This review focuses on classical and state‐of‐the‐art methods for the identification and quantification of RNA molecules in a variety of subcellular locations.

This review focuses on classical and state‐of‐the‐art methods for the identification and quantification of RNA molecules in a variety of subcellular locations.

Regulatory noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) are thought to play important roles in both the development and insecticide resistance of the diamondback moth.

Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are covalently closed RNA circles and have become a favorite research topic.
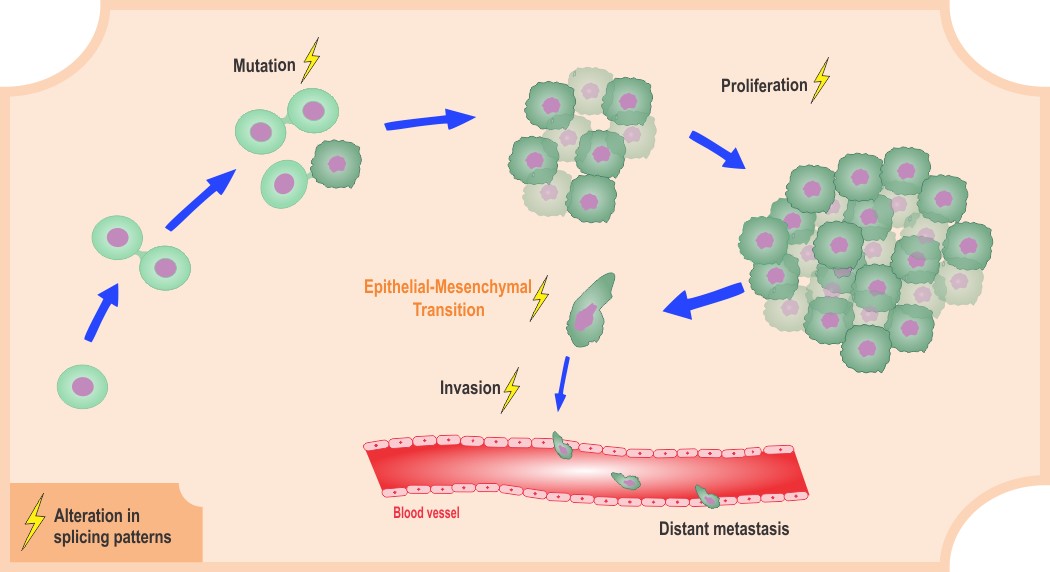
A fundamental challenge in the study of cancer biology is to uncover molecular mechanisms that lead to malignant cellular transformation.

Small RNAs and their associated RNA interference (RNAi) pathways underpin diverse mechanisms of gene regulation and genome defense across all three kingdoms of life and are integral to virus–host interactions.

Processing and maturation of precursor RNA species is coupled to RNA polymerase II transcription. Co‐transcriptional RNA processing helps to ensure efficient and proper capping, splicing, and 3′ end processing of different RNA species to help ensure quality control of the transcriptome.

Novel findings suggest that miR‐146a‐5p may be useful as a noninvasive biomarker and as a targeted therapeutic in several cancers.
Proteins with similar domain structures and activities have been found throughout eukaryotes, demonstrating that this protein family arose from an ancient ancestor.
In response to stress, cells must quickly reprogram gene expression to adapt and survive. This is achieved in part by altering levels of mRNAs and their translation into proteins.

Recent high‐resolution cryoEM structures of various spliceosomal complexes reveal unprecedented details of this large molecular machine.