Fitting hydrogels with aptamer-based ligands can open doors for a range of new biomedical applications.


Fitting hydrogels with aptamer-based ligands can open doors for a range of new biomedical applications.
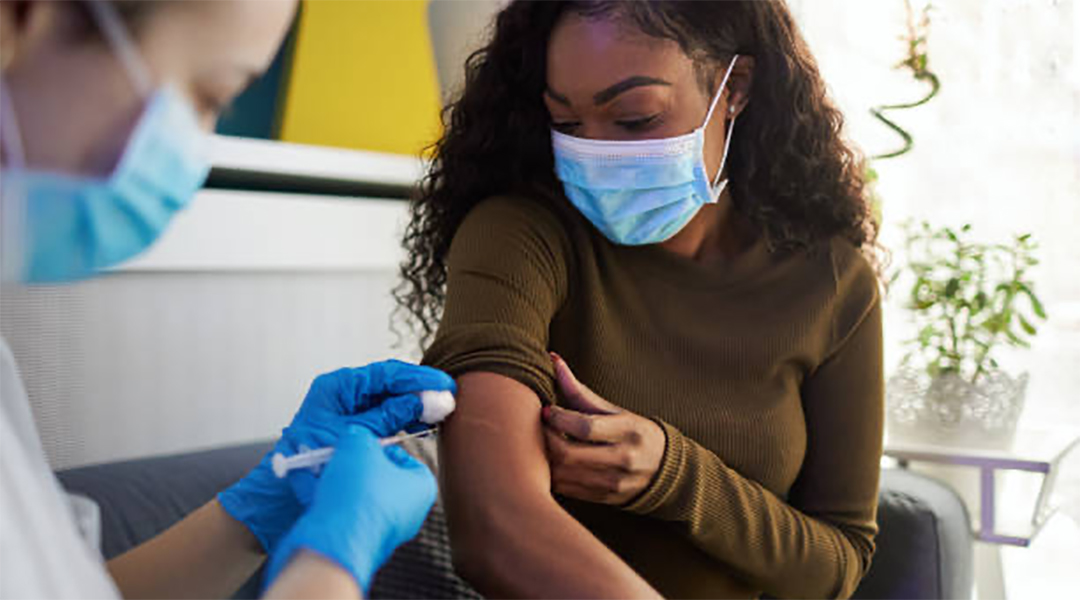
Integrating vaccines with biomaterials could help minimize the need for refrigeration and booster shots.
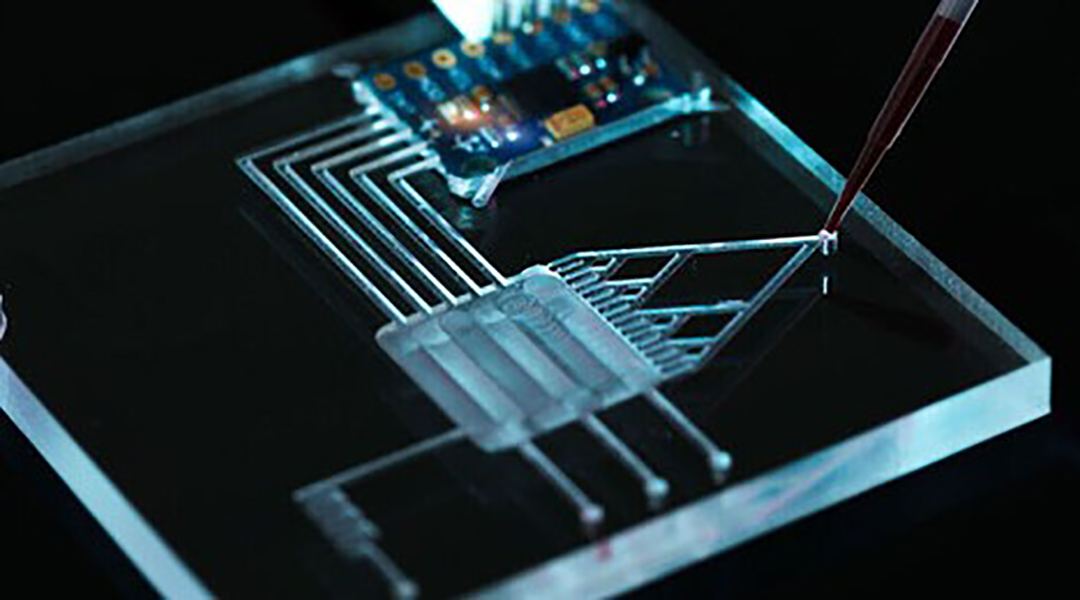
Recent advances in micro- and nanoscale sensing technologies may help diagnose sepsis early and with greater accuracy.
Graphene-based biosensors incorporated in arrays of microneedles are emerging as an alternative to hypodermic needles and could be the next generation of blood sampling devices.
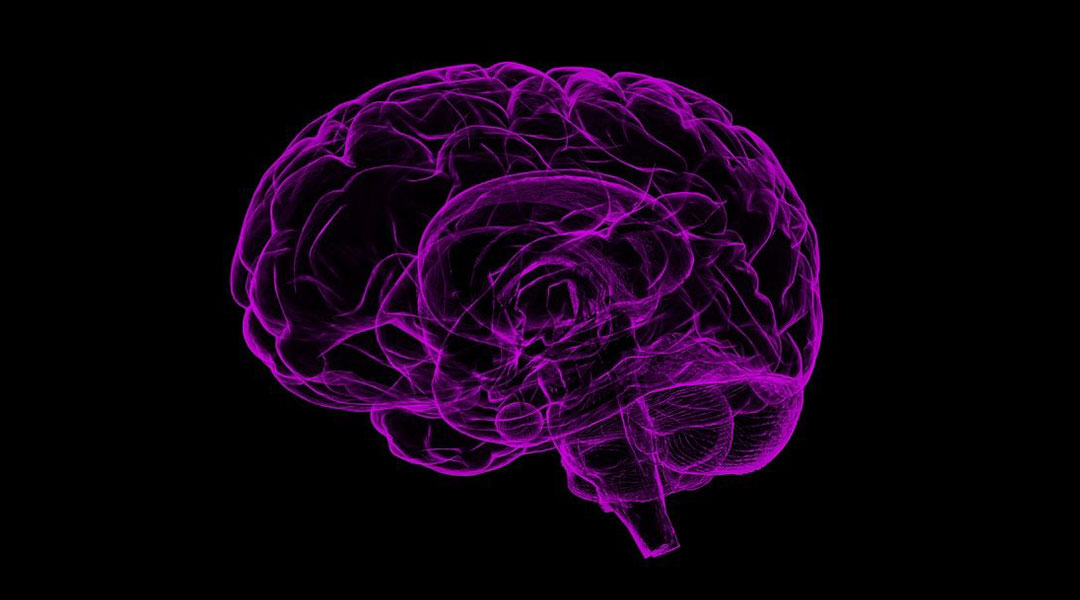
Personalized medicine for diseases that affect the central nervous system requires renewed focus on visualising the behaviour of drugs in the brain.

Hybridizing biofabrication processes will lead us to superior “living” tissue and organ substitutes that can be used to treat patients in lieu of donor grafts and metal and plastic devices.
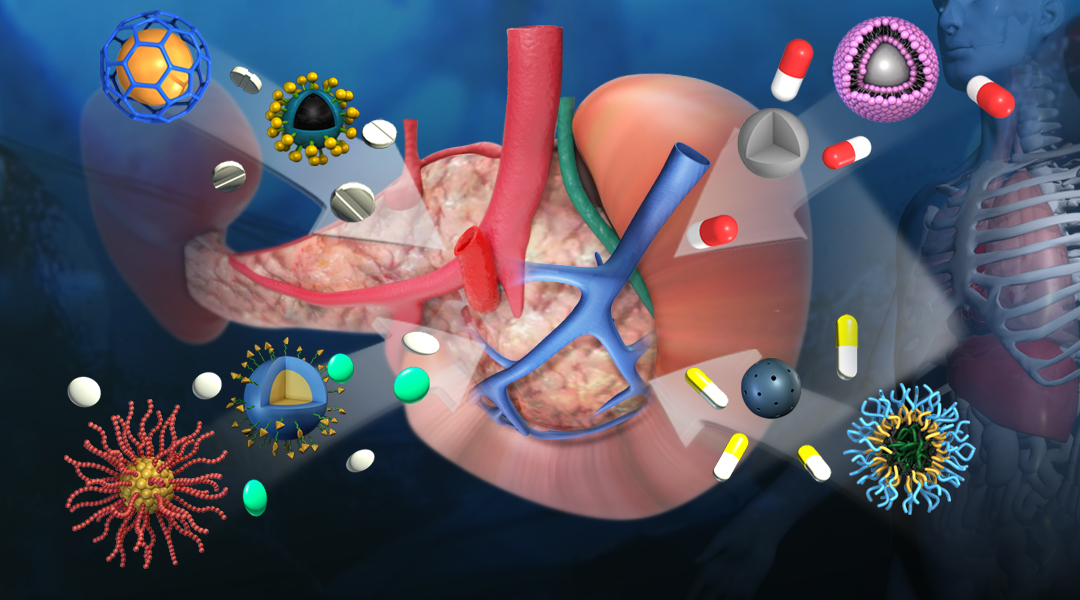
Nanotechnology is poised to revolutionize the diagnosis and treatment of patients with type 1 diabetes.
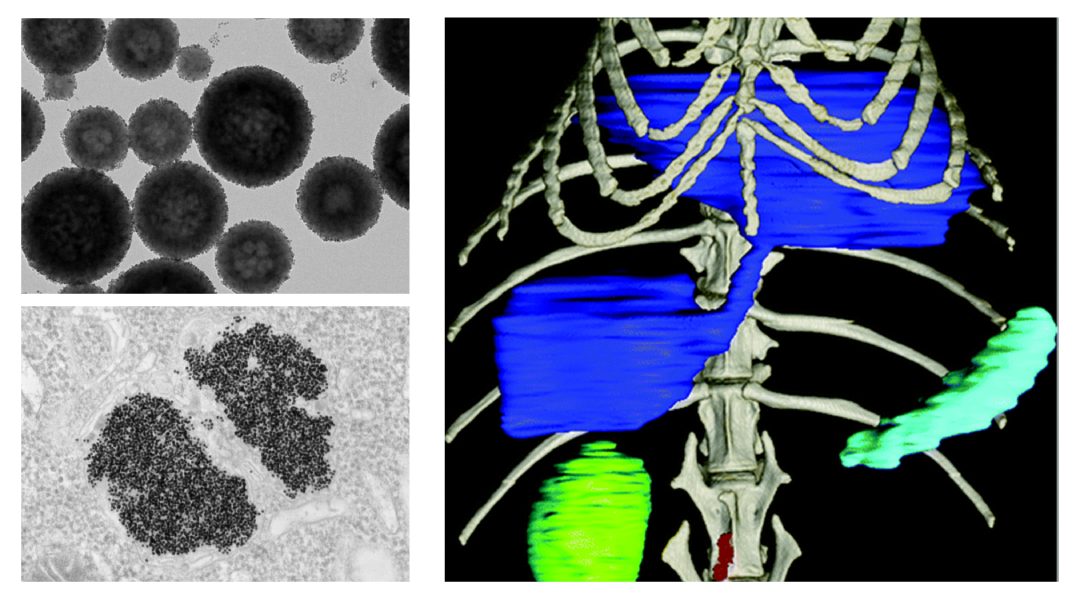
A new study explores how metal nanoparticles designed for new X-ray imaging technologies can improve the diagnosis of diseases, as well as understand the underlying cellular processes.

Cutting-edge fluorine-19 imaging of inflammation extends the frontiers of MRI.

Micro- and nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems are revolutionizing medicine, from minimizing the toxicity of therapeutics to improving their efficacy.