Silk’s highly tunable range of mechanical properties, degradation rates and material formats arise from subtle changes at the microscopic level.


Silk’s highly tunable range of mechanical properties, degradation rates and material formats arise from subtle changes at the microscopic level.

Polymer therapeutics represent promising novel chemical entities under development for addressing CNS disorders, in which intravenous and intranasal administration are the most appealing strategies to achieve this paramount goal.
The potential of rapid diagnostics and screening has led to burgeoning interest in droplets, as it is increasingly used to detect novel disease biomarker targets.
An overview of the most recent literature relevant to mRNA delivery helps readers to obtain an overall concept and direction of nanoscale platforms for mRNA delivery.
In situ vaccination therapy has immense potential in cancer treatment for clinical use. To date, in situ vaccination is already used to treat bladder cancer and melanoma, and with further study could become an important approach to expand immune-based cancer treatment.
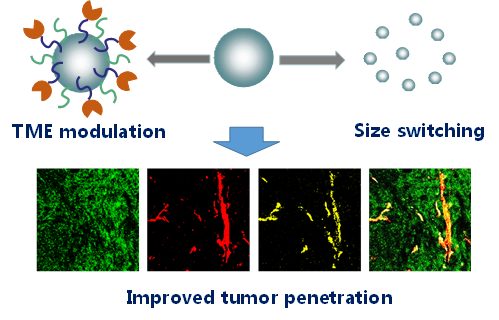
Rational design of nanoparticles with state-of-the-art strategies can effectively improve the penetration as well as therapeutic efficacy of cancer nanomedicines
DNA origami nanobiosensor: The binding of the bioanalyte (left) with the ssDNA-associated bioreceptor (center) on the surface of the DNA origami is transduced as a measurable change in properties (right) that can be recognized and quantified by a detector.
Multipartite designer nanoparticles are formed from the phage lambda decoration protein and can be used in a variety of theranostic applications.

In a WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology review, a discussion about the need for a unifying interpretation of the available experimental data regarding nanomedicines is presented.
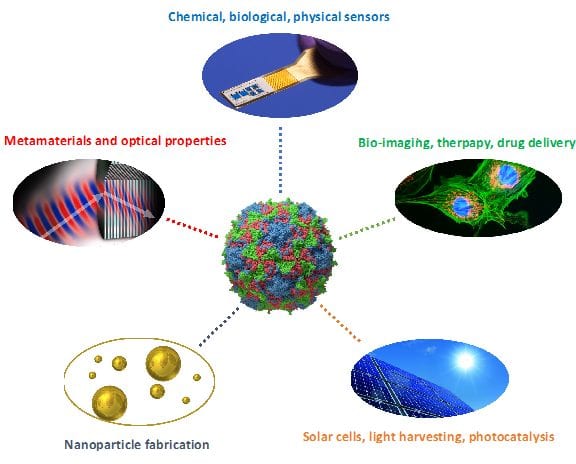
Researchers are taking advantage of 4 billion years of viral evolution to produce robust protein cages for a wide range of applications in nanotechnology.