Large-scale recoding of virus genomes has the potential for use in vaccine design.
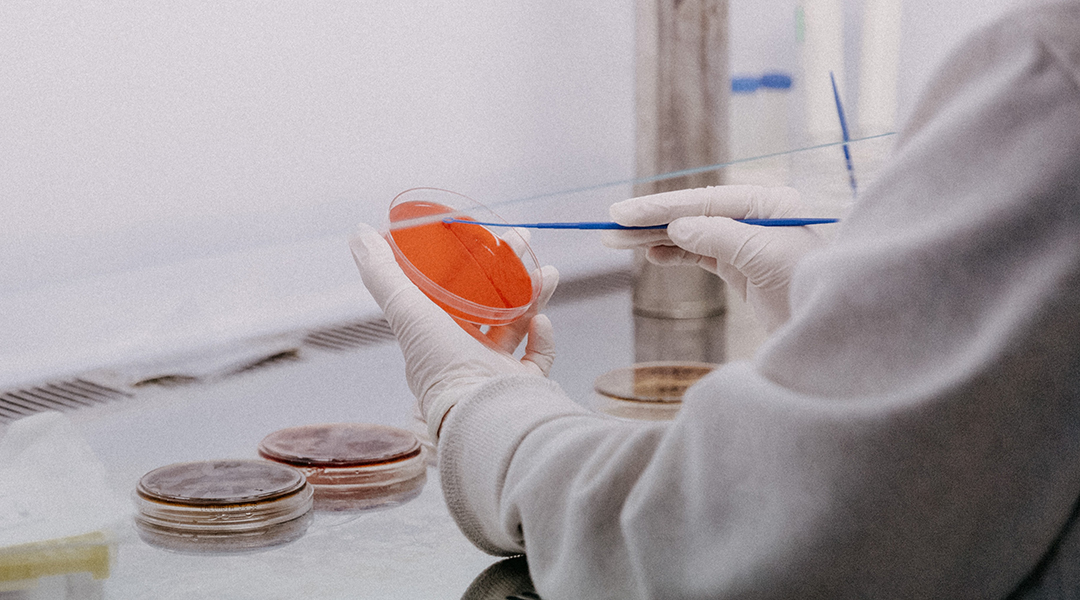


Large-scale recoding of virus genomes has the potential for use in vaccine design.

New evidence suggests a hidden “intelligence” of a life-sustaining pathway.
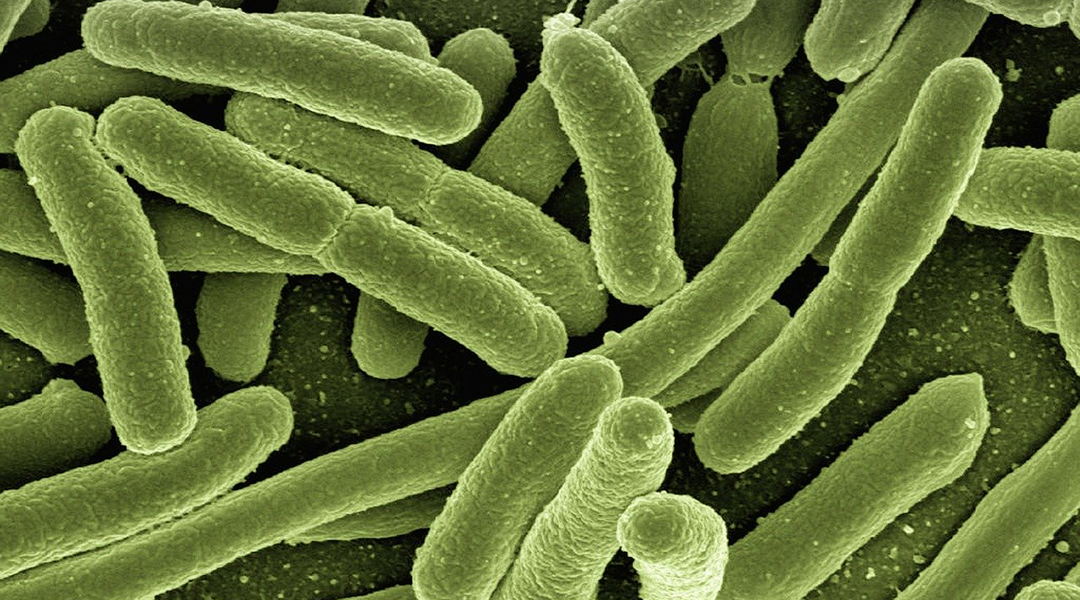
Similar to eukaryotes, prokaryotic cells can spatiotemporally regulate localization of RNAs, which is crucial for the survival and proper function of these tiny organisms.
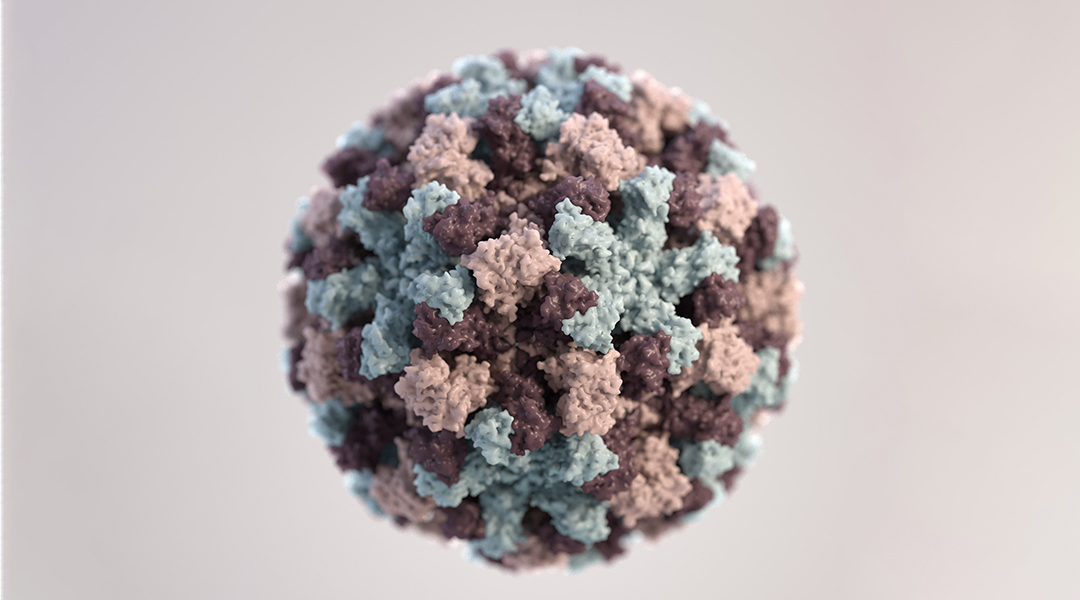
Researchers explore the different mechanisms viruses have evolved to effectively seize host cell ribosomes, and the role they play in the virus’ life cycle.
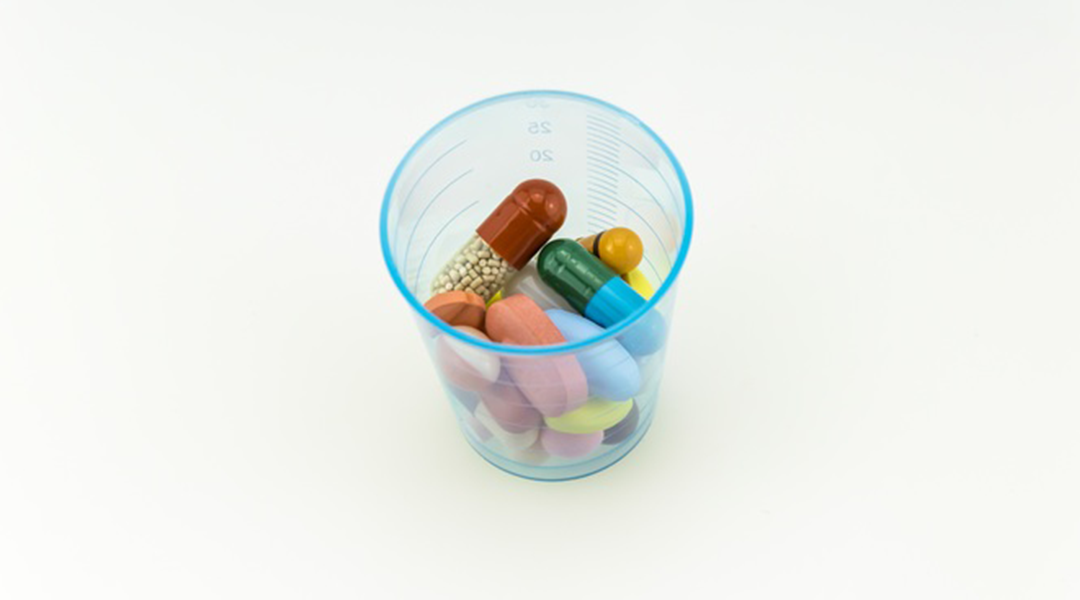
RNA “sandwiches” perform crucial roles in a range of bacterial metabolic pathways.
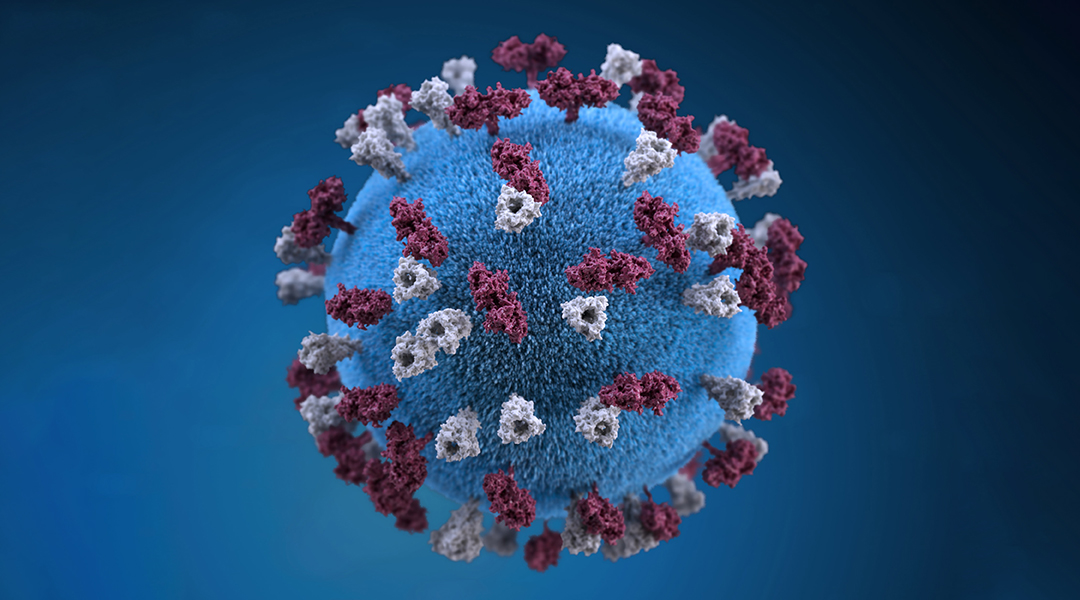
RNA-related processes that are key to the biology of the cell are at risk during coronavirus infections.

RNA plays a fundamental role in our health and biology, and advancements in imaging techniques are expanding our understanding of its life cycle.
RNA elements that are found in the genomes of numerous representatives within the same virus family provide new opportunities to expand the repertoire of targets for the development of antiviral therapy.

A blackboard of therapeutic innovation: Researchers seek to understand how antisense oligonucleotides can “erase” disorders.
Understanding how mRNA localization changes during healthy brain functions and pathological conditions.