Nanoparticles can assist in treatment of Head and Neck Cancer patients by optimizing distribution of chemotherapy drugs for better outcomes and less side effects.
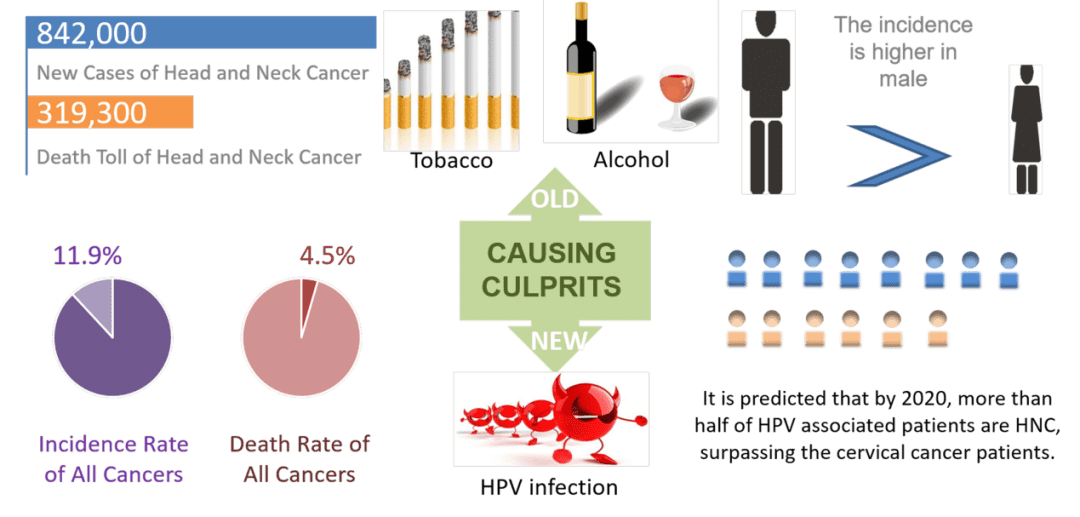

Nanoparticles can assist in treatment of Head and Neck Cancer patients by optimizing distribution of chemotherapy drugs for better outcomes and less side effects.
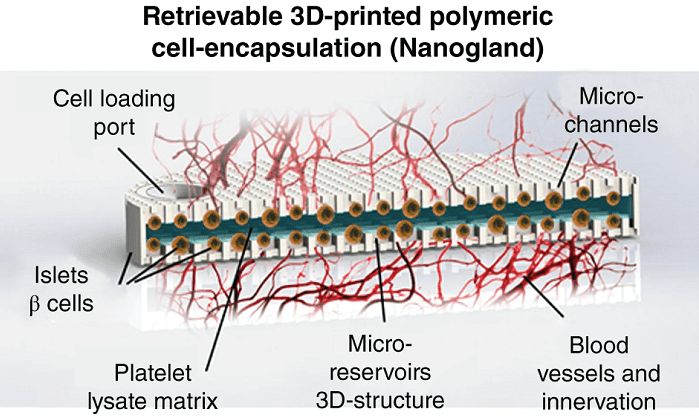
Nanofluidic implantables represent a recent advance in a broad effort for developing personalized, point-of-care medical technologies.
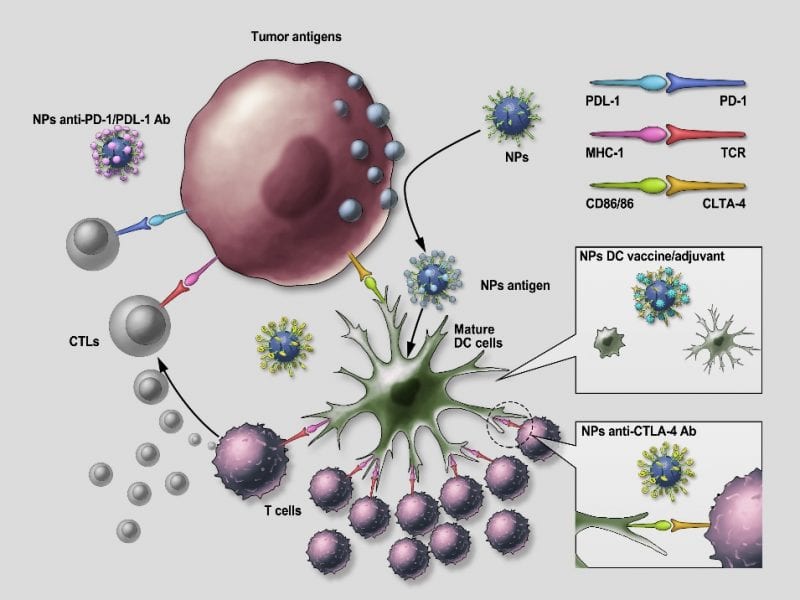
A diverse range of nanomaterials with different physicochemical characteristics have been developed to stimulate the immune system and battle cancer.
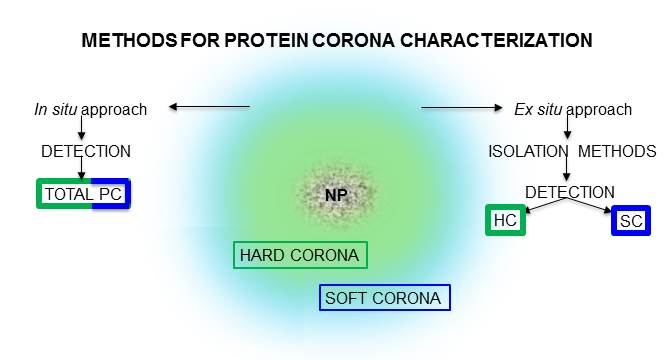
The application and the clinical development of nanomedicines strongly requires a deep study on the complex dynamics that happen after in vivo administration. Particularly, plasma proteins tend to associate to nanoparticles, forming a new surface named the “protein corona” that can have a strong impact on biodistribution, targeting efficacy, and toxicity.
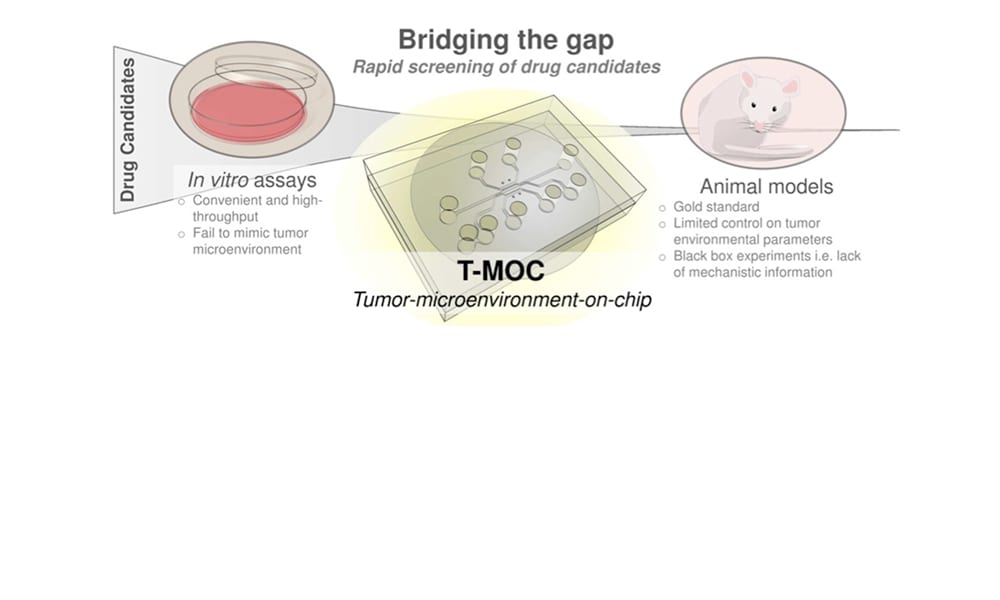
Microfluidics offer significant advantages over traditional macroscale cell cultures by enabling recapitulation of the tumor microenvironment through precise control of physiological cues such as hydrostatic pressure, shear stress, oxygen, and nutrient gradients.
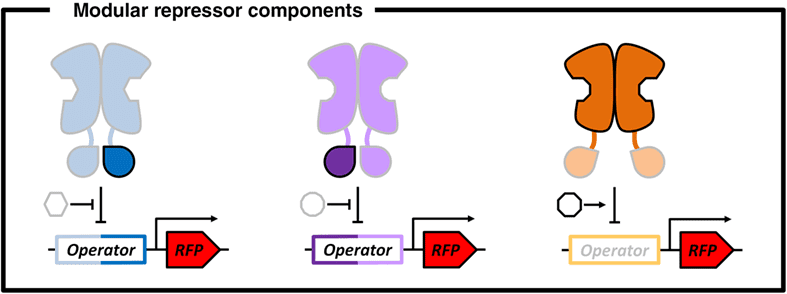
The control of gene expression is an important tool for metabolic engineering, the design of synthetic gene networks, gene-function analysis, and protein manufacturing. This review article discusses the potential of the modular design of novel regulatory proteins fashioned after the topology and mechanochemical properties of the lactose repressor.
An introduction to the mechanisms governing internalization and trafficking in cells; and a discussion of methods to detect endosomal escape and recent advances in controlling endosomal escape from polymer- and lipid-based nanoparticles are presented in this recent Review.
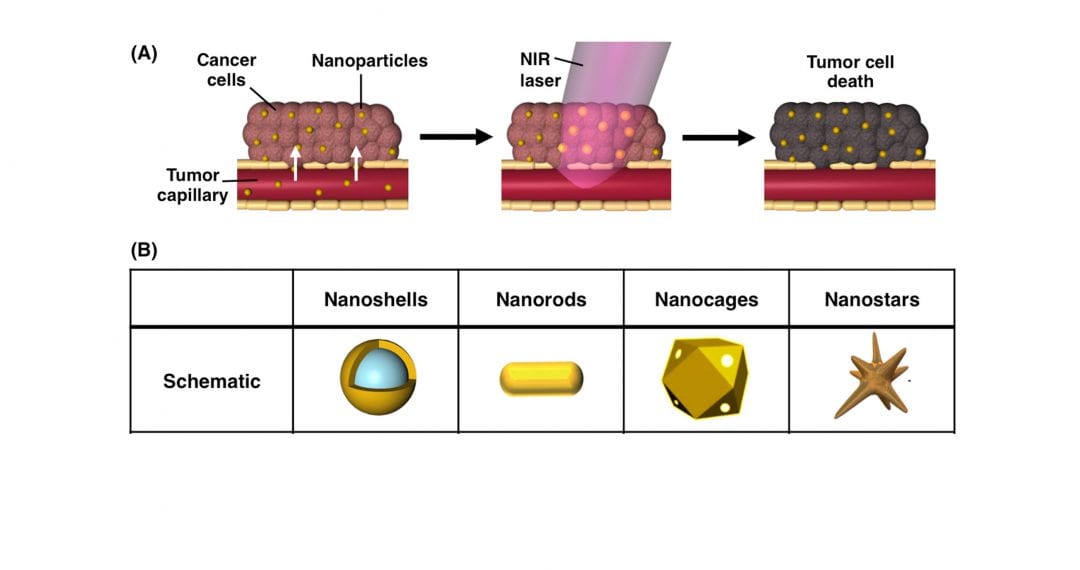
Photothermal therapy that uses gold nanoparticles to convert light to heat is effective against cancer both alone and combined with other therapeutic strategies is reviewed.
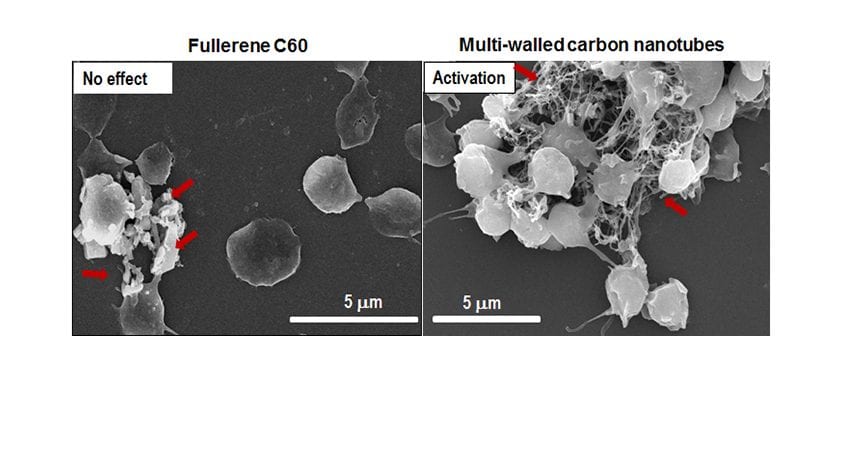
Investigating how nanomaterials interact with the components involved in blood coagulation is an important step towards utilizing nanomedicine safely without causing dysregulation of hemostasis that could result in serious thrombotic and/or hemorrhagic pathologies.
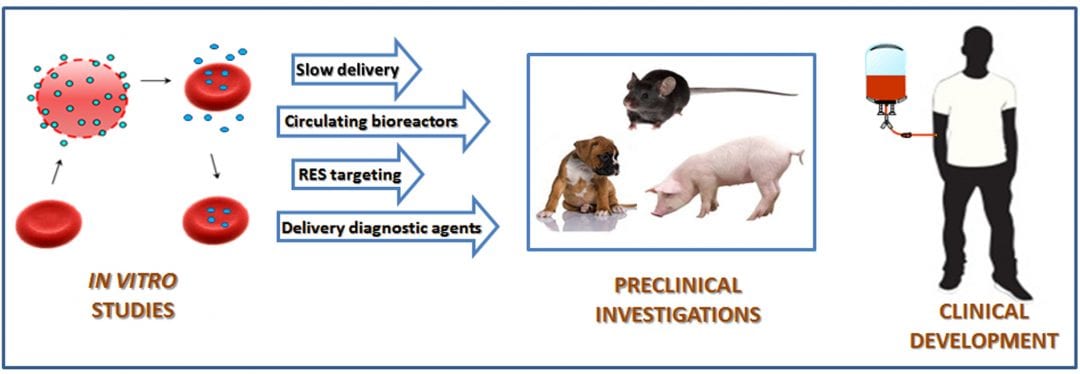
Red blood cells can be opened and resealed without affecting their functional characteristics, allowing scientists new opportunities in therapeutics and diagnostics.