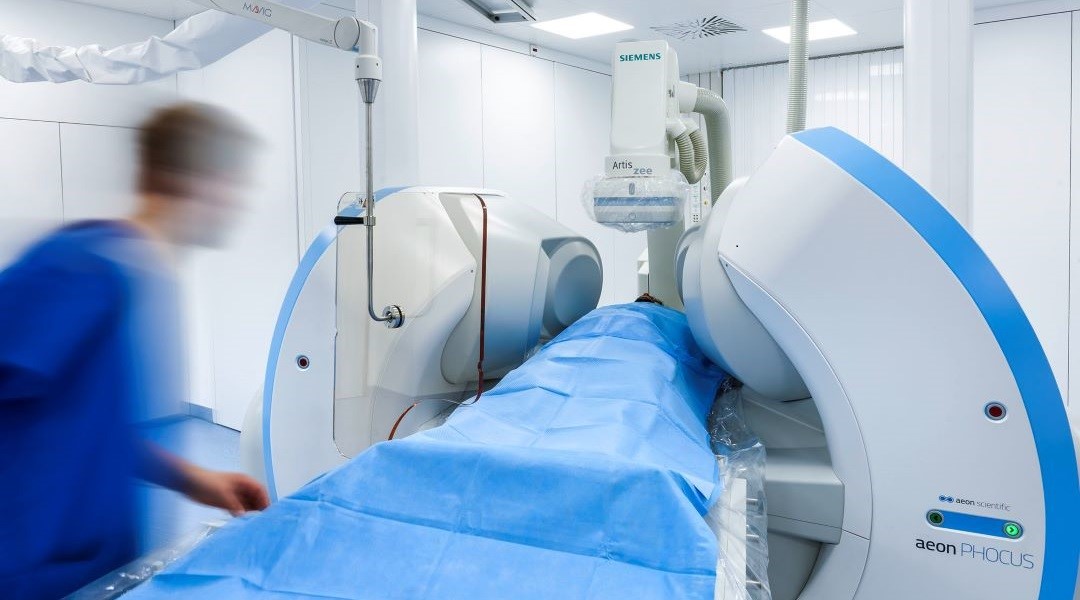
Enhancing the safety of minimally invasive surgical instruments through external magnetic control.

New plasma techniques are contributing to the rapid development of new micro-electromechanical systems.