Uridylation is a widespread post-transcriptional modification impacting the fate of coding and non-coding RNAs in eukaryotes.
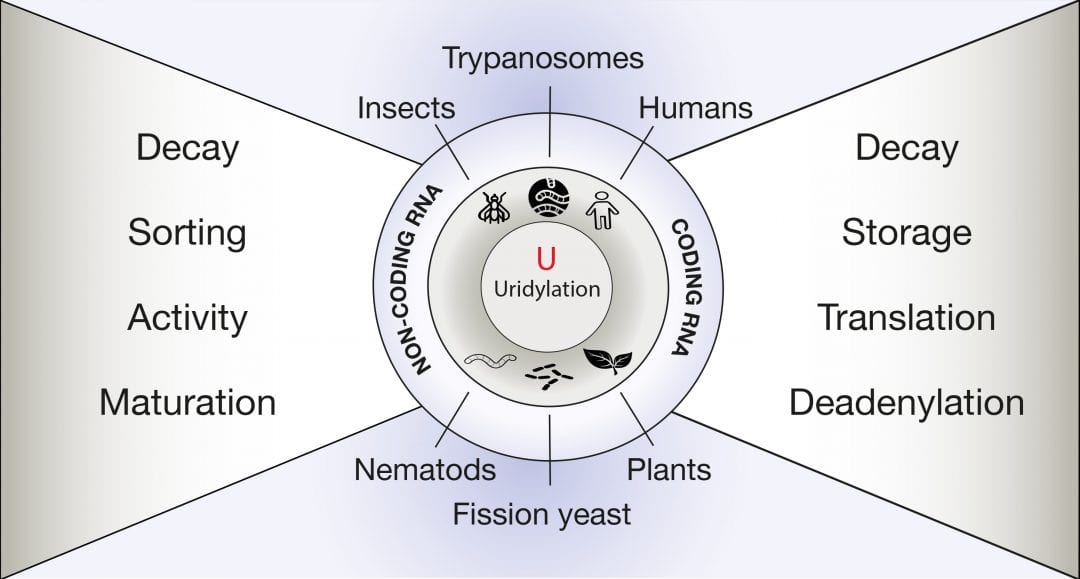

Uridylation is a widespread post-transcriptional modification impacting the fate of coding and non-coding RNAs in eukaryotes.
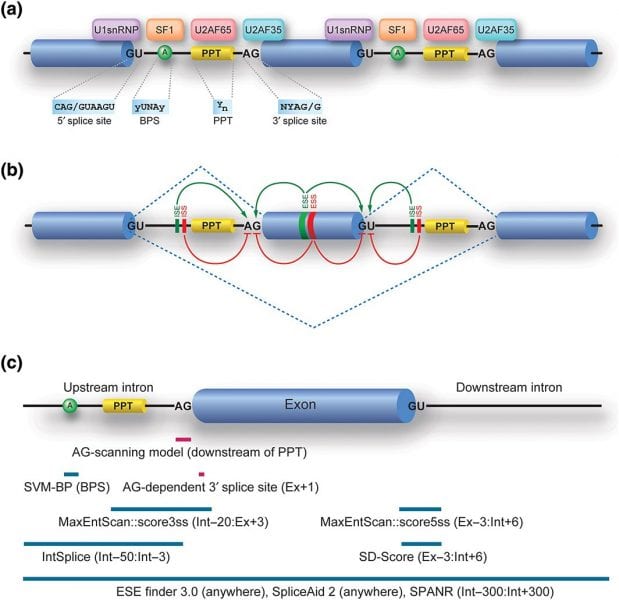
The current tools available to predict RNA splicing effects are explored in a recent review.
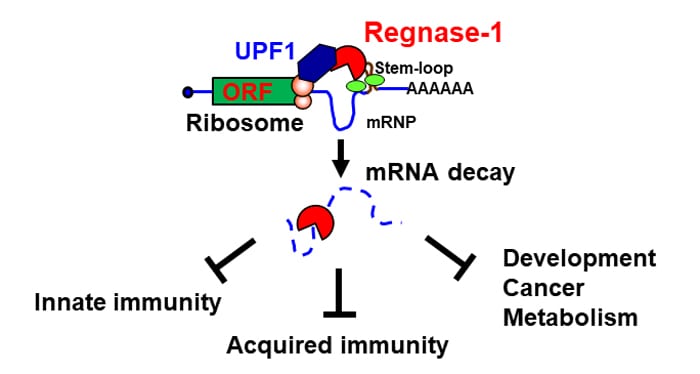
Regnase-1 is critical for the degradation of mRNAs involved in immune responses as well as other various biological processes.
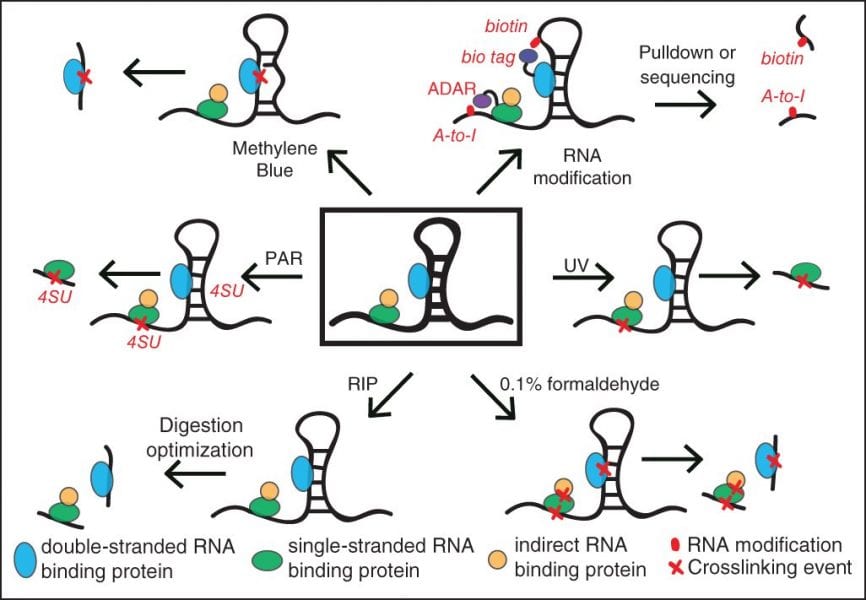
Methods to capture protein-RNA interactions. Different techniques are required to capture single-stranded (green), double-stranded (blue), and indirect (yellow) RNA interactions. Crosses (X) in red mark RNA sites that are crosslinked to the RNA binding protein.
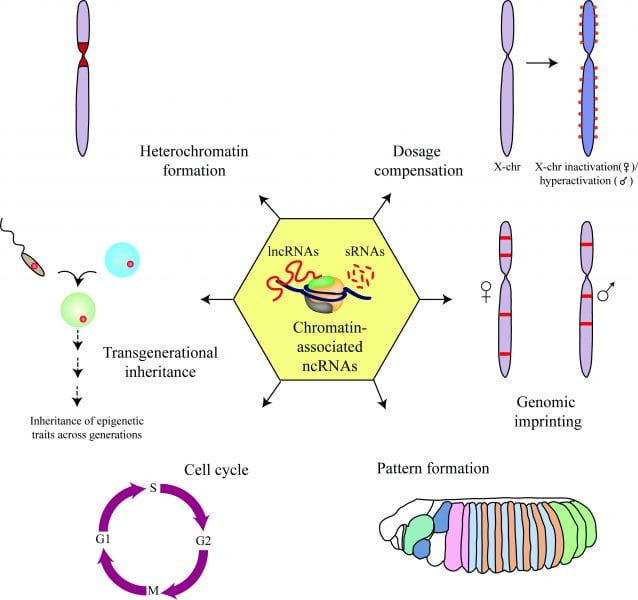
The diverse roles of chromatin-associated non-coding RNAs.
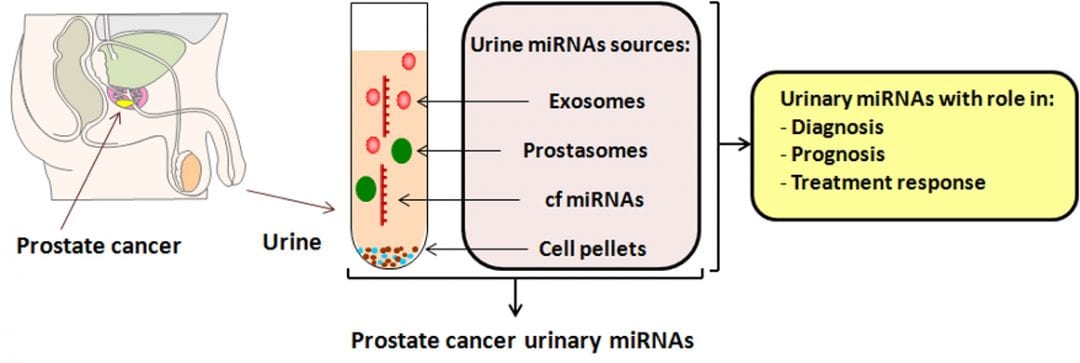
Despite the tremendous progress in research over the years, a suitable minimally invasive prostate cancer (PCa) biomarker is yet to be discovered.
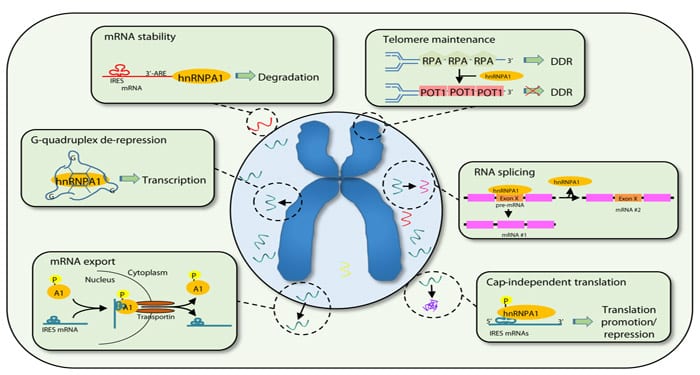
hnRNPA1 is involved in multiple biological processes within the cell nucleus and cytoplasm.
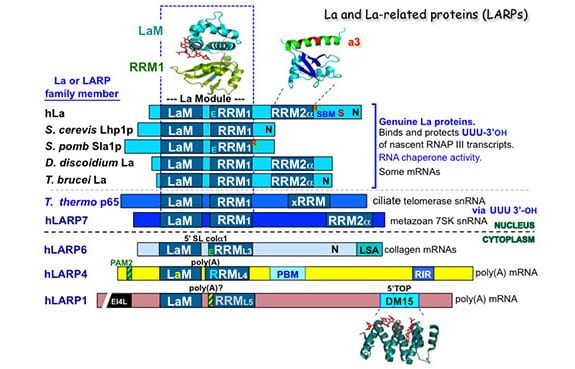
La and its link to RNA polymerase III were significant in the great expansions of the tRNAomes that occurred in eukaryotes. Four families of La-related proteins (LARPs) emerged during eukaryotic evolution with specialized functions.
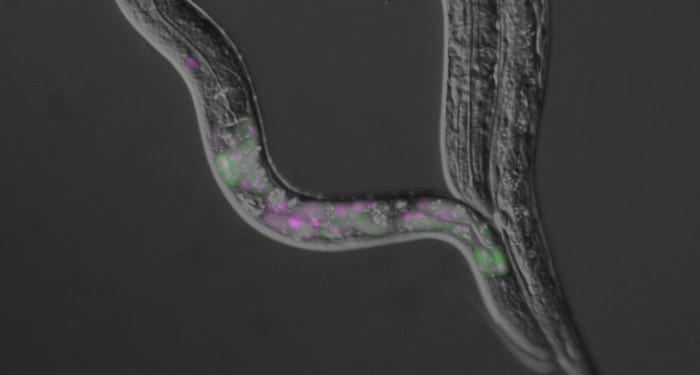
Dichromatic fluorescence reporter system enables visualization of expression profiles of alternative pre-mRNA processing patterns in a nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans
In a recent WIREs RNA review, researchers discuss the recent explosion of data in the field of post-transcriptional regulation in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. (Image credit: Gio.tto/Shutterstock)